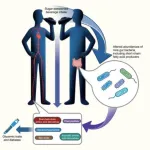
(Press-News.org) It is well known that consuming sugary drinks increases the risk of diabetes, but the mechanism behind this relationship is unclear. Now, in a paper publishing January 31 in the Cell Press journal Cell Metabolism, researchers show that metabolites produced by gut microbes might play a role. In a long-term cohort of US Hispanic/Latino adults, the researchers identified differences in the gut microbiota and blood metabolites of individuals with a high intake of sugar-sweetened beverages. The altered metabolite profile seen in sugary beverage drinkers was associated with a higher risk of developing diabetes in the subsequent 10 years. Since some of these metabolites are produced by gut microbes, this suggests that the microbiome might mediate the association between sugary beverages and diabetes.
“Our study suggests a potential mechanism to explain why sugar-sweetened beverages are bad for your metabolism,” says senior author Qibin Qi, an epidemiologist at Albert Einstein College of Medicine. “Although our findings are observational, they provide insights for potential diabetes prevention or management strategies using the gut microbiome.”
Sugar-sweetened beverages are the main source of added sugar in the diets of US adults—in 2017 and 2018, US adults consumed an average of 34.8g of added sugar each day from sugary beverages such as soda and sweetened fruit juice. Compared to added sugars in solid foods, added sugar in beverages “might be more easily absorbed, and they have a really high energy density because they’re just sugar and water,” says Qi.
Previous studies in Europe and China have shown that sugar-sweetened beverages alter gut microbiome composition, but this is the first study to investigate whether this microbial change impacts host metabolism and diabetes risk. It’s also the first study to investigate the issue in US-based Hispanic/Latino population—a group that experiences high rates of diabetes and is known to consume high volumes of sugar-sweetened beverages.
The team used data from the ongoing Hispanic Community Health Study/Study of Latinos (HCHS/SOL), a large-scale cohort study with data from over 16,000 participants living in San Diego, Chicago, Miami, and the Bronx. At an initial visit, participants were asked to recall their diet from the past 24 hours and had blood drawn to characterize their serum metabolites. The researchers collected fecal samples and characterized the gut microbiomes of a subset of the participants (n = 3,035) at a follow-up visit and used these data to identify association between sugar-sweetened beverage intake, gut microbiome composition, and serum metabolites.
They found that high sugary beverage intake—defined as two or more sugary beverages per day—was associated with changes in the abundance of nine species of bacteria. Four of these species are known to produce short-chain fatty acids—molecules that are produced when bacteria digest fiber and that are known to positively impact glucose metabolism. In general, bacterial species that were positively associated with sugary beverage intake correlated with worse metabolic traits. Interestingly, these bacteria were not associated with sugar ingested from non-beverage sources.
The researchers also found associations between sugary beverage consumption and 56 serum metabolites, including several metabolites that are produced by gut microbiota or are derivatives of gut-microbiota-produced metabolites. These sugar-associated metabolites were associated with worse metabolic traits, including higher levels of fasting blood glucose and insulin, higher BMIs and waist-to-hip ratios, and lower levels of high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (“good” cholesterol). Notably, individuals with higher levels of these metabolites had a higher likelihood of developing diabetes in the 10 years following their initial visit.
“We found that several microbiota-related metabolites are associated with the risk of diabetes,” says Qi. “In other words, these metabolites may predict future diabetes.”
Because gut microbiome samples were only collected from a subset of the participants, the researchers had an insufficient sample size to determine whether any species of gut microbes were directly associated with diabetes risk, but this is something they plan to study further.
“In the future, we want to test whether the bacteria and metabolites can mediate or at least partially mediate the association between sugar-sweetened beverages and risk of diabetes,” says Qi.
The team plans to validate their findings in other populations and to extend their analysis to investigate whether microbial metabolites are involved in other chronic health issues linked to sugar consumption, such as cardiovascular disease.
###
This research was supported by the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases, the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute, the National Institute on Minority Health and Health, the New York Regional Center for Diabetes Translation Research, the National Institute of Environmental Health Sciences, and the JLH Foundation.
Cell Metabolism, Zhang et al., “Sugar-sweetened beverage intake, gut microbiota, circulating metabolites, and diabetes risk in Hispanic Community Health Study/Study of Latinos.” https://www.cell.com/cell-metabolism/fulltext/S1550-4131(24)00486-8.
Cell Metabolism (@Cell_Metabolism), published by Cell Press, is a monthly journal that publishes reports of novel results in metabolic biology, from molecular and cellular biology to translational studies. The journal aims to highlight work addressing the molecular mechanisms underlying physiology and homeostasis in health and disease. Visit http://www.cell.com/cell-metabolism. To receive Cell Press media alerts, contact press@cell.com.
END
Researchers from the Tanenbaum group at the Hubrecht Institute have developed a new microscopy technique to observe how ribosomes function in cells. With this method, they can monitor individual ribosomes as they convert mRNA into proteins. The researchers discovered that ribosomes help each other when encountering difficulties, a process they refer to as ‘ribosome cooperativity’. This technique and the findings, published in Cell, provide insights into how proteins are made and offer other researchers a tool to better study mRNA translation.
Our DNA contains genetic information essential for ...
About The Study: This cross-sectional study found that compared with trends from the early 2000s, early adult (ages 25-44) mortality in the U.S. has risen substantially in 2 stages: 2011 to 2019 and 2020 to 2023. Although mortality rates decreased after the core pandemic years, excess mortality remained higher than expected based on pre-pandemic levels. The largest portion of 2023 excess mortality was driven by drug poisoning, but many other external and natural causes exceeded what prior trends would have projected.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Elizabeth Wrigley-Field, PhD, email ewf@umn.edu.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our ...
About The Study: In this cohort study, most patients with overweight or obesity discontinued glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonist (GLP-1 RA) therapy within 1 year, but those without type 2 diabetes had higher discontinuation rates and lower reinitiation rates. Inequities in access and adherence to effective treatments have the potential to exacerbate disparities in obesity.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Ezekiel J. Emanuel, MD, PhD, email zemanuel@upenn.edu.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2024.57349)
Editor’s ...
About The Study: High ultraprocessed food consumption during early childhood was associated with obesity development, primarily in males in this cohort study of Canadian children. These findings can inform targeted public health initiatives for early childhood centers and caregiver education programs to reduce ultraprocessed food intake and prevent obesity.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Kozeta Miliku, MD, PhD, email kozeta.miliku@utoronto.ca.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2024.57341)
Editor’s Note: Please see the ...
A group of 211 international experts from 79 countries has today published a new framework to facilitate the design, development and implementation of digital health curricula in medical education worldwide.
Published in JAMA Network Open, the Digital Health Competencies in Medical Education (DECODE) framework is designed to help medical institutions better equip future physicians for the ongoing digital transformation in healthcare.
The framework is already beginning to be adopted across the globe, including in the UK where it has influenced ...
Researchers at the University of Toronto are sounding the alarm about the high consumption of ultra-processed foods among preschool-aged children in Canada and its association with obesity development.
“We saw that ultra-processed foods contributed to almost half of a child’s total daily energy intake,” says Kozeta Miliku, assistant professor of nutritional sciences at U of T’s Temerty Faculty of Medicine.
The findings, published today in JAMA Network Open, are the first to describe sex-driven differences in the effects of ultra-processed food on obesity risk among Canadian children, with stronger ...
LOS ANGELES — A team of international researchers led by scientists at City of Hope, one of the largest and most advanced cancer research and treatment organizations in the United States, with its National Medical Center in Los Angeles ranked among the nation’s top 5 cancer centers by U.S. News & World Report, have demonstrated a way to boost thymic function after damage in preclinical studies. The team’s study results, published today in the journal Immunity, outline their discovery of a specific type ...
Predicting and mitigating the effects of climate change while preserving biodiversity is a top priority for both scientists and policymakers. As climate change intensifies, leading to more frequent and severe droughts, understanding the impact on natural ecosystems has become increasingly important. One of the main challenges is forecasting changes in species richness due to shifts in precipitation patterns. While it’s established that, on a broad geographic scale, regions with more water generally support greater plant diversity, results vary at ...
A recent study published in PeerJ Life and Environment unveils refined techniques for in vitro fertilization (IVF) in four key Caribbean coral species, offering a crucial advancement in coral reef restoration efforts. Researchers from SECORE International, the CARMABI Foundation, and the University of Amsterdam have developed new insights into the optimal conditions for coral breeding, which could significantly enhance larval production and bolster declining coral populations.
Study Focus
The study examined four broadcast-spawning ...
While many studies have reported a link between a mother’s health condition during pregnancy and her child’s risk of autism, a new study shows that nearly all of these “associations” can otherwise be explained by factors such as genetics, exposure to pollution, and access to healthcare.
Led by researchers at NYU Langone Health, the study revealed that, of the few conditions truly associated with autism, all were actually complications with the fetus — leading the authors to believe ...