(Press-News.org) New research from the University of Minnesota and Boston University School of Public Health (BUSPH) shows that death rates for early adults, or adults aged 25-44, rose sharply during the COVID-19 pandemic and remain higher than expected post-pandemic.
Heightened death rates during the COVID-19 pandemic intensified an already negative trend for early adults, which began around 2010. As a result, early adult death rates in 2023 were about 70 percent higher than they might have been if death rates had not begun to rise about a decade before the pandemic.
The researchers analyzed death rates between 1999-2023. Published in JAMA Network Open, the study found:
For early adults, there was a large jump in the death rate between 2019 and 2021, which are considered the core pandemic years. In 2023, the death rate remained nearly 20 percent higher than in 2019.
Drug-related deaths are the single largest cause of 2023 excess mortality, compared with the mortality that would have been expected had earlier trends continued.
Other important contributing causes were a variety of natural causes, including cardiometabolic and nutritional causes, and a variety of other external causes, including transport deaths.
"The rise in opiate deaths has been devastating for Americans in early and middle adulthood,” said Elizabeth Wrigley-Field, lead author and an associate professor in the University of Minnesota College of Liberal Arts and Institute for Social Research and Data Innovation. “What we didn't expect is how many different causes of death have really grown for these early adults. It's drug and alcohol deaths, but it's also car collisions, it's circulatory and metabolic diseases—causes that are very different from each other. That tells us this isn't one simple problem to fix, but something broader."
"Our findings underscore the urgent need for comprehensive policies to address the structural factors driving worsening health among recent generations of young adults,” said study coauthor Andrew Stokes, associate professor of global health at BUSPH. “Solutions may include expanding access to nutritious foods, strengthening social services and increasing regulation of industries that affect public health.”
Future research will explore ongoing consequences of the COVID-19 pandemic and the trends that were already in place when it began.
Funding was provided by the Eunice Kennedy Shriver National Institute of Child Health and Human Development, the Robert Wood Johnson Foundation, the National Institute on Aging, the W.K. Kellogg Foundation and the Minnesota Population Center.
**
About Boston University School of Public Health
Founded in 1976, Boston University School of Public Health is one of the top ten ranked schools of public health in the world. It offers master's- and doctoral-level education in public health. The faculty in six departments conduct policy-changing public health research around the world, with the mission of improving the health of populations—especially the disadvantaged, underserved, and vulnerable—locally and globally.
About the University of Minnesota College of Liberal Arts
For more than 150 years, the College of Liberal Arts has played a central and enduring role in shaping lives, for the good of Minnesota and the world. CLA is the largest college in the University of Minnesota system with nearly 500 world-class faculty instructing more than 12,000 undergraduate and 1,400 graduate students. CLA is home to 31 academic departments and 20+ interdisciplinary research centers in the arts, social sciences, and humanities. Learn more at cla.umn.edu.
About the University of Minnesota School of Public Health
The University of Minnesota School of Public Health improves the health and wellbeing of populations and communities around the world by bringing innovative research, learning, and concrete actions to today’s biggest health challenges. We prepare some of the most influential leaders in the field, and partner with health departments, communities, and policymakers to advance health equity for all. Learn more at sph.umn.edu.
END
Early adult mortality is higher than expected in US post-COVID
New research from Boston University School of Public Health and the University of Minnesota shows that death rates for early adults, or adults aged 25-44, rose sharply during the COVID-19 pandemic and remain higher than expected post-pandemic.
2025-01-31
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Recycling lithium-ion batteries cuts emissions and strengthens supply chain
2025-01-31
Recycling lithium-ion batteries to recover their critical metals has significantly lower environmental impacts than mining virgin metals, according to a new Stanford University lifecycle analysis published in Nature Communications. On a large scale, recycling could also help relieve the long-term supply insecurity – physically and geopolitically – of critical battery minerals.
Lithium-ion battery recyclers source materials from two main streams: defective scrap material from battery manufacturers, and so-called “dead” batteries, mostly ...
Study offers new hope for relieving chronic pain in dialysis patients
2025-01-31
People undergoing hemodialysis treatment for kidney failure often experience chronic pain related to their condition, but it can be difficult to manage with opioid medication and other conventional treatments.
A new study published in JAMA Internal Medicine finds that offering these patients pain coping skills training (PCST) significantly reduced their suffering and improved their quality of life.
“This is particularly important for these patients, since the therapeutic choices for pain management are limited and the use of opioids has been shown ...
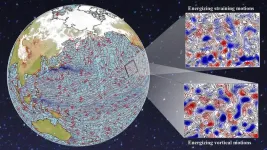
How does the atmosphere affect ocean weather?
2025-01-31
Much like the windy weather patterns that affect the Earth’s surface, our planet’s oceans experience their own distinct weather patterns. These weather patterns, known as eddies, are circular currents of water that are typically about 100 kilometers wide.
A new study of satellite imagery and high-resolution climate model data by scientists at the University of Rochester upends previous assumptions and provides insight about how those surface and ocean weather patterns interact. Scientists formerly believed atmospheric wind had a damping effect, ...
Robots get smarter to work in sewers
2025-01-31
The ambitious project PIPEON* will develop new robotic and AI-based technologies for mapping, monitoring, and maintaining Europe’s sewer networks using autonomous “thinking” robots and AI-based modelling and analysis tools.
The development and application of such new technologies would have major societal, environmental and economic impact. Instead of repairing in-sewer defects and removing blockages after streets and homes have been flooded with sewage, defects can be quickly identified and repaired and blockages removed when they are still small. Early, preventative repair and maintenance actions will limit the frequency and ...
Speech Accessibility Project data leads to recognition improvements on Microsoft Azure
2025-01-31
Microsoft's Azure AI Speech platform achieved “significant improvements” in recognizing non-standard English speech thanks to recordings and transcripts from University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign Speech Accessibility Project participants. Its accuracy gains range from 18% to 60%, depending on the speaker’s disability.
The changes are currently rolling out on Microsoft's Cloud endpoint for third-party customers.
Until now, the majority of voice recognition technology trained using recordings and transcriptions from audiobooks. But an audiobook narrator and an individual with aphasia after a stroke sound different.
When the Speech ...
Tigers in the neighborhood: How India makes room for both tigers and people
2025-01-31
In India, tigers haven’t just survived − they’ve made a comeback. Despite a growing population and increasing pressure on their habitats, the number of wild tigers is rising. The reason? A combination of ecological restoration, economic initiatives, and political stability. And just as important: a deeply rooted reverence for tigers that has fostered a culture where humans and predators can coexist.
How do you protect an endangered species when that species is a tiger − a predator that also poses a threat to humans? India has found a way by combining protected reserves with areas where tigers and people share space. The result? A 30% increase in ...
Grove School’s Arthur Paul Pedersen publishes critical essay on scientific measurement literacy
2025-01-31
Arthur Paul Pedersen, faculty research scientist with the CUNY Remote Sensing Earth Systems (CREST) Institute and adjunct assistant professor of computer science at The City College of New York’s Grove School of Engineering, is lead author of a critical essay on measurement in scientific discourse. The essay, published in the journal of Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, warns of the dangerous implications of measurement illiteracy in contemporary scientific discourse and urges broad, ...
Moffitt study finds key biomarker to predict KRASG12C inhibitor effectiveness in lung cancer
2025-01-31
TAMPA, Fla. (Jan. 31, 2025) — A new study from Moffitt Cancer Center could help doctors predict how well patients with a specific type of lung cancer will respond to new therapies. The research, published in Clinical Cancer Research, found that measuring the interaction between two proteins, RAS and RAF, could provide valuable insights into the effectiveness of treatments for patients with KRASG12C-mutant non-small cell lung cancer, a type of lung cancer known for being particularly difficult to treat.
The findings revealed that tumors with higher levels ...
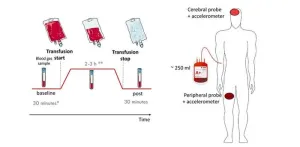
Improving blood transfusion monitoring in critical care patients: Insights from diffuse optics
2025-01-31
Red blood cell transfusions (RBCTs) are life-saving treatments for critically ill patients suffering from anemia, a condition where the body lacks enough healthy red blood cells to deliver oxygen effectively. While effective in increasing oxygen levels in the blood, transfusions can disrupt blood flow and oxygen distribution, potentially causing harm to vital organs like the brain. To address this, researchers are exploring new tools to monitor these effects more precisely.
A recent study reported in Biophotonics Discovery investigated a novel technology called hybrid diffuse optics (DO), which uses near-infrared light to continuously measure changes in blood flow and oxygen ...
Powerful legal and financial services enable kleptocracy, research shows
2025-01-31
Powerful legal and financial service industries are enabling kleptocracy and corrupt elites to operate with relative impunity, a new study shows.
The research details how “enablers” from these industries exploit deregulation and the under-enforcement of the law to game the system. They can offshore their clients' wealth, and enhance their reputations and influence via philanthropy, political donations, and the use of the UK's punitive libel regime.
Most of this “enabling” is likely ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Trapping light on thermal photodetectors shatters speed records
New review highlights the future of tubular solid oxide fuel cells for clean energy systems
Pig farm ammonia pollution may indirectly accelerate climate warming, new study finds
Modified biochar helps compost retain nitrogen and build richer soil organic matter
First gene regulation clinical trials for epilepsy show promising results
Life-changing drug identified for children with rare epilepsy
Husker researchers collaborate to explore fear of spiders
Mayo Clinic researchers discover hidden brain map that may improve epilepsy care
NYCST announces Round 2 Awards for space technology projects
How the Dobbs decision and abortion restrictions changed where medical students apply to residency programs
Microwave frying can help lower oil content for healthier French fries
In MS, wearable sensors may help identify people at risk of worsening disability
Study: Football associated with nearly one in five brain injuries in youth sports
Machine-learning immune-system analysis study may hold clues to personalized medicine
A promising potential therapeutic strategy for Rett syndrome
How time changes impact public sentiment in the U.S.
Analysis of charred food in pot reveals that prehistoric Europeans had surprisingly complex cuisines
As a whole, LGB+ workers in the NHS do not experience pay gaps compared to their heterosexual colleagues
How cocaine rewires the brain to drive relapse
Mosquito monitoring through sound - implications for AI species recognition
UCLA researchers engineer CAR-T cells to target hard-to-treat solid tumors
New study reveals asynchronous land–ocean responses to ancient ocean anoxia
Ctenophore research points to earlier origins of brain-like structures
Tibet ASγ experiment sheds new light on cosmic rays acceleration and propagation in Milky Way
AI-based liquid biopsy may detect liver fibrosis, cirrhosis and chronic disease signals
Hope for Rett syndrome: New research may unlock treatment pathway for rare disorder with no cure
How some skills become second nature
SFU study sheds light on clotting risks for female astronauts
UC Irvine chemists shed light on how age-related cataracts may begin
Machine learning reveals Raman signatures of liquid-like ion conduction in solid electrolytes
[Press-News.org] Early adult mortality is higher than expected in US post-COVIDNew research from Boston University School of Public Health and the University of Minnesota shows that death rates for early adults, or adults aged 25-44, rose sharply during the COVID-19 pandemic and remain higher than expected post-pandemic.