(Press-News.org)
A new study from the University of Chicago Medicine reveals that people with alcohol use disorder (AUD) and depression experience high levels of stimulation and pleasure when intoxicated, similar to drinkers who do not have depression.
The findings counter the long-held belief that the pleasure people experience when drinking alcohol decreases with addiction and that drinking to intoxication is mainly to reduce negative feelings as a form of self-medication.
"We have this folklore that people drink excessively when they're feeling depressed and that it's really about self-medicating," said Andrea King, PhD, Professor of Psychiatry and Behavioral Neuroscience at UChicago and lead author of the study. "In this study of natural environment drinking and smart phone-based reports of the effects of alcohol in real-time, participants with AUD and a depressive disorder reported feeling acute, sustained positive and rewarding alcohol effects — just like their non-depressed counterparts."
Published February 1 in the American Journal of Psychiatry, the research challenges conventional notions about alcohol’s effects in depressed people who drink excessively and could improve treatment approaches by focusing medication and behavioral approaches more on alcohol's pleasure reward pathways and less on stress-responsive systems.
"Currently, the focus of treatment is often on resolving stress and symptoms of depression, but that is only addressing one side of the coin if we don't also address the heightened stimulation, liking and wanting more alcohol that occur in both depressed and non-depressed people with AUD," said King, who has been conducting human research for decades to test responses to alcohol that lead to addiction.
The effects of alcohol on the brain are complex, and improved understanding of the factors that affect an individual's vulnerability to AUD and depression is critical to identify and initiate early, effective treatment. However, few studies have examined how people with AUD respond to alcohol either in controlled laboratory settings or the natural environment; including individuals with AUD and another co-morbid diagnosis adds to the complexity.
The research followed 232 individuals across the U.S. between the ages of 21 to 35, corresponding to the period when most heavy drinking occurs in a person's lifetime. Half of the study group met criteria for AUD in the past year and were evenly divided in terms of those who had or had not experienced a major depressive disorder in the past year. Individuals who had suicidal ideation were excluded for safety reasons, as were people who had severe alcohol withdrawal symptoms.
Through their smartphones, participants answered questions every half hour for three hours during one typical alcohol drinking episode and a non-alcohol episode. The researchers found that alcohol consumption reduced negative feelings, although the reduction was small and nonspecific to their depression or AUD status. The positive effects of alcohol were much higher in individuals with AUD than those without AUD and contrary to lore, similar in those with AUD and depression and those without depression.
"For nearly a decade, our group has been improving methods to use mobile technologies to measure real time clinically meaningful outcomes in people with AUD and those at risk for alcohol-related problems," said study co-author Daniel Fridberg, PhD, Associate Professor of Psychiatry and Behavioral Neuroscience at UChicago. "These approaches allow us to bridge the gap between the lab and real life and have led to new insights that could one day result in better treatments.”
The study's findings call into question the predominant theory that alcohol addiction arises from the brain's attempt to maintain stability despite repeated heavy drinking. That theory describes a “dark side of addiction” where repeated heavy drinking over time leads to changes in the brain systems involved in stress and reward. As a result of those changes, it is hypothesized that individuals shift from drinking for pleasure to drinking to avoid withdrawal and stress.
King says this theory does not account for the high levels of stimulation and pleasure that she likens to an accelerator pedal fueling more dependency.
"As treatment providers, we're taught people with AUD are drinking to self-medicate and feel better," said King. "But what exactly are they feeling? From our study, it seems to be high levels of stimulation and pleasurable effects, with a modest decrease in negative states.”
King's next study examines whether adults between 40 to 65 years old who have had AUD for decades also experience similar heightened feelings of pleasure when drinking versus older drinkers without AUD. The prevailing theory would suggest these individuals would show blunted positive responses and high levels of tolerance to alcohol. King will examine whether they show a long-term sensitivity to alcohol’s enjoyable effects, much like in this study of depressed drinkers.
END
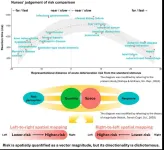
Tokyo, Japan – Researchers from Tokyo Metropolitan University have studied how nurses perceive words showing high and low risk ailments. They looked for directional bias, e.g. whether words denoting lower (higher) risk led to a quicker response when placed on the left (right) side or vice versa. They found faster response for significantly higher or lower risk, but different people had different directional biases. Their findings might inform better ways to present clinical information.
With every incoming medical emergency, nurses are required ...
High-risk pregnancy specialists from the Raquel and Jaime Gilinski Department of Obstetrics, Gynecology and Reproductive Science at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai are presenting research at the Annual Pregnancy Meeting of the Society for Maternal-Fetal Medicine (SMFM) in Denver from January 27- February 1.
The Mount Sinai doctors are available for interview about their research findings, and can also provide commentary on other women’s health topics, breaking news, and studies.
PRESENTATIONS and POSTER SESSIONS
*All abstracts are under embargo until the below listed times*
Thursday, ...
University of Cambridge media release
‘Altar tent’ discovery puts Islamic art at the heart of medieval Christianity
UNDER STRICT EMBARGO UNTIL 00:01AM (UK TIME) ON SATURDAY 1ST FEBRUARY 2025
A 13th-century fresco rediscovered in Ferrara, Italy, provides unique evidence of medieval churches using Islamic tents to conceal their high altars. The 700-year-old fresco is thought to be the only surviving image of its kind, offering precious evidence of a little-known Christian practice.
The partially-visible fresco, identified by Cambridge University historian Dr Federica Gigante, almost certainly depicts a real tent, ...
Prison violence remains a significant yet underreported issue in the U.S. criminal justice system, leading to unsafe conditions for both incarcerated persons and staff. To address this pressing problem, a team of researchers has conducted a study aimed at understanding prison violence to develop strategies for reducing and preventing it in correctional facilities nationwide.
The researchers present their work in two recently released policy briefs — “The Dark Figure of Prison Violence: A Multi-Strategy Approach to Uncovering the Prevalence of Prison Violence” and “Sources and Consequences ...
New research from the University of Minnesota and Boston University School of Public Health (BUSPH) shows that death rates for early adults, or adults aged 25-44, rose sharply during the COVID-19 pandemic and remain higher than expected post-pandemic.
Heightened death rates during the COVID-19 pandemic intensified an already negative trend for early adults, which began around 2010. As a result, early adult death rates in 2023 were about 70 percent higher than they might have been if death rates had not begun to rise about a decade before the pandemic.
The researchers analyzed death rates between 1999-2023. Published in JAMA ...
Recycling lithium-ion batteries to recover their critical metals has significantly lower environmental impacts than mining virgin metals, according to a new Stanford University lifecycle analysis published in Nature Communications. On a large scale, recycling could also help relieve the long-term supply insecurity – physically and geopolitically – of critical battery minerals.
Lithium-ion battery recyclers source materials from two main streams: defective scrap material from battery manufacturers, and so-called “dead” batteries, mostly ...
People undergoing hemodialysis treatment for kidney failure often experience chronic pain related to their condition, but it can be difficult to manage with opioid medication and other conventional treatments.
A new study published in JAMA Internal Medicine finds that offering these patients pain coping skills training (PCST) significantly reduced their suffering and improved their quality of life.
“This is particularly important for these patients, since the therapeutic choices for pain management are limited and the use of opioids has been shown ...
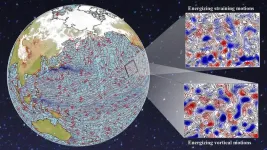
Much like the windy weather patterns that affect the Earth’s surface, our planet’s oceans experience their own distinct weather patterns. These weather patterns, known as eddies, are circular currents of water that are typically about 100 kilometers wide.
A new study of satellite imagery and high-resolution climate model data by scientists at the University of Rochester upends previous assumptions and provides insight about how those surface and ocean weather patterns interact. Scientists formerly believed atmospheric wind had a damping effect, ...
The ambitious project PIPEON* will develop new robotic and AI-based technologies for mapping, monitoring, and maintaining Europe’s sewer networks using autonomous “thinking” robots and AI-based modelling and analysis tools.
The development and application of such new technologies would have major societal, environmental and economic impact. Instead of repairing in-sewer defects and removing blockages after streets and homes have been flooded with sewage, defects can be quickly identified and repaired and blockages removed when they are still small. Early, preventative repair and maintenance actions will limit the frequency and ...
Microsoft's Azure AI Speech platform achieved “significant improvements” in recognizing non-standard English speech thanks to recordings and transcripts from University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign Speech Accessibility Project participants. Its accuracy gains range from 18% to 60%, depending on the speaker’s disability.
The changes are currently rolling out on Microsoft's Cloud endpoint for third-party customers.
Until now, the majority of voice recognition technology trained using recordings and transcriptions from audiobooks. But an audiobook narrator and an individual with aphasia after a stroke sound different.
When the Speech ...