(Press-News.org) The risk of being admitted to the hospital with heart disease is twice as high the year after birth for mothers of twins compared to singleton births, according to research published in the European Heart Journal [1] today (Monday). The risk is even higher in mothers of twins who had a high blood pressure condition during pregnancy.
The research was led by Professor Cande Ananth from the Department of obstetrics, gynecology, and reproductive sciences at Rutgers Robert Wood Johnson Medical School, New Jersey, USA.
He said: “The rate of twin pregnancies worldwide has risen in recent decades, driven by fertility treatments and older maternal ages. Previous studies have shown no long-term increased risk of cardiovascular disease when following people with twin pregnancies for decades after delivery. However, this is counterintuitive to what we observe clinically when caring for patients with twin pregnancies.
“Given the unacceptably high rate of maternal mortality in the first year after birth due to cardiovascular disease, we wanted to examine whether twin pregnancies increase this risk.”
The researchers studied data on 36 million hospital deliveries taken from the US Nationwide Readmissions Database of US hospitals from 2010 to 2020. They divided pregnant patients into four groups: those who had twins but normal blood pressure during pregnancy, those who had twins and hypertensive disease of pregnancy (high blood pressure conditions), those who had singleton pregnancies with normal blood pressure, and those who had singleton pregnancies with hypertensive disease of pregnancy.
Hypertensive disease of pregnancy includes gestational hypertension, pre-eclampsia, eclampsia, and superimposed pre-eclampsia.
For each group, researchers calculated the proportion of patients who were readmitted to the hospital within a year of childbirth with any type of cardiovascular disease, including heart attack, heart failure, or stroke.
Researchers found that the proportion of readmissions for cardiovascular disease within a year of giving birth was higher overall for those with twins (1,105.4 per 100,000 deliveries) than singleton pregnancies (734.1 per 100,000 deliveries).
Compared to singleton pregnancies with normal blood pressure, people with twins with normal blood pressure were around twice as likely to be hospitalised with cardiovascular disease. For those with twins with high blood pressure during pregnancy, the risk is more than eight times higher.
However, one year after birth, deaths from any cause, including heart disease, were higher among patients with singleton pregnancies who had high blood pressure conditions compared to patients with twins with high blood pressure conditions. This suggests that the risk to mothers of twins decreases in the longer term, while the mothers of singletons may have other pre-existing cardiovascular risk factors.
The researchers were not able to examine essential risk factors for cardiovascular disease, such as race/ethnicity, smoking, obesity, and drug use, because these were not consistently recorded in the database.
Dr Ruby Lin, a maternal-foetal medicine fellow at Rutgers Robert Wood Johnson Medical School and the study’s lead author, said: “The maternal heart works harder for twin pregnancies than for singleton pregnancies, and it takes weeks for the maternal heart to return to its pre-pregnancy state.
“People with twin pregnancies should be aware of the short-term increase in cardiovascular disease complications in the first year after birth, even if they had a pregnancy that was not complicated by high blood pressure conditions, such as pre-eclampsia.
“For patients having fertility treatments, especially for those with other cardiovascular risk factors, such as older age, obesity, diabetes, high blood pressure or heart disease, patients should be advised that twin pregnancies may increase cardiovascular disease complications in the short term.
“Given these higher risks, healthcare providers and health insurance companies should continue to provide follow-up for up to a year after birth for high-risk pregnancies such as twin pregnancies.”
In an accompanying editorial [2] Dr Katherine Economy from Brigham and Women's Hospital, Boston, USA, and colleagues said: “Greater understanding of risk factors for cardiovascular disease (CVD) during pregnancy are of substantial interest in light of current maternal morbidity rates in the USA and data revealing that ∼33% of pregnancy-related deaths are attributable to cardiovascular events.
“A particular knowledge gap in pregnancy and CVD centres around twin pregnancies. Twin pregnancies comprise 31 per 1000 births (3.1%) and roughly two-thirds are spontaneously conceived while the remaining third are conceived with assisted reproductive technologies (ART) such as in vitro fertilization (IVF) or ovulation induction therapies.
“To address this gap in knowledge, in the current issue of the European Heart Journal, Lin et al. present new data from the Nationwide Readmissions Database (NRD) that highlight differences in 1 year risk of CVD hospitalizations and mortality between singleton and twin pregnancies with and without hypertensive diseases of pregnancy (HDP).
“Remarkably, the authors observed significantly higher readmission rates for CVD events after a twin pregnancy compared with singletons, with an adjusted hazard ratio (HR) of 8.21 (95% confidence interval [CI] 7.48–9.01) and 1.95 (95% CI 1.75–2.17) among women with and without HDP, respectively.
“We must embrace the fourth trimester (12 weeks after delivery) as a critical time period to make impactful changes that will influence long-term cardiovascular health. Collaboration among obstetricians, cardiologists, and other medical specialists is essential to address the crisis of maternal mortality and to reduce post-partum complications, including improving the accessibility and quality of post-partum care.”
END
Mothers of twins face a higher risk of heart disease in the year after birth
2025-02-03
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
A new approach to detecting Alzheimer’s disease
2025-02-03
Research led by Lancaster University has revealed clear evidence that changes in the orchestration of brain oxygenation dynamics and neuronal function in Alzheimer’s disease contribute to the neurodegeneration.
The study “Neurovascular phase coherence is altered in Alzheimer’s Disease” is published in Brain Communications. The lead author is Aneta Stefanovska with Juliane Bjerkan, Gemma Lancaster, Peter McClintock and Trevor Crawford from Lancaster University and Bernard Meglič and Jan Kobal from the University of Ljubljana Medical Centre in Slovenia.
Professor Stefanovska said: “Alzheimer's can be hypothesised as being a result ...
Could the contraceptive pill reduce risk of ovarian cancer?
2025-02-02
It’s a little pill with big responsibilities. But despite its primary role to prevent pregnancy, the contraceptive pill (or ‘the Pill’) could also help reduce the risk of ovarian cancer, according to new research from the University of South Australia.
Screening for risk factors of ovarian cancer using artificial intelligence, UniSA researchers found that the oral contraceptive pill reduced the risk of ovarian cancer by 26% among women who had ever used the Pill, and by 43% for women who had used the Pill after the age of 45.
The study also identified some biomarkers associated with ovarian cancer risk, including several characteristics of red blood ...
Launch of the most comprehensive, and up to date European Wetland Map
2025-02-02
2nd February 2025 Greifswald/Aarhus/Helsinki - On time for World Wetlands Day, the European Wetland Map (‘EWM’) significantly enhances knowledge of wetlands across Europe by locating, assessing and merging the latest geospatial data. It combines various geographic information system (GIS) data on wetland types and their distribution on mineral soil in coastal environments, floodplains, and a large variety of peatlands in one most comprehensive, easily accessible resource.
"Over a period of two years, we collected, checked and merged more than 200 geodata on wetlands and especially ...
Lurie Children’s campaign urges parents to follow up right away if newborn screening results are abnormal
2025-02-01
Ann & Robert H. Lurie Children’s Hospital of Chicago launched a newborn screening awareness campaign, with signage on public transit and billboards across Chicago urging parents to contact their child’s pediatrician immediately if results are out of normal range. For some conditions, such as cystic fibrosis, that are included in newborn screening, timely diagnosis and early treatment are key to optimal health, while delays can lead to more severe disease.
All U.S. states screen for at least 33 metabolic and ...
Does drinking alcohol really take away the blues? It's not what you think
2025-02-01
A new study from the University of Chicago Medicine reveals that people with alcohol use disorder (AUD) and depression experience high levels of stimulation and pleasure when intoxicated, similar to drinkers who do not have depression.
The findings counter the long-held belief that the pleasure people experience when drinking alcohol decreases with addiction and that drinking to intoxication is mainly to reduce negative feelings as a form of self-medication.
"We have this folklore that people drink excessively when they're feeling depressed ...
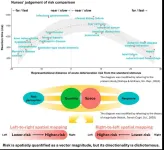
Speed of risk perception is connected to how information is arranged
2025-02-01
Tokyo, Japan – Researchers from Tokyo Metropolitan University have studied how nurses perceive words showing high and low risk ailments. They looked for directional bias, e.g. whether words denoting lower (higher) risk led to a quicker response when placed on the left (right) side or vice versa. They found faster response for significantly higher or lower risk, but different people had different directional biases. Their findings might inform better ways to present clinical information.
With every incoming medical emergency, nurses are required ...
High-risk pregnancy specialists analyze AI system to detect heart defects on fetal ultrasound exams
2025-02-01
High-risk pregnancy specialists from the Raquel and Jaime Gilinski Department of Obstetrics, Gynecology and Reproductive Science at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai are presenting research at the Annual Pregnancy Meeting of the Society for Maternal-Fetal Medicine (SMFM) in Denver from January 27- February 1.
The Mount Sinai doctors are available for interview about their research findings, and can also provide commentary on other women’s health topics, breaking news, and studies.
PRESENTATIONS and POSTER SESSIONS
*All abstracts are under embargo until the below listed times*
Thursday, ...
‘Altar tent’ discovery puts Islamic art at the heart of medieval Christianity
2025-02-01
University of Cambridge media release
‘Altar tent’ discovery puts Islamic art at the heart of medieval Christianity
UNDER STRICT EMBARGO UNTIL 00:01AM (UK TIME) ON SATURDAY 1ST FEBRUARY 2025
A 13th-century fresco rediscovered in Ferrara, Italy, provides unique evidence of medieval churches using Islamic tents to conceal their high altars. The 700-year-old fresco is thought to be the only surviving image of its kind, offering precious evidence of a little-known Christian practice.
The partially-visible fresco, identified by Cambridge University historian Dr Federica Gigante, almost certainly depicts a real tent, ...
Policy briefs present approach for understanding prison violence
2025-01-31
Prison violence remains a significant yet underreported issue in the U.S. criminal justice system, leading to unsafe conditions for both incarcerated persons and staff. To address this pressing problem, a team of researchers has conducted a study aimed at understanding prison violence to develop strategies for reducing and preventing it in correctional facilities nationwide.
The researchers present their work in two recently released policy briefs — “The Dark Figure of Prison Violence: A Multi-Strategy Approach to Uncovering the Prevalence of Prison Violence” and “Sources and Consequences ...
Early adult mortality is higher than expected in US post-COVID
2025-01-31
New research from the University of Minnesota and Boston University School of Public Health (BUSPH) shows that death rates for early adults, or adults aged 25-44, rose sharply during the COVID-19 pandemic and remain higher than expected post-pandemic.
Heightened death rates during the COVID-19 pandemic intensified an already negative trend for early adults, which began around 2010. As a result, early adult death rates in 2023 were about 70 percent higher than they might have been if death rates had not begun to rise about a decade before the pandemic.
The researchers analyzed death rates between 1999-2023. Published in JAMA ...