(Press-News.org) About The Study: Using passive sensing on a sample of U.S. adolescents, this study found half of adolescents use their smartphones during school for at least 66 minutes daily, primarily using messaging and social media. These findings extend a prior study limited to Android devices that found adolescents spent a median of 43 minutes on their phones during school.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Lauren Hale, PhD, email Lauren.Hale@stonybrookmedicine.edu.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamapediatrics.2024.6627)
Editor’s Note: Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and affiliations, conflict of interest and financial disclosures, and funding and support.
# # #
Embed this link to provide your readers free access to the full-text article This link will be live at the embargo time https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jamapediatrics/fullarticle/10.1001/jamapediatrics.2024.6627?guestAccessKey=6431bed4-cdf0-4f68-b245-0d72f44225f5&utm_source=for_the_media&utm_medium=referral&utm_campaign=ftm_links&utm_content=tfl&utm_term=020325
END
Adolescent smartphone use during school hours
JAMA Pediatrics
2025-02-03
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Alarming rise in rates of advanced prostate cancer in California
2025-02-03
Alarming Rise in Rates of Advanced Prostate Cancer in California
Following a change in screening guidelines, the incidence went up across the state, even more than it has nationally.
The incidence of advanced prostate cancer in California rose markedly in the decade since doctors stopped routinely screening all men for the disease, according to a new study by UC San Francisco.
After declining for many years, the death rate from the disease also plateaued in most regions across the state.
The findings reinforce the need for screening that can identify potentially fatal tumors without raising false alarms about ones that pose no threat to the patient.
The ...
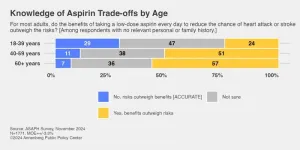
Nearly half of adults mistakenly think benefits of daily aspirin outweigh risks
2025-02-03
For years, healthy older adults were advised by doctors to take a low-dose aspirin daily as a way to reduce the risk of heart attack. But in March 2019, the American College of Cardiology and the American Heart Association (AHA) announced new guidelines and no longer routinely recommended a daily dose of aspirin for healthy adults over the age of 70 because the risk of gastrointestinal bleeding outweighs the benefits.
Nearly five years later, many Americans still have not received the message.
The Annenberg Public Policy Center (APPC) of the University of Pennsylvania finds in a new health survey that nearly half (48%) of U.S. ...
Cardiovascular disease medications underused globally
2025-02-03
Secondary prevention medications for cardiovascular diseases (CVD) are underused globally and additional strategies to increase their use are needed to improve CVD management and reduce premature mortality rates, according to study published today in JACC, the flagship journal of the American College of Cardiology. The study observed participants with CVD from 17 countries over 12 years and found that medication use remains low with little improvement.
Secondary prevention of CVD focuses on preventing further health problems in people already diagnosed with CVD. This includes managing risk factors through lifestyle changes, medications and ...
Amazon Pharmacy's RxPass program improves medication adherence, helps prime members save money, study finds
2025-02-03
Approximately half of all Americans do not take their medication as prescribed by their doctor. This medication non-adherence causes an estimated 125,000 additional deaths and as much as $300 billion a year in additional medical appointments, emergency department visits, and hospitalizations.
A new study published in the Journal of the American Medical Association (JAMA) Network Open finds Amazon Pharmacy’s subscription service for common medications, RxPass, leads to significant improvements in medication adherence while reducing out-of-pocket costs for patients. This first-of-its-kind study evaluated the potential of subscription models to support prescription medication access ...
Tufts University School of Medicine, ATI Physical Therapy launch first-of-its-kind collaboration to make physical therapy education and career advancement more accessible and affordable
2025-02-03
With demand for physical therapy services projected to increase 27 percent by 2030, Tufts University School of Medicine (TUSM) and ATI Physical Therapy (ATI), a leading provider of physical therapy services across the United States, are launching a joint initiative aimed at expanding the physical therapist workforce and making the Doctor of Physical Therapy (DPT) Programs at TUSM more accessible.
As part of the first-of-its-kind collaboration, TUSM and ATI will contribute scholarships each semester for up to 45 ATI employees in TUSM’s DPT programs each academic year. The accelerated ...
Could lycopene—a plant extract—be an effective antidepressant?
2025-02-03
Emerging evidence suggests that lycopene—a natural plant extract—may have antidepressant properties. New research in Food Science & Nutrition reveals the mechanisms behind its antidepressant effects.
In mice with depressive-like behaviors, brain analyses revealed impairments in the hippocampus. Lycopene treatment lessened these impairments and reversed the animals’ depressive-like traits.
Lycopene treatment boosted the expression of brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF), a protein with roles in many aspects of brain function. Experiments indicated that a signaling pathway involving BDNF (called the BDNF-TrkB pathway, ...
Study shows urine test for prostate cancer could be used at home
2025-02-03
Researchers at Vanderbilt and the University of Michigan have shown that a simple at-home urine test for prostate cancer screening is highly accurate. The exciting new results, published in The Journal of Urology, build upon a prior Vanderbilt study of prostate cancer screening that required a digital rectal exam.
The results are important because this could enable at-home testing and increased access to testing for patients undergoing telehealth care or living in remote areas.
Traditional prostate cancer screening with PSA testing and biopsy has been shown to lead to unnecessary procedures and overdiagnosis of low-grade cancers, according to ...
Shaping future of displays: clay/europium-based technology offers dual-mode versatility
2025-02-03
The world of display technology is on the cusp of a transformative breakthrough, with electrochemical stimuli-responsive materials gaining more attraction. Based on external stimuli, such as low voltage, these materials can instantaneously undergo electrochemical reactions. These electrochemical reactions can result in the production of different colors, revolutionizing the age of display solutions. An electrochemical system consists of electrodes and electrolytes. Combining the luminescent and coloration molecules on the electrodes instead of the electrolyte can offer higher efficiencies and stability for display devices.
To this end, a research team ...
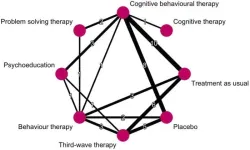
Optimizing ADHD treatment: revealing key components of cognitive–behavioral therapy
2025-02-03
Attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) is a well-known neurodevelopmental disorder that affects the brain's ability to regulate attention and control impulses. It poses many challenges to those affected, typically making it difficult for them to sustain focus, follow through with instructions, and maintain a calm and restful state. As one of the most common neurodevelopmental disorders, ADHD impacts individuals throughout their lives, creating a breadth of social, emotional, academic, and workplace challenges.
Despite its high ...
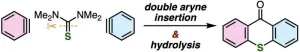
Breaking barriers in thioxanthone synthesis: a double aryne insertion strategy
2025-02-03
Thioxanthones are fascinating organic compounds that have found their way into many industrial and everyday applications. In the printing industry, for example, they help inks dry faster when exposed to light thanks to their light-absorption properties, making the printing process quicker and more efficient. Some thioxanthones have been developed into FDA-approved drugs used to treat parasitic infections and cancer. Additionally, their effectiveness as photocatalysts has led some researchers to explore their potential as stabilizers against electrical breakdown. Thioxanthones have also been ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
How an alga makes the most of dim light
Race against time to save Alpine ice cores recording medieval mining, fires, and volcanoes
Inside the light: How invisible electric fields drive device luminescence
A folding magnetic soft sheet robot: Enabling precise targeted drug delivery via real-time reconfigurable magnetization
Sylvester Cancer Tip Sheet for March 2026
New tools and techniques accelerate gallium oxide as next-generation power semiconductor
Researchers discover seven different types of tension
Report calls for AI toy safety standards to protect young children
VR could reduce anxiety for people undergoing medical procedures
Scan that makes prostate cancer cells glow could cut need for biopsies
Mechanochemically modified biochar creates sustainable water repellent coating and powerful oil adsorbent
New study reveals hidden role of larger pores in biochar carbon capture
Specialist resource centres linked to stronger sense of belonging and attainment for autistic pupils – but relationships matter most
Marshall University, Intermed Labs announce new neurosurgical innovation to advance deep brain stimulation technology
Preclinical study reveals new cream may prevent or slow growth of some common skin cancers
Stanley Family Foundation renews commitment to accelerate psychiatric research at Broad Institute
What happens when patients stop taking GLP-1 drugs? New Cleveland Clinic study reveals real world insights
American Meteorological Society responds to NSF regarding the future of NCAR
Beneath Great Salt Lake playa: Scientists uncover patchwork of fresh and salty groundwater
Fall prevention clinics for older adults provide a strong return on investment
People's opinions can shape how negative experiences feel
USC study reveals differences in early Alzheimer’s brain markers across diverse populations
300 million years of hidden genetic instructions shaping plant evolution revealed
High-fat diets cause gut bacteria to enter brain, Emory study finds
Teens and young adults with ADHD and substance use disorder face treatment gap
Instead of tracking wolves to prey, ravens remember — and revisit — common kill sites
Ravens don’t follow wolves to dinner – they remember where the food is
Mapping the lifelong behavior of killifish reveals an architecture of vertebrate aging
Designing for hard and brittle lithium needles may lead to safer batteries
Inside the brains of seals and sea lions with complex vocal behavior learning
[Press-News.org] Adolescent smartphone use during school hoursJAMA Pediatrics