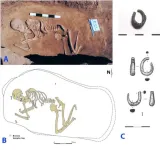
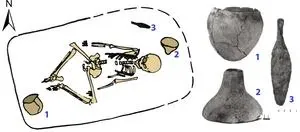
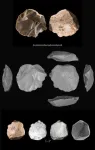
(Press-News.org) Where lies the origin of the Indo-European language family? Ron Pinhasi and his team in the Department of Evolutionary Anthropology at the University of Vienna contribute a new piece to this puzzle in collaboration with David Reich's ancient DNA laboratory at Harvard University. They analyzed ancient DNA from 435 individuals from archaeological sites across Eurasia between 6.400–2.000 BCE. They found out that a newly recognized Caucasus-Lower Volga population can be connected to all Indo-European-speaking populations. The new study is published in Nature.
Indo-European languages (IE), which number over 400 and include major groups such as Germanic, Romance, Slavic, Indo-Iranian, and Celtic, are spoken by nearly half the world's population today. Originating from the Proto-Indo-European (PIE) language, historians and linguists since the 19th century have been investigating its origins and spread as there is still a knowledge gap.
The new study published in Nature, also involving Tom Higham and Olivia Cheronet from the University of Vienna, analyzes ancient DNA from 435 individuals from archaeological sites across Eurasia between 6400–2000 BCE. Earlier genetic studies had shown that the Yamnaya culture (3.300-2.600 BCE) of the Pontic-Caspian steppes north of the Black and Caspian Seas expanded into both Europe and Central Asia beginning about 3.100 BCE, accounting for the appearance of "steppe ancestry" in human populations across Eurasia 3.100-1.500 BCE. These migrations out of the steppes had the largest effect on European human genomes of any demographic event in the last 5.000 years and are widely regarded as the probable vector for the spread of Indo-European languages.
The only branch of Indo-European language (IE) that had not exhibited any steppe ancestry previously was Anatolian, including Hittite, probably the oldest branch to split away, uniquely preserving linguistic archaisms that were lost in all other IE branches. Previous studies had not found steppe ancestry among the Hittites because, the new paper argues, the Anatolian languages were descended from a language spoken by a group that had not been adequately described before, an Eneolithic population dated 4.500-3.500 BCE in the steppes between the North Caucasus Mountains and the lower Volga. When the genetics of this newly recognized Caucasus-Lower Volga (CLV) population are used as a source, at least five individuals in Anatolia dated before or during the Hittite era show CLV ancestry.
Newly recognized population with broad influence
The new study shows the Yamnaya population to have derived about 80% of its ancestry from the CLV group, which also provided at least one-tenth of the ancestry of Bronze Age central Anatolians, speakers of Hittite. "The CLV group therefore can be connected to all IE-speaking populations and is the best candidate for the population that spoke Indo-Anatolian, the ancestor of both Hittite and all later IE languages," explains Ron Pinhasi. The results further suggest that the integration of the proto-Indo-Anatolian language, shared by both Anatolian and Indo-European peoples, reached its zenith among the CLV communities between 4.400 BC and 4.000 BC.
"The discovery of the CLV population as the missing link in the Indo-European story marks a turning point in the 200-years-old quest to reconstruct the origins of the Indo-Europeans and the routes by which these people spread across Europe and parts of Asia", concludes Ron Pinhasi.
END
Missing link in Indo-European languages' history found
New insights into our linguistic roots via ancient DNA analysis
2025-02-05
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Cancer vaccine shows promise for patients with stage III and IV kidney cancer
2025-02-05
Boston – Dana-Farber Cancer Institute researchers report that all nine patients in a clinical trial being treated for stage III or IV clear cell renal cell carcinoma (a form of kidney cancer), generated a successful anti-cancer immune response after initiation of a personalized cancer vaccine. The vaccines were administered after surgery to remove the tumor and are designed to train the body’s immune system to recognize and eliminate any remaining tumor cells. At the time of data cut-off (median of 34.7 months), ...
Only seven out of 100 people worldwide receive effective treatment for their mental health or substance-use disorders
2025-02-05
New research estimates that globally, only 6.9 per cent of people with mental health or substance-use disorders receive effective treatment for their disorders.
Researchers from the University of British Columbia and Harvard Medical School analyzed survey data from nearly 57,000 participants in 21 countries collected over a 19-year period, to provide the clearest picture yet of where people discontinue their path to effective treatment for nine common anxiety, mood and substance-use disorders.
The biggest barrier to effective ...
Ancient engravings shed light on early human symbolic thought and complexity in the levantine middle palaeolithic
2025-02-05
New study demonstrates that certain incised stone artefacts from the Levantine Middle Palaeolithic, specifically from Manot, Qafzeh, and Quneitra caves, were deliberately engraved with geometric patterns, indicating advanced cognitive and symbolic behaviour among early humans. In contrast, artefacts from Amud Cave, with shallow and unpatterned incisions, are consistent with functional use. This research highlights the intentionality behind the engravings, providing key insights into the development of abstract thinking and the cultural complexity of Middle Palaeolithic societies.
Link ...
The sexes have different strengths for achieving their goals
2025-02-05
Many factors are needed to achieve our goals. Now researchers have looked at passion, drive and people’s ability to find flow.
“This is the first study to look at these factors together,"says Professor Hermundur Sigmundsson at the Norwegian University of Science and Technology (NTNU’s) Department of Psychology.
The researchers have found differences between the sexes. The results indicate that the sexes each have their own strengths when it comes to success.
Men are more passionate than women when it comes to achieving their goals. They also often have an easier time finding flow.
Women, ...
College commuters: Link between students’ mental health, vehicle crashes
2025-02-05
Young adults are a higher risk group for being in a crash while driving due likely to inexperience with driving, driving under the influence, and a greater propensity to take risks while driving. Although research has explored sociodemographic links of driver crashes based on age, sex and socioeconomic status, reports on the relationship between crashes and mental health are sparse.
A new Florida Atlantic University study fills a notable gap by exploring the correlation between commuter college students’ mental health status and being in a crash while driving. Commuter students, often lower-income, older, or balancing family responsibilities, face greater ...
Using sugars from peas speeds up sour beer brewing
2025-02-05
Sour beers have become a fixture on microbrewery menus and store shelves. They’re enjoyed for their tart, complex flavors, but some can require long and complicated brewing processes. Researchers reporting in ACS’ Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry brewed new sours in less time using a seemingly strange ingredient: field peas. The experimental beers had fruity — not “beany” — flavors and other attributes comparable to a commercial Belgian-style sour, but with shorter, simpler brewing steps.
“Sour beer is the beer enthusiast’s alternative to Champagne. By using sugars derived from peas that yeast ...
Stormwater pollution sucked up by specialized sponge
2025-02-05
Reusable sponge platform has successfully removed oil, phosphate and metal from contaminated water
New development allows capture of valuable minerals and reuse of the sponge
Water pollution concentrations move from 0.8 parts per million to undetectable levels
EVANSTON, Ill. --- As more waterways contend with algae blooms and pollution caused by minerals from agricultural runoff and industrial manufacturing processes, new methods to remove pollutants like phosphate, copper and zinc are emerging across fields.
While solutions exist, they tend to be costly ...
Value-added pancakes: WSU using science to improve nutrition of breakfast staple
2025-02-05
PULLMAN, Wash. — Typical breakfast pancakes are soft, fluffy and delicious but, sadly, not terribly healthy.
Food scientists at Washington State University are working to change that by boosting the popular morning favorite’s nutritional value while enhancing its taste and texture.
“Generally, pancakes are made with refined flours, contributing to empty calories,” said Girish Ganjyal, a professor and food processing specialist in WSU’s School of Food Science. “We wanted to see if it’s ...
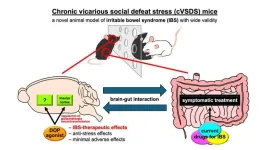
Beyond the gut: A new frontier in IBS treatment by targeting the brain
2025-02-05
Irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) is a common digestive disorder that affects the intestine, causing symptoms such as abdominal pain, bloating, gas, and changes in bowel habits, including diarrhea, constipation, or both. Although this condition affects about a tenth of the global population, the underlying causes and mechanisms of IBS remain unclear. Consequently, treatments for IBS primarily focus on managing symptoms rather than addressing the root cause of the disorder.
At Tokyo University of Science ...
New spin on quantum liquids: Quasi-1D dynamics in molecular spin systems
2025-02-05
Quantum spin liquids (QSLs) are fascinating and mysterious states of matter that have intrigued scientists for decades. First proposed by Nobel laureate Philip Anderson in the 1970s, these materials break the conventional rules of magnetism by never settling into a stable magnetic state, even at temperatures close to absolute zero. Instead, the spins of the atoms within them remain constantly fluctuating and entangled, creating a kind of magnetic “liquid.” This unusual behavior is driven by a phenomenon called magnetic frustration, where competing forces prevent the system from reaching a single, ordered configuration. QSLs are notoriously ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Could ultrasound help save hedgehogs?
attexis RCT shows clinically relevant reduction in adult ADHD symptoms and is published in Psychological Medicine
Cellular changes linked to depression related fatigue
First degree female relatives’ suicidal intentions may influence women’s suicide risk
Specific gut bacteria species (R inulinivorans) linked to muscle strength
Wegovy may have highest ‘eye stroke’ and sight loss risk of semaglutide GLP-1 agonists
New African species confirms evolutionary origin of magic mushrooms
Mining the dark transcriptome: University of Toronto Engineering researchers create the first potential drug molecules from long noncoding RNA
IU researchers identify clotting protein as potential target in pancreatic cancer
Human moral agency irreplaceable in the era of artificial intelligence
Racial, political cues on social media shape TV audiences’ choices
New model offers ‘clear path’ to keeping clean water flowing in rural Africa
Ochsner MD Anderson to be first in the southern U.S. to offer precision cancer radiation treatment
Newly transferred jumping genes drive lethal mutations
Where wells run deep, biodiversity runs thin
Q&A: Gassing up bioengineered materials for wound healing
From genetics to AI: Integrated approaches to decoding human language in the brain
Leora Westbrook appointed executive director of NR2F1 Foundation
Massive-scale spatial multiplexing with 3D-printed photonic lanterns achieved by researchers
Younger stroke survivors face greater concentration, mental health challenges — especially those not employed
From chatbots to assembly lines: the impact of AI on workplace safety
Low testosterone levels may be associated with increased risk of prostate cancer progression during surveillance
Analysis of ancient parrot DNA reveals sophisticated, long-distance animal trade network that pre-dates the Inca Empire
How does snow gather on a roof?
Modeling how pollen flows through urban areas
Blood test predicts dementia in women as many as 25 years before symptoms begin
Female reproductive cancers and the sex gap in survival
GLP-1RA switching and treatment persistence in adults without diabetes
Gnaw-y by nature: Researchers discover neural circuit that rewards gnawing behavior in rodents
Research alert: How one receptor can help — or hurt — your blood vessels
[Press-News.org] Missing link in Indo-European languages' history foundNew insights into our linguistic roots via ancient DNA analysis