(Press-News.org) A study of fruit flies shows some species are highly susceptible to a wide range of viruses.
In the study – by the University of Exeter – 35 fruit fly species were exposed to 11 different viruses of diverse types.
As expected, fly species that were less affected by a certain virus also tended to respond well to related viruses.
But the findings also show “positive correlations in susceptibility” to viruses in general. In other words, fly species that were resistant to one virus were generally resistant to others – including very different types of virus.
“Large-scale tests like this help us understand how pathogens shift to new host species, with findings broadly applicable to other animals – including humans,” said Dr Ryan Imrie, now at the MRC-University of Glasgow Centre for Virus Research.
“These flies shared a common ancestor 50 million years ago, giving them equivalent diversity to mammals, and so we are asking questions over the evolutionary distances which host shifts typically occur.
“Lots of people are trying to predict the next pandemic.
“It’s impossible to test every virus, so we need to try and understand general rules about how viruses behave in new hosts.”
Professor Ben Longdon, of the Centre for Ecology and Conservation on Exeter’s Penryn Campus in Cornwall, added: “Information about new viruses can partly be inferred from their relatedness to existing viruses.
“However, a small number of mutations can change that – giving new viruses very different properties than their close relatives.
“Studies like this can help reveal the fundamental processes behind this.”
Susceptibility in the study was measured by “viral load” – how much a virus had replicated and persisted two days into an infection.
Explaining why some fly species might be generally poor at resisting viruses, Dr Longdon said: “Immunity is very costly, so the highly susceptible species in our study may be ones that evolved in an environment with relatively few viruses, or species that viruses are particularly well able to hijack and successfully infect.
“We found no negative correlations (where high resistance to one virus came with low resistance to another).
“This could suggest that, as fruit fly immune systems have evolved in response to infection, they have not resulted in ‘trade-offs’ where increased resistance to one virus has decreased resistance to others.”
The study was funded by the Wellcome Trust and the Royal Society.
The paper, published in the journal Evolution Letters, is entitled: “Positive correlations in susceptibility to a diverse panel of viruses across Drosophilidae host species.”
END
Study shows some species are susceptible to broad range of viruses
2025-02-06
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
How life's building blocks took shape on early Earth: the limits of membraneless polyester protocell formation
2025-02-06
One leading theory on the origins of life on Earth proposes that simple chemical molecules gradually became more complex, ultimately forming protocells—primitive, non-living structures that were precursors of modern cells. A promising candidate for protocells is polyester microdroplets, which form through the simple polymerisation of alpha-hydroxy acids (αHAs), compounds believed to have accumulated on early Earth possibly formed by lightning strikes or delivered via meteorites, into protocells, followed by simple rehydration ...
Survey: Many Americans don’t know long-term risks of heart disease with pregnancy
2025-02-06
COLUMBUS, Ohio – Pregnancy-related deaths in the U.S. have risen 140% over the past three decades with heart disease a major cause, according to the American Heart Association. A new national survey commissioned by The Ohio State University Wexner Medical Center found that many Americans are not aware of the long-term risks of heart disease with pregnancy and the critical care needed before, during and after pregnancy.
“During pregnancy there are a lot of different hormone shifts that happen to accommodate growth of the baby and health of the mom. The result is that the mom’s heart rate increases along with the amount ...
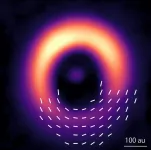
Dusting for stars’ magnetic fingerprints
2025-02-06
For the first time astronomers have succeeded in observing the magnetic field around a young star where planets are thought to be forming. The team was able to use dust to measure the three-dimensional structure “fingerprint” of the magnetic field. This will help improve our understanding of planet formation.
Planets form in turbulent disks of gas and dust called protoplanetary disks around young stars. It is thought that the first step in planet formation is dust grains colliding and sticking together. The movement of ...
Relief could be on the way for UTI sufferers dealing with debilitating pain
2025-02-06
Relief could be on the way for UTI sufferers dealing with debilitating pain
New insights into what causes the painful and disruptive symptoms of urinary tract infections (UTIs) could offer hope for improved treatment.
UTIs are one of the most prevalent bacterial infections globally, with more than 400 million cases reported every year. Nearly one in three women will experience UTIs before the age of 24, and many elderly people and those with bladder issues from spinal cord injuries can experience multiple UTI’s in a single year.
Findings from a new study led by Flinders University’s ...
Testing AI with AI: Ensuring effective AI implementation in clinical practice
2025-02-06
Using a pioneering artificial intelligence platform, Flinders University researchers have assessed whether a cardiac AI tool recently trialled in South Australian hospitals actually has the potential to assist doctors and nurses to rapidly diagnose heart issues in emergency departments.
“AI is becoming more common in healthcare, but it doesn’t always fit in smoothly with the vital work of our doctors and nurses,” says Flinders University’s Dr Maria Alejandra Pinero de Plaza, who led the research.
“We need to confirm these systems are trustworthy and work ...
Researchers find improved method for treating rare, aggressive, pregnancy-related cancer
2025-02-06
PORTLAND, Ore. – A new drug delivery system shows promise for treating a rare, aggressive form of cancer affecting pregnant women and new mothers, and it has potential with other cancers as well.
Scientists led by Olena Taratula, a nanomedicine researcher at Oregon State University, have found a way to better ensure the drug used to combat the disease reaches tumor cells without damaging healthy tissue.
Findings of the study into choriocarcinoma, which occurs in the United States at a rate of about four cases per 100,000 pregnancies, ...
Half of the fish you eat comes from the Great Barrier Reef’s marine reserves
2025-02-06
A new study of the Great Barrier Reef has revealed that the network of no-take marine reserves supplies nearly half of the region’s coral trout fishery catch.
The research, led by Professor Michael Bode from the QUT School of Mathematical Sciences and published in Science Advances, revealed that despite covering only 30 per cent of the reef’s habitat, these protected areas account for 47 per cent of the coral trout catch in fishing areas and contribute 55 per cent of the species’ reproduction.
The Great Barrier Reef is protected by a network of marine reserves designed to conserve ...
McDonald’s thwarts council efforts to stop new branches by claiming it promotes ‘healthier lifestyles’
2025-02-06
McDonald's is overturning council attempts to prevent new fast food outlets by claiming they will encourage healthier lifestyles, reveals an investigation published by The BMJ today.
Based on Freedom of Information requests, it shows that the firm has won planning appeals against local authorities in some of the most deprived areas of England, where around 1 in 4 children are obese by the time they leave primary school.
Its tactics include arguing that customers can order salad from its drive-through branches, that they could cycle or walk there, and that its sponsorship ...
Is CBD use during pregnancy as safe as people think? New study uncovers potential risks to babies
2025-02-06
Cannabidiol (CBD), the component in cannabis often used for therapeutic treatments, is increasingly being used during pregnancy as a means of managing symptoms such as nausea, anxiety and sleep. Though the public perception is that CBD – particularly when consumed orally – is safer and helpful for symptom management, little is known about the impact of CBD on pregnancy.
A new study from McMaster University researchers fills that gap in knowledge and has uncovered potential risks, including impaired fetal growth, associated with the use of both tetrahydrocannabinol (THC), the ...
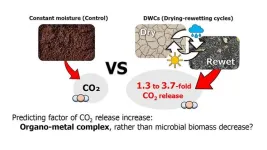
Drying and rewetting cycles substantially increased soil CO2 release
2025-02-06
Niigata, Japan - The amount of carbon dioxide (CO2) released by microbial decomposition of soil organic carbon on a global scale is approximately five times greater than the amount of anthropogenic CO2 emissions. Thus, it is essential to clarify the impact of climate change on soil CO2 release dynamics.
A collaborative research group consisting of Dr. Hirohiko Nagano and Ms. Yuri Suzuki of Niigata University with researchers of Kyushu University and the Japan Atomic Energy Agency conducted incubation experiments on forest and pastureland soils at 10 locations across Japan. The research group revealed ...