(Press-News.org) DETROIT — Physics-based computer simulations are essential tools for understanding the relationship between atomic-level interactions and physically observable properties of materials. It is from knowledge of these structure-property relationships that new materials can be designed with properties specifically tailored to address the problem of interest.
With the help of a new grant from the National Science Foundation (NSF), a team of Wayne State University College of Engineering researchers are developing new software to support computational materials design. Built on a 15-year collaborative effort, Jeffrey Potoff, Ph.D., chair of chemical engineering and materials science will lead the study, alongside his co-principal investigator, Loren Schwiebert, Ph.D., professor of computer science.
This three-year, $600,000 grant from the Office of Advanced Cyberinfrastructure of the NSF, “ELEMENTS: py-MCMD: software for hybrid Monte Carlo/molecular dynamics simulations,” focuses on the development of the high-performance Monte Carlo software known as GOMC (https://gomc-wsu.org/). The goals of this effort are to reduce latency in Monte Carlo/molecular dynamics (MC/MD) cycles and enable rigorous multi-scale simulations, where the resolution of the molecular models may be changed quickly to optimize sampling efficiency.
Ultimately, this work will provide open-source software to the research community that will allow researchers to simulate systems of larger scale and fidelity than is possible with current software.
“Monte Carlo and molecular dynamics algorithms are very different, but each has unique features that users would like to combine in a single simulation,” said Potoff. “However, the code bases are complex and challenging to integrate. Our approach to use a separate Python driver program to control interactions between two separate codes, which remain largely unchanged, is designed to substantially reduce development time while providing respectable code performance. We expect our software to be used in a wide variety of fields, from the design of novel adsorbents for gas separation and storage, to the development of new surfactants for rare earth element separation.”
In addition to open-source software, the project aims to lower barriers for new users by producing training materials, including as Python workflows and videos, that provide instructions on how to perform common molecular dynamics, Monte Carlo and hybrid MC/MD simulations.
“Drs. Potoff and Schwiebert’s cutting-edge work is an example of innovative collaborative research at Wayne State University that may have an impact in numerous industries,” said Ezemenari M. Obasi, Ph.D., vice president for research & innovation at Wayne State University. “I look forward to the results of their diverse perspectives that aim to address complex problems.”
The award number for this grant from the Office of Advanced Cyberinfrastructure of the National Science Foundation is 2410153.
# # #
About Wayne State University
Wayne State University is one of the nation’s pre-eminent public research universities in an urban setting. Through its multidisciplinary approach to research and education, and its ongoing collaboration with government, industry and other institutions, the university seeks to enhance economic growth and improve the quality of life in the city of Detroit, state of Michigan and throughout the world. For more information about research at Wayne State University, visit research.wayne.edu.
Wayne State University’s research efforts are dedicated to a prosperity agenda that betters the lives of our students, supports our faculty in pushing the boundaries of knowledge and innovation further, and strengthens the bonds that interconnect Wayne State and our community. To learn more about Wayne State University’s prosperity agenda, visit president.wayne.edu/prosperity-agenda.
END
New software developed at Wayne State University will help study chemical and biological systems
2025-02-06
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
uOttawa study unveils new insights into how neural stem cells are activated in the adult human brain
2025-02-06
A University of Ottawa neuroscientist has led a Canadian research team to reveal important new insights into the activation dynamics of neural stem cells (NSCs). These are the stem cells that build our central nervous systems and the self-renewing.
The collaborative team led by the University of Ottawa’s Dr. Armen Saghatelyan aimed to shed light on how neural stem cells integrate a multitude of signals from different cell types in the brain – and how they decode these signals.
These are big questions because how NSCs react to signals in their cellular environment controls whether they remain in their ...
Cystic fibrosis damages the immune system early on
2025-02-06
Despite new medication, cystic fibrosis often leads to permanent lung damage. Working with an international team, researchers from the Technical University of Munich (TUM) have discovered that the disease causes changes in the immune system early in life, presumably even in newborns. These changes lead to frequent inflammation and are not affected by drugs targeting the altered mucus production.
Cystic fibrosis is caused by hereditary genetic mutations that impair or halt the production of the CFTR protein. The respiratory tract ...
Novel ‘living’ biomaterial aims to advance regenerative medicine
2025-02-06
UNIVERSITY PARK, Pa. — A biomaterial that can mimic certain behaviors within biological tissues could advance regenerative medicine, disease modeling, soft robotics and more, according to researchers at Penn State.
Materials created up to this point to mimic tissues and extracellular matrices (ECMs) — the body’s biological scaffolding of proteins and molecules that surrounds and supports tissues and cells — have all had limitations that hamper their practical applications, according to the team. To overcome some of those limitations, ...
Warding off superbugs with a pinch of turmeric
2025-02-06
In 2017, a tragic incident unfolded in a Nevada hospital. A woman, admitted for pneumonia, tragically succumbed to multiple organ failure and sepsis. The culprit? A strain of bacteria that had developed resistance to a staggering 26 different antibiotics. These superbugs, or antibiotic-resistant bacteria, stand as one of the most pressing public health threats globally.
Joining the effort to fight these deadly pathogens, researchers at Texas A&M have now shown that curcumin, the compound that gives turmeric its characteristic bright yellow color, can potentially be used to reduce antibiotic resistance.
The ...
Ophthalmic complications in patients on antidiabetic GLP-1 medications are concerning neuro-ophthalmologists
2025-02-06
BUFFALO, N.Y. — A small percentage of patients taking the extraordinarily popular GLP-1 medications have experienced vision problems, but a direct causal link with the drugs has not been established. That is the conclusion of a retrospective study published online on Jan. 30 in JAMA Ophthalmology.
The study focused on nine patients who had experienced vision problems while using semaglutide (brand names Wegovy and Ozempic) and tirzepatide (brand names Mounjaro and Zepbound).
The paper is one of several in the past ...
Physicians committee research policy director speaks today at hearing on taxpayer funded animal cruelty
2025-02-06
WASHINGTON, D.C. — Research Policy Director Elizabeth Baker from the Physicians Committee for Responsible Medicine, a national medical ethics and health advocacy group of 17,000 physicians, spoke today, Feb. 6, at a Congressional hearing focused on ending federally funded animal cruelty in research.
The U.S. House Oversight and Government Reform Subcommittee on Cybersecurity, Information Technology, and Government Innovation Chairwoman Nancy Mace (R-S.C.) announced the hearing in a news release on Monday, with plans to evaluate current animal cruelty funded by the federal government and explore opportunities ...
New technology lights way for accelerating coral reef restoration
2025-02-06
COLUMBUS, Ohio – Scientists have developed a novel tool designed to protect and conserve coral reefs by providing them with an abundance of feeding opportunities.
The device, dubbed the Underwater Zooplankton Enhancement Light Array (UZELA), is an autonomous, programmable underwater light that works to draw in nearby zooplankton, microscopic organisms that coral feed on.
After testing the submersible on two species of coral native to Hawaii over six months, researchers found that UZELA could ...
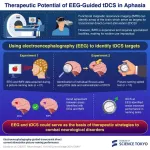
Electroencephalography may help guide treatments for language disorders
2025-02-06
Electroencephalography (EEG) may offer a more accessible alternative to functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) for guiding transcranial direct current stimulation (tDCS) when treating aphasia. Researchers from Institute of Science Tokyo found an 80% agreement between EEG and fMRI in identifying brain regions activated during language tasks. Furthermore, EEG-guided tDCS improved picture-naming speed in participants, indicating its potential for innovative therapies in language disorders.
Many neurological disorders are directly linked to damage or deterioration in specific regions of the brain. For example, ...
Multinational research project shows how life on Earth can be measured from space
2025-02-06
Measurements and data collected from space can be used to better understand life on Earth.
An ambitious, multinational research project funded by NASA and co-led by UC Merced civil and environmental engineering Professor Erin Hestir demonstrated that Earth’s biodiversity can be monitored and measured from space, leading to a better understanding of terrestrial and aquatic ecosystems. Hestir led the team alongside University of Buffalo geography Professor Adam Wilson and Professor Jasper Slingsby from the University ...
Essential genome of malaria parasite Plasmodium knowlesi mapped
2025-02-06
Embargoed for release: Thursday, February 6, 2025, 2:00 PM ET
Key points:
Comprehensive genetic mapping of Plasmodium knowlesi, a zoonotic parasite that causes malaria, has revealed the genes required for malaria infection of the blood, and those driving drug resistance.
By identifying specific druggable targets and determinants of resistance, the map provides insights that could help the development of new therapeutics.
Boston, MA—A new, comprehensive map of all the genes essential for blood infections in Plasmodium knowlesi (P. ...