(Press-News.org) A first-of-its-kind study provides a snapshot of the substantial mental health burden on nurses around the world. Published in the journal International Nursing Review, the research documents the impact of three years of intense working conditions brought on by the COVID-19 pandemic.
“Our study describes how nurses are affected by stressors in their workplace and shows how the stress carries over into their home life. The personal losses from the pandemic complicate this picture as there could easily be lingering grief in a third of the workforce,” said Allison Squires, a professor at NYU Rory Meyers College of Nursing and the study’s lead author.
Stress and burnout among nurses working during the COVID-19 pandemic are well-documented, but most studies come from high-income countries. To address the gap in knowledge from other countries around the world, Squires founded the Global Consortium of Nursing and Midwifery Studies. The international research collaboration, which now includes nurses and other health professionals from 82 countries, is examining the long-term effects of the COVID-19 pandemic on the nursing workforce.
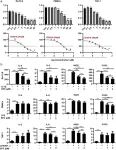
In the current study, the researchers surveyed 9,387 nurses from 35 countries between July 2022 and October 2023. They were asked about their mental health and other related factors, including loss, burnout, experiencing aggression from the public, access to mental health services, and self-care practices.
The researchers found widespread mental health challenges among nurses working during the pandemic, with rates of anxiety and depression ranging from 23% to 61%. Nurses consistently experienced more mental health symptoms at work compared to at home; the most common work-related issues were feeling tired (57%), anxiety (44%), and feeling overwhelmed (41%).
Rates of mental health issues varied widely among countries, likely reflecting cultural factors associated with psychological stressors or stigma related to mental illness. For instance, 69.9% of nurses in Brazil reported workplace-related anxiety, compared to 23.8% in Indonesia, while 80.9% of nurses in Turkey reported feeling overwhelmed at work, compared to 6.7% in Thailand.
Loss and public aggression were also identified as challenges to nurses’ mental health. Notably, 20% of nurses suffered the loss of a family member, 35% lost a friend, and 34% a coworker to COVID-19.
“The staggering personal losses of friends, family, and coworkers and their effects on nurses’ mental health should not be underestimated,” Squires and her coauthors write.
In addition, nearly half (48%) of nurses surveyed reported experiencing violence and aggression from the public due to their identity as a nurse—”an extremely concerning finding and ongoing health worker safety issue,” noted Squires.
Only 24% of nurses reported that their employers provided adequate mental health services, leaving many without support or relying on self-care strategies. Most nurses reported more frequently engaging in self-care—including exercise, spiritual practices, and leaning on family and other relationships—compared with before the pandemic.
“The increased engagement in self-care practices suggests that nurses, given the intensity of the pandemic’s working conditions, may have turned to these activities to cope with adverse mental health symptoms experienced at work,” said Squires. “However, promoting self-care will not address the scope of the problems we’ve identified; we need to develop targeted and accessible mental health support in order to foster a resilient nursing workforce.”
The researchers call on policymakers and healthcare organizations to increase mental health services available to nurses worldwide and address issues in the clinical work environment in an effort to support the psychological safety of nurses and other frontline workers.
“Given our findings, it is not surprising that we see nurses moving within the nursing workforce to lower stress roles, leaving their positions or countries for better working conditions, or leaving the profession altogether,” said Squires. “This poses a threat to health system sustainability worldwide, and the impact is likely to affect the most vulnerable systems that were already stretched and stressed to their limits prior to the pandemic.”
“This study supports what ICN has been reporting since the pandemic: we are seeing alarmingly high levels of stress and burnout in nurses across the world,” said Pamela Cipriano, president of the International Council of Nurses (ICN). “This is causing some nurses to leave the profession, which added to the aging workforce, will only exacerbate an already severe global shortage of nurses. We need governments to invest in nursing and improve working conditions and salaries in order to retain the nurses they have and attract more to the profession. ICN has published evidence to show that investing in nurses saves money, strengthens economies and saves lives.”
END
Nurses worldwide experience stress, loss, and violence
More than 9,000 nurses surveyed across 35 countries share mental health challenges coming out of the COVID-19 pandemic
2025-02-10
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
New treatment offers quick cure for common cause of high blood pressure
2025-02-10
Doctors at Queen Mary University of London, Barts Health NHS Trust, and University College London have led the development of a simple, minimally invasive Targeted Thermal Therapy (Triple T) that has the potential to transform medical management of a common, but commonly overlooked, cause of high blood pressure.
This breakthrough, published today in The Lancet, could, after further testing, help millions of people worldwide who currently go undiagnosed and untreated.
In the UK, Triple T, known scientifically as endoscopic ultrasound-guided radiofrequency ablation, was rigorously tested, in collaboration with researchers from ...
Satire more damaging to reputations than direct criticism
2025-02-10
WASHINGTON - In our digital times as we are inundated with YouTube videos, memes and social media, satire is everywhere, but it can be more damaging to people's reputations than direct criticism, according to research published by the American Psychological Association.
Seemingly innocuous satire may be more harmful than direct criticism because it can dehumanize people and reduce them to caricatures, the study found. The research was published online in the Journal of Experimental Psychology: General.
“Most people think satire is just humorous and playful, but dehumanization exists on a spectrum and can include things like forgetting ...
E64FC26, a protein disulfide isomerase inhibitor, ameliorates articular cartilage damage and disease severity in a mouse model of rheumatoid arthritis
2025-02-10
Background and objectives
Protein disulfide isomerases (PDIs) are essential enzymes that facilitate the proper folding of proteins and maintain protein quality within the endoplasmic reticulum. Dysregulation of PDIs has been correlated with numerous disorders, including cancer and rheumatoid arthritis (RA). E64FC26 (EFC), a small molecule that inhibits a wide range of PDI family members, has shown promise as a therapeutic agent in oncology. However, its effects on RA have not yet been studied. This research investigates the efficacy of EFC as a potential treatment for RA.
Methods
To investigate EFC’s effects on RA fibroblast-like ...
KERI’s faster and higher-quality argyrodite structures for ASSBs!
2025-02-10
Dr. Ha Yoon-Cheol's team at KERI's Next Generation Battery Research Center has developed an 'enhanced coprecipitation method' that enables faster and higher-quality production of lithium superionic conductors for ASSBs.
ASSB replaces the ‘electrolyte’, which transfers ions between the anode and cathode, with a solid instead of a liquid, significantly reducing the risk of fire or explosion..
Solid electrolytes are difficult to manufacture and expensive. However, in 2021, Dr. Ha Yoon-Cheol's team garnered significant attention by proposing the 'coprecipitation method', ...
FAU Engineering designs new autonomous system to monitor Arctic’s melting ice
2025-02-10
The rapid melting and thinning of the Arctic ice have sparked serious concerns in the scientific community. In addition, sea ice thickness also has decreased, which makes ice cover more vulnerable to warming air and ocean temperature.
Understanding the ecological role of sea ice in the Arctic is crucial, particularly because the extent of sea ice in the region has been decreasing at an unprecedented rate. What would happen to the Arctic marine ecosystem if the sea ice melted even faster? To answer these questions, a long-term monitoring and data collection system is necessary in the harsh Arctic environment.
However, ...
The link between finances and loneliness in older adults
2025-02-10
Older adults who didn’t have enough savings to cover emergency expenses during the early months of the COVID-19 pandemic faced another surprising problem: higher levels of loneliness.
In a new study, researchers at The Ohio State University found that adults over the age of 65 faced increases in loneliness during the pandemic, regardless of income level or wealth.
But those who said they would have to use a credit card to pay off an emergency expense over time were more likely to report high levels of loneliness.
“Our ...
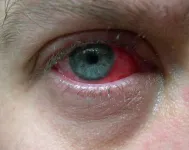
Stem cell shots: Unveiling a safer way to treat inflammatory eye diseases
2025-02-10
Graft-versus-host disease (GVHD) is a common and severe complication that occurs after stem cell transplantation, where the donor’s immune cells attack the recipient’s tissues. Ocular manifestation of GVHD is among the most challenging to treat, often leading to chronic inflammation and corneal tissue damage, which can result in loss of vision. Conventional treatments, including corticosteroids, are frequently used to manage ocular inflammation associated with GVHD. However, these therapies come with significant side effects, including the risk of glaucoma and other ocular complications.
Mesenchymal stromal cells (MSCs), a heterogeneous population of cells present in various ...
Researchers from South Korea reveal how gender shapes perceptions of safety in urban parking spaces
2025-02-10
Multifamily residential buildings with multiple floors are common in South Korea. These buildings usually have pilotis—support structures like pillars that elevate the building, creating an open ground floor generally used for parking vehicles. These piloti parking spaces are often risky to navigate for pedestrians and residents due to limited visibility, unclear boundaries between adjacent areas, and poor management. For instance, these spaces have blind spots that criminals could exploit, which induces fear among people.
Though evidence-based architectural design strategies ...
Nanoscale tin catalyst discovery paves the way for sustainable CO2 conversion
2025-02-10
Researchers have developed a sustainable catalyst that increases its activity during use while converting carbon dioxide (CO2) into valuable products. This discovery offers a blueprint for designing next-generation electrocatalysts.
A collaborative team from the University of Nottingham's School of Chemistry and the University of Birmingham have developed a catalyst made of tin microparticles supported by a nanotextured carbon structure. The interactions between the tin particles and graphitised ...
Biomarker test can detect Alzheimer's pathology earlier, Pitt study shows
2025-02-10
Years before tau tangles show up in brain scans of patients with Alzheimer's disease, a biomarker test developed at the University of Pittsburgh School of Medicine can detect small amounts of the clumping-prone tau protein and its misfolded pathological forms that litter the brain, cerebrospinal fluid and potentially blood, new research published today in Nature Medicine suggests.
The cerebrospinal fluid biomarker test correlates with the severity of cognitive decline, independent of other factors, including brain amyloid deposition, thereby opening doors for early-stage disease diagnosis ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Race against time to save Alpine ice cores recording medieval mining, fires, and volcanoes
Inside the light: How invisible electric fields drive device luminescence
A folding magnetic soft sheet robot: Enabling precise targeted drug delivery via real-time reconfigurable magnetization
Sylvester Cancer Tip Sheet for March 2026
New tools and techniques accelerate gallium oxide as next-generation power semiconductor
Researchers discover seven different types of tension
Report calls for AI toy safety standards to protect young children
VR could reduce anxiety for people undergoing medical procedures
Scan that makes prostate cancer cells glow could cut need for biopsies
Mechanochemically modified biochar creates sustainable water repellent coating and powerful oil adsorbent
New study reveals hidden role of larger pores in biochar carbon capture
Specialist resource centres linked to stronger sense of belonging and attainment for autistic pupils – but relationships matter most
Marshall University, Intermed Labs announce new neurosurgical innovation to advance deep brain stimulation technology
Preclinical study reveals new cream may prevent or slow growth of some common skin cancers
Stanley Family Foundation renews commitment to accelerate psychiatric research at Broad Institute
What happens when patients stop taking GLP-1 drugs? New Cleveland Clinic study reveals real world insights
American Meteorological Society responds to NSF regarding the future of NCAR
Beneath Great Salt Lake playa: Scientists uncover patchwork of fresh and salty groundwater
Fall prevention clinics for older adults provide a strong return on investment
People's opinions can shape how negative experiences feel
USC study reveals differences in early Alzheimer’s brain markers across diverse populations
300 million years of hidden genetic instructions shaping plant evolution revealed
High-fat diets cause gut bacteria to enter brain, Emory study finds
Teens and young adults with ADHD and substance use disorder face treatment gap
Instead of tracking wolves to prey, ravens remember — and revisit — common kill sites
Ravens don’t follow wolves to dinner – they remember where the food is
Mapping the lifelong behavior of killifish reveals an architecture of vertebrate aging
Designing for hard and brittle lithium needles may lead to safer batteries
Inside the brains of seals and sea lions with complex vocal behavior learning
Watching a lifetime in motion reveals the architecture of aging
[Press-News.org] Nurses worldwide experience stress, loss, and violenceMore than 9,000 nurses surveyed across 35 countries share mental health challenges coming out of the COVID-19 pandemic