(Press-News.org) About The Study: The results of this comparative effectiveness research study suggest that sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 inhibitors and glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists (GLP-1RAs) were associated with a reduced risk of moderate or severe chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) exacerbations compared with dipeptidyl peptidase 4 inhibitors in adults with type 2 diabetes and active COPD. This may inform prescribing of glucose-lowering medications among patients with type 2 diabetes and active COPD.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Elisabetta Patorno, MD, DrPH, email epatorno@bwh.harvard.edu.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamainternmed.2024.7811)
Editor’s Note: Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and affiliations, conflict of interest and financial disclosures, and funding and support.
# # #
Embed this link to provide your readers free access to the full-text article This link will be live at the embargo time https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jamainternalmedicine/fullarticle/10.1001/jamainternmed.2024.7811?guestAccessKey=fdd29a59-a219-4e07-83c0-78ab5ed08c4a&utm_source=for_the_media&utm_medium=referral&utm_campaign=ftm_links&utm_content=tfl&utm_term=021025
END
Glucose-lowering medications and risk of COPD exacerbations in patients with type 2 diabetes
JAMA Internal Medicine
2025-02-10
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Low to moderate prenatal alcohol exposure and facial shape of children at ages 6 to 8
2025-02-10
About The Study: Low to moderate prenatal alcohol exposure was associated with characteristic changes in the faces of children, which persisted until at least 6 to 8 years of age. A linear association between alcohol exposure levels and facial shape was not supported.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Evelyne Muggli, MPH, email evi.muggli@mcri.edu.au.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamapediatrics.2024.6151)
Editor’s Note: Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, ...
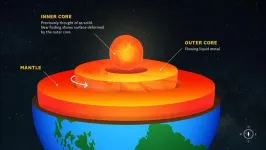
Earth’s inner core is less solid than previously thought
2025-02-10
The surface of the Earth’s inner core may be changing, as shown by a new study from USC scientists that detected structural changes near the planet’s center, published today in Nature Geoscience.
The changes of the inner core has long been a topic of debate for scientists. However, most research has been focused on assessing rotation. John Vidale, Dean’s Professor of Earth Sciences at the USC Dornsife College of Letters, Arts and Sciences and principal investigator of the study, said the researchers “didn’t set out to define the physical nature of the inner core.”
“What we ended up discovering is evidence that the near surface of Earth’s ...
Discovering the genetics of climate adaptation
2025-02-10
As climate change accelerates, plants face mounting pressure to adapt to shifting ecosystems and environmental conditions. This challenge is especially urgent for crops – plants resilient to drought and heat are essential to secure food supply in an unpredictable future. Fortunately, plants can adapt remarkably well to diverse environments and climates: Arabidopsis thaliana, for example, thrives in regions as climatically distinct as Sweden and Italy.
Understanding how plants naturally adapt to different ...
How does the brain differentiate new stimuli from old ones?
2025-02-10
The cerebral cortex is the largest part of a mammal’s brain, and by some measures the most important. In humans in particular, it’s where most things happen—like perception, thinking, memory storage and decision-making. One current hypothesis suggests that the cortex’s primary role is to predict what’s going to happen in the future by identifying and encoding new information it receives from the outside world and comparing it with what was expected to occur.
A new study published today in the ...
Eating gradually increasing doses of store-bought peanut butter enables children with high-threshold allergy to safely consume peanuts
2025-02-10
Children with high-threshold peanut allergy who ate gradually larger doses of store-bought peanut butter achieved significantly higher and long-lasting rates of desensitization compared to those who avoided peanuts, according to a new study led by researchers at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai.
Results of the trial, sponsored and funded by the National Institutes of Health’s National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases, appear in the Monday, February 10 issue of NEJM Evidence [https://doi.org/10.1056/EVIDoa2400306].
“Our study results suggest a safe, inexpensive and effective pathway ...
Therapy helps peanut-allergic kids tolerate tablespoons of peanut butter
2025-02-10
Eating gradually increasing doses of store-bought, home-measured peanut butter for about 18 months enabled 100% of children with peanut allergy who initially could tolerate the equivalent of at least half a peanut to consume three tablespoons of peanut butter without an allergic reaction, researchers report. This easy-to-implement treatment strategy could potentially fulfill an unmet need for about half of children with peanut allergy, who already can tolerate the equivalent of at least half a peanut, considered a high threshold. The findings come from a trial sponsored and funded by the National Institutes of Health’s National ...
Fly with a fake termite face capable of infiltrating and socialising in a termite mound
2025-02-10
Nature is full of impostors, and many of them are found in the insect world. Certain species, such as the bee fly or the ant spider, are experts at misdirection and their ability to confuse predators or prey is on a par with that of John Travolta in Face/Off and Arya Stark in Game of Thrones. However, never before has a blow fly been observed successfully living in cognito among termites.
Now, for the first time ever, an international study led by the Institute of Evolutionary Biology (IBE), a joint centre of the Consejo Superior de Investigaciones Científicas (CSIC) (the Spanish National Research Council (CSIC)) and Pompeu Fabra University (UPF), ...
Impact of intermediate-term oral contraceptive use on oxidative stress, lipid profile, and liver function in Iraqi women
2025-02-10
Background and objectives
Oral contraceptive pills (OCPs) are commonly used for contraception, but their long-term effects on oxidative stress, lipid profiles, and liver function remain unclear. This study aimed to evaluate the impact of intermediate-term OCP use (Yasmin) on oxidative stress, lipid profile, and liver function, with particular emphasis on antioxidant markers, lipid metabolism, and hepatic enzyme activity, to better understand the potential metabolic and hepatic effects.
Methods
A case-control study was conducted in Maysan Governorate, Iraq, involving 150 women (100 OCP users and 50 ...
Nurses worldwide experience stress, loss, and violence
2025-02-10
A first-of-its-kind study provides a snapshot of the substantial mental health burden on nurses around the world. Published in the journal International Nursing Review, the research documents the impact of three years of intense working conditions brought on by the COVID-19 pandemic.
“Our study describes how nurses are affected by stressors in their workplace and shows how the stress carries over into their home life. The personal losses from the pandemic complicate this picture as there could easily be lingering grief in a third of the workforce,” said Allison Squires, ...
New treatment offers quick cure for common cause of high blood pressure
2025-02-10
Doctors at Queen Mary University of London, Barts Health NHS Trust, and University College London have led the development of a simple, minimally invasive Targeted Thermal Therapy (Triple T) that has the potential to transform medical management of a common, but commonly overlooked, cause of high blood pressure.
This breakthrough, published today in The Lancet, could, after further testing, help millions of people worldwide who currently go undiagnosed and untreated.
In the UK, Triple T, known scientifically as endoscopic ultrasound-guided radiofrequency ablation, was rigorously tested, in collaboration with researchers from ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
AMS Science Preview: Mississippi River, ocean carbon storage, gender and floods
High-altitude survival gene may help reverse nerve damage
Spatially decoupling active-sites strategy proposed for efficient methanol synthesis from carbon dioxide
Recovery experiences of older adults and their caregivers after major elective noncardiac surgery
Geographic accessibility of deceased organ donor care units
How materials informatics aids photocatalyst design for hydrogen production
BSO recapitulates anti-obesity effects of sulfur amino acid restriction without bone loss
Chinese Neurosurgical Journal reports faster robot-assisted brain angiography
New study clarifies how temperature shapes sex development in leopard gecko
Major discovery sparks chain reactions in medicine, recyclable plastics - and more
Microbial clues uncover how wild songbirds respond to stress
Researchers develop AI tools for early detection of intimate partner violence
Researchers develop AI tool to predict patients at risk of intimate partner violence
New research outlines pathway to achieve high well-being and a safe climate without economic growth
How an alga makes the most of dim light
Race against time to save Alpine ice cores recording medieval mining, fires, and volcanoes
Inside the light: How invisible electric fields drive device luminescence
A folding magnetic soft sheet robot: Enabling precise targeted drug delivery via real-time reconfigurable magnetization
Sylvester Cancer Tip Sheet for March 2026
New tools and techniques accelerate gallium oxide as next-generation power semiconductor
Researchers discover seven different types of tension
Report calls for AI toy safety standards to protect young children
VR could reduce anxiety for people undergoing medical procedures
Scan that makes prostate cancer cells glow could cut need for biopsies
Mechanochemically modified biochar creates sustainable water repellent coating and powerful oil adsorbent
New study reveals hidden role of larger pores in biochar carbon capture
Specialist resource centres linked to stronger sense of belonging and attainment for autistic pupils – but relationships matter most
Marshall University, Intermed Labs announce new neurosurgical innovation to advance deep brain stimulation technology
Preclinical study reveals new cream may prevent or slow growth of some common skin cancers
Stanley Family Foundation renews commitment to accelerate psychiatric research at Broad Institute
[Press-News.org] Glucose-lowering medications and risk of COPD exacerbations in patients with type 2 diabetesJAMA Internal Medicine