(Press-News.org) When U.S. children die in mass shootings, most of the time the perpetrator is a family member, new Stanford Medicine-led research shows.
The findings, which will be published online Feb. 10 in JAMA Pediatrics, come from the first analysis of the relationships between mass shooting perpetrators and pediatric victims, those who are younger than 18 years old.
“It was surprising that domestic violence was so pervasive, that 59% of kids who died in mass shootings were at the hands of a family member,” said the study’s senior author, Stephanie Chao, MD, associate professor of surgery. The lead author is Pamela Emengo, MD, a research fellow in pediatric surgery.
In 2020, gun violence surpassed car accidents as the No. 1 killer of children in the United States, underscoring the need to protect kids from firearm injuries, Chao said. Yet most of the public does not understand where the threat comes from, especially with regard to mass shootings.
“When American parents are surveyed about their concerns, everyone is worried about school shootings,” she said. “The message from our data is really simple: Our fears are incorrectly placed. Our homes may, in fact, be more dangerous than schools.”
Understanding gun deaths
Chao’s team used a strict definition of mass shootings in their analysis, studying incidents that resulted in at least four fatalities, excluding the perpetrator. The researchers examined 121 such mass shootings, all of which took place in the United States between Jan. 27, 2009, and Dec. 25, 2020, and included at least one fatality in a victim under 18 years of age. These incidents caused a total of 308 pediatric deaths. The races and ethnicities of the victims were similar to the racial and ethnic profile of the U.S. population as a whole.
More than 40% of pediatric mass shooting victims were killed by a parent, the analysis found, and 59% of them died at the hands of a relative, including parents, aunts and uncles, siblings, grandparents, and cousins.
After relatives, the most common categories of relationship between shooter and victim were acquaintance (14.6%), stranger (12%), classmate (6.8%), neighbor (2.6%) and criminal associate (0.6%). In about 4% of pediatric deaths, the research team could not determine the relationship between the victim and shooter.
Chao hopes the new findings will be used to increase awareness about the most prominent sources of gun violence.
“People tend to think that gun violence occurs mostly at random events that they cannot protect their child against,” she said, adding that this perception is heightened by media’s focus on rare shootings at schools, concerts and public events. “Domestic violence doesn’t make headlines because it happens with more frequency. But that is precisely why it is more dangerous, because of the frequency. Over 22 million U.S. children live in a home with a gun. If a domestic disturbance arises in those homes, the risk of death dramatically increases.”
The data points to tactics for how to reduce pediatric gun deaths. For example, Chao said, there may be opportunities to prevent incidents of domestic violence by removing firearms from homes where relationships between adults are deteriorating or mental health concerns are rising.
“We need research and policies that approach gun violence as a public health problem, so we can best understand how to prevent it and treat it,” Chao said.
In addition to their research on the epidemiology of firearm violence, Chao’s team is developing a curriculum to educate children in K-12 schools about firearm injuries, called PLEDGE.
A researcher from the Eastern Virginia Medical School contributed to the study. The research was funded by the National Center for Advancing Translational Sciences (grant KL2TR003143).
END
Majority of kids who die in mass shootings killed by family members, Stanford Medicine-led study shows
Pediatric mass shooting deaths
2025-02-10
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
How perception may shape health safety-related assessments
2025-02-10
Perceiving whether another person is a personal health risk requires quickly assessing their trustworthiness. With limited characteristics available, implicit assumptions often influence risk perception. Research in this area has pointed to brain regions that may be involved in perceiving others as untrustworthy or as carriers of sexually transmitted diseases (STDs). However, the relationship between brain activity, perceived trustworthiness of others, and perceived likelihood of acquiring an STD was unclear prior to a recent study published in eNeuro. In the study led by Daniela Mier at ...
Potential new strategy for relieving anxiety
2025-02-10
Understanding the neural circuits that drive anxiety may help researchers discover circuit-specific targets and therefore increase the precision of treatment strategies. Previous studies have separately suggested that increased serotonin levels and the cerebellum may play roles in anxiety. To explore the relationship between these ideas, Pei Chin, from the University of Pennsylvania, and George Augustine, from Temasek Life Sciences Laboratory, probed whether serotonin in the cerebellum causes anxiety behavior in mice. Contrary to previous ...
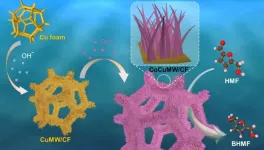
Scientists develop corrosion-induced electrodes for biomass upgrading
2025-02-10
A research team led by Prof. ZHANG Jian from the Ningbo Institute of Materials Technology and Engineering (NIMTE) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS) has utilized metal corrosion to prepare high-performance electrodes, enabling efficient and cost-effective upgrading of bio-based 5-hydroxymethylfurfural (HMF). This study was published in Chem Catalysis.
Corrosion is a common phenomenon that can lead to material failure and economic losses. However, researchers are exploring its potential for beneficial applications, particularly in biomass upgrading.
Biomass is among the most abundant renewable resources on earth. Through catalytic conversion, ...
Contemporary hormonal contraception and risk of venous thromboembolism
2025-02-10
About The Study: This study showed venous thromboembolism (VTE) risk variation across hormonal contraceptives with highest rates for combined pills, especially those containing third-generation progestins, and no significant difference in risk for intrauterine devices (IUDs) relative to no use. For patches and implants, the increased VTE risk was uncertain due to limited data. Variation in VTE risk across products underscores the importance of personalized contraceptive counseling.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Harman Gailan Hassan Yonis, MD, email harman@live.dk.
To ...
Victim-shooter relationships in mass shootings involving child victims
2025-02-10
About The Study: The findings of this study indicate that from 2009 through 2020, a child was most likely to be killed in a mass shooting by a parent or family member, rather than a stranger or a peer. While school shootings dominate media coverage, this study suggests that domestic violence plays a larger role in child mass shootings.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Stephanie Chao, MD, email sdchao1@stanford.edu.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamapediatrics.2024.6609)
Editor’s ...
Health care company payouts favor shareholders, new research shows
2025-02-10
It’s widely recognized that health care is a growing expense for many Americans. However, what health care companies do with their profits — some made through government programs such as Medicare — remains murky.
To investigate this question, researchers at Yale School of Medicine (YSM) analyzed financial reports from 92 large U.S. health care companies. The results were published on Feb. 10 in a research letter in JAMA Internal Medicine.
The research team focused on U.S. health care companies on the Standard & Poor’s 500 (S&P 500), which follows the 500 largest companies traded on stock exchanges, to ...
Glucose-lowering medications and risk of COPD exacerbations in patients with type 2 diabetes
2025-02-10
About The Study: The results of this comparative effectiveness research study suggest that sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 inhibitors and glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists (GLP-1RAs) were associated with a reduced risk of moderate or severe chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) exacerbations compared with dipeptidyl peptidase 4 inhibitors in adults with type 2 diabetes and active COPD. This may inform prescribing of glucose-lowering medications among patients with type 2 diabetes and active COPD.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Elisabetta Patorno, MD, DrPH, email epatorno@bwh.harvard.edu.
To access ...
Low to moderate prenatal alcohol exposure and facial shape of children at ages 6 to 8
2025-02-10
About The Study: Low to moderate prenatal alcohol exposure was associated with characteristic changes in the faces of children, which persisted until at least 6 to 8 years of age. A linear association between alcohol exposure levels and facial shape was not supported.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Evelyne Muggli, MPH, email evi.muggli@mcri.edu.au.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamapediatrics.2024.6151)
Editor’s Note: Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, ...
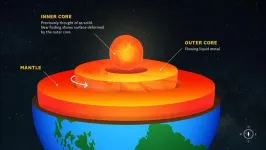
Earth’s inner core is less solid than previously thought
2025-02-10
The surface of the Earth’s inner core may be changing, as shown by a new study from USC scientists that detected structural changes near the planet’s center, published today in Nature Geoscience.
The changes of the inner core has long been a topic of debate for scientists. However, most research has been focused on assessing rotation. John Vidale, Dean’s Professor of Earth Sciences at the USC Dornsife College of Letters, Arts and Sciences and principal investigator of the study, said the researchers “didn’t set out to define the physical nature of the inner core.”
“What we ended up discovering is evidence that the near surface of Earth’s ...
Discovering the genetics of climate adaptation
2025-02-10
As climate change accelerates, plants face mounting pressure to adapt to shifting ecosystems and environmental conditions. This challenge is especially urgent for crops – plants resilient to drought and heat are essential to secure food supply in an unpredictable future. Fortunately, plants can adapt remarkably well to diverse environments and climates: Arabidopsis thaliana, for example, thrives in regions as climatically distinct as Sweden and Italy.
Understanding how plants naturally adapt to different ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Why do we get a skip in our step when we’re happy? Thank dopamine
UC Irvine scientists uncover cellular mechanism behind muscle repair
Platform to map living brain noninvasively takes next big step
Stress-testing the Cascadia Subduction Zone reveals variability that could impact how earthquakes spread
We may be underestimating the true carbon cost of northern wildfires
Blood test predicts which bladder cancer patients may safely skip surgery
Kennesaw State's Vijay Anand honored as National Academy of Inventors Senior Member
Recovery from whaling reveals the role of age in Humpback reproduction
Can the canny tick help prevent disease like MS and cancer?
Newcomer children show lower rates of emergency department use for non‑urgent conditions, study finds
Cognitive and neuropsychiatric function in former American football players
From trash to climate tech: rubber gloves find new life as carbon capturers materials
A step towards needed treatments for hantaviruses in new molecular map
Boys are more motivated, while girls are more compassionate?
Study identifies opposing roles for IL6 and IL6R in long-term mortality
AI accurately spots medical disorder from privacy-conscious hand images
Transient Pauli blocking for broadband ultrafast optical switching
Political polarization can spur CO2 emissions, stymie climate action
Researchers develop new strategy for improving inverted perovskite solar cells
Yes! The role of YAP and CTGF as potential therapeutic targets for preventing severe liver disease
Pancreatic cancer may begin hiding from the immune system earlier than we thought
Robotic wing inspired by nature delivers leap in underwater stability
A clinical reveals that aniridia causes a progressive loss of corneal sensitivity
Fossil amber reveals the secret lives of Cretaceous ants
Predicting extreme rainfall through novel spatial modeling
The Lancet: First-ever in-utero stem cell therapy for fetal spina bifida repair is safe, study finds
Nanoplastics can interact with Salmonella to affect food safety, study shows
Eric Moore, M.D., elected to Mayo Clinic Board of Trustees
NYU named “research powerhouse” in new analysis
New polymer materials may offer breakthrough solution for hard-to-remove PFAS in water
[Press-News.org] Majority of kids who die in mass shootings killed by family members, Stanford Medicine-led study showsPediatric mass shooting deaths