(Press-News.org) Glaciers, sediments, and pollen can be used to reconstruct the climate of the past. Beyond ‘nature’s archive,’, other sources, such as diaries, travel notes, parish or monastery registers, and other written documents – known at the ‘society’s archive’ – contain reports and observations about local climates in bygone centuries.
In contrast, the second half of the century was characterized by heavy rainfall and floods, particularly in the 1590s.
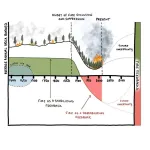
The western parts of the European continent cooled significantly when in the 16th century a period known as the ‘Little Ice Age’ intensified. During the second half of the century, temperatures dropped by 0.5°C. In Transylvania, however, hot weather was recorded much more frequently than cold weather during the 16th century. “This makes us believe that the Little Ice Age could have manifested itself later in this part of Europe,” said Caciora. Later writings, in which more cold waves and severe winters are mentioned, support this thesis.
Delayed ice age
The sources tell of a particularly hot and dry first half of the century. “One compelling passage comes from a historical document describing the summer of 1540. ‘The springs dried up, and the rivers dwindled to mere trickles. Livestock fell in the fields, and the air was thick with despair as the people gathered in processions, praying for rain,’” said Caciora. “This vivid account underscores the emotional and spiritual dimensions of living through climatic extremes.”
In contrast, the second half of the century was characterized by heavy rainfall and floods, particularly in the 1590s. Compared to the western parts of the European continent, which cooled significantly when in the 16th century a period known as the ‘Little Ice Age’, intensified. During the second half of the century, temperatures dropped by 0.5°C.
In Transylvania, however, hot weather was recorded much more frequently than cold weather during the 16th century. “This makes us believe that the Little Ice Age could have manifested itself later in this part of Europe,” said Caciora. Later writings, in which more cold waves and severe winters are mentioned, support this thesis.
Climate catastrophes
Such weather variations often resulted in catastrophes, related directly or indirectly to the climate. These included 30 years during which the Black Death ravaged the land, 23 years or famine, and nine years during which locust invasions were recorded.
However tragic, weather extremes and resulting calamities could have driven changes in settlement patterns, the researchers said. “Towns might have adopted flood-resistant infrastructure or migrated to more favorable areas. The challenges might also have spurred technological innovations, such as improved irrigation systems or storage facilities,” Caciora explained.
The human element
“Chronicles and diaries reveal how people perceived, responded to, and were impacted by these events,” Caciora continued.
Despite the insights it provides, the study faces several limitations, the researchers pointed out. Few people were literate, reports are often subjective, or only true on local scales. In addition, the records are fragmented. For example, the researchers were not able to include any records about 15 years of the 16th century, either because no records existed, or they were too contradictory for inclusion.
Nevertheless, these writings not only provide a glimpse into how people in the past might have lived, but are also relevant for modern climate resilience strategies, particularly in understanding the socio-economic consequences of extreme weather events and their role in shaping human history. “Studying climate records from the society’s archive is as crucial as analyzing natural proxies,” Caciora explained. “It provides a human-centric perspective on past climatic events.”
END
500-year-old Transylvanian diaries show how the Little Ice Age completely changed life and death in the region
Tapping into ‘society’s archive’, researchers have examined written sources from the 16th century that chronicle famine, excessive flooding, and plagues in what today is Romania
2025-02-12
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Overcoming nicotine withdrawal: Clues found in neural mechanisms of the brain
2025-02-12
According to the World Health Organization (WHO), over 22% of the global population smokes, with more than 9 million smoking-related deaths reported annually. Effective treatments to alleviate nicotine withdrawal symptoms caused by smoking cessation are essential for successful smoking cessation. Currently, approved treatments for nicotine withdrawal include Bupropion and Varenicline, but there is a pressing need for new therapeutic options to improve smoking cessation success rates.
The research team led by Dr. Heh-In Im at the Center for Brain Disorders of the Korea Institute of Science and Technology (KIST) has identified a novel brain region and neural mechanism ...
Survey: Women prefer female doctors, but finding one for heart health can be difficult
2025-02-12
EMBARGOED UNTIL WEDNESDAY, FEBRUARY 12, 2025
Mountain View, CA (Feb. 12, 2025) – According to the U.S. Physician Workforce Data Dashboard, only about 17% of cardiologists are women, ranking as one of the lowest specialties among female physicians, yet heart disease remains the number one killer of women, accounting for one in five female deaths. El Camino Health is innovating a solution to address the unique symptoms and risk factors of heart disease in women.
A new national survey conducted by El Camino Health found women (59%) are ...
Leaf color mysteries unveiled: the role of BoYgl-2 in cabbage
2025-02-12
A new study has uncovered a novel P-type PPR protein, BoYgl-2, which plays a crucial role in chloroplast RNA editing and chlorophyll biosynthesis in cabbage. This discovery sheds new light on the molecular mechanisms governing leaf color formation and chloroplast development, filling a significant knowledge gap in plant physiology. By identifying a spontaneous yellow-green leaf mutant and deciphering the function of BoYgl-2, the research paves the way for innovative crop breeding strategies that could enhance plant productivity and agricultural sustainability.
Leaf color is more than just an aesthetic trait—it is a vital agronomic characteristic ...
NUS Medicine study: Inability of cells to recycle fats can spell disease
2025-02-12
Accumulation of fat molecules is detrimental to the cell. Researchers from the Yong Loo Lin School of Medicine, National University of Singapore (NUS Medicine), have made a breakthrough in understanding how our cells manage to stay healthy by recycling important fat molecules. Their study, published in the journal Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (PNAS), reveals how a protein called Spinster homolog 1 (Spns1) helps transport fats out of cell compartments known as lysosomes.
Led by Associate Professor Nguyen Nam Long, from the Department of Biochemistry and Immunology Translational Research Programme (TRP) at NUS Medicine, the team found that Spns1 is like a cellular ...
D2-GCN: a graph convolutional network with dynamic disentanglement for node classification
2025-02-12
Classic Graph Convolutional Networks (GCNs) often learn node representation holistically, which would ignore the distinct impacts from different neighbors when aggregating their features to update a node's representation. Disentangled GCNs have been proposed to divide each node's representation into several feature channels. However, current disentangling methods do not try to figure out how many inherent factors the model should assign to help extract the best representation of each node.
To solve the problems, a research team led by Chuliang WENG published their new ...
Female hoverflies beat males on long-distance migrations
2025-02-12
Male hoverflies are outflown by females when it comes to long-distance migration, new research shows.
Marmalade hoverflies leave northern Europe each autumn to escape the cold winter.
The study – by the University of Exeter – compared the number of males and females migrating at a northern point (Denmark) and further south (Spain).
At the northern point, 50% of hoverflies were male and 50% were female – but at the southern point about 90% were female, suggesting males are “poor long-distance fliers”.
“We carried out a range of tests and found females were better adapted for long-distance ...
Study finds consumer openness to smoke-impacted wines, offering new market opportunities
2025-02-12
CORVALLIS, Ore. – Certain groups of consumers appear to be open to drinking smoke-impacted wines, a finding in a new study that could provide market opportunities for winemakers increasingly dealing with the effects of wildfire smoke on grapes.
The study by researchers at Oregon State University and in New Zealand found that consumers, particularly those that like smokey flavors in food and beverages, are open to drinking smoke-impacted wines. They also found that the type of information on the label can modulate consumer acceptance.
“This ...
Why we need to expand the search for climate-friendly microalgae
2025-02-12
New research has highlighted microalgae’s capacity as a solution in the fight against climate change, but researchers warn that “smart microalgal bioprospecting” is needed to unlock its full potential.
The study highlights the vast, largely unexplored capacity of microalgae to mitigate CO2 emissions while driving sustainable industry.
“Microalgae have remarkable properties that make them an ideal tool for tackling climate change,” said lead author, PhD candidate Joan Labara Tirado from the University of Technology Sydney (UTS).
The review paper, The need for smart microalgal bioprospecting was ...
Fewer forest fires burn in North America today than in the past—and that's a bad thing
2025-02-12
Fewer wildfires burn in North American forests today than in previous centuries, increasing the risk of more severe wildfires, according to research published this week in Nature Communications. The findings may seem counterintuitive, but frequent low-lying surface fires often maintain balance in forests by reducing fuel sources across large areas.
The new study led by the Cooperative Institute for Research in Environmental Sciences (CIRES) at the University of Colorado Boulder and the U.S. Forest Service’s Rocky Mountain Research Station ...
Older people in England are happier now than before the COVID pandemic, new national study suggests
2025-02-12
Older people have greater general happiness, life satisfaction and sense of purpose than they did before the Covid-19 pandemic.
That’s according to a new study which tracked 3,999 over 50s in England for 11 years, published today in the peer-reviewed journal, Aging and Mental Health.
Analysing data to understand positive psychological well-being and depression within this group, an expert team from UCL (University College London), funded by the National Institute of Ageing, a consortium of UK government departments coordinated by the National Institute ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Spring fatigue cannot be empirically proven
Do prostate cancer drugs interact with certain anticoagulants to increase bleeding and clotting risks?
Many patients want to talk about their faith. Neurologists often don't know how.
AI disclosure labels may do more harm than good
The ultra-high-energy neutrino may have begun its journey in blazars
Doubling of new prescriptions for ADHD medications among adults since start of COVID-19 pandemic
“Peculiar” ancient ancestor of the crocodile started life on four legs in adolescence before it began walking on two
AI can predict risk of serious heart disease from mammograms
New ultra-low-cost technique could slash the price of soft robotics
Increased connectivity in early Alzheimer’s is lowered by cancer drug in the lab
Study highlights stroke risk linked to recreational drugs, including among young users
Modeling brain aging and resilience over the lifespan reveals new individual factors
ESC launches guidelines for patients to empower women with cardiovascular disease to make informed pregnancy health decisions
Towards tailor-made heat expansion-free materials for precision technology
New research delves into the potential for AI to improve radiology workflows and healthcare delivery
Rice selected to lead US Space Force Strategic Technology Institute 4
A new clue to how the body detects physical force
Climate projections warn 20% of Colombia’s cocoa-growing areas could be lost by 2050, but adaptation options remain
New poll: American Heart Association most trusted public health source after personal physician
New ethanol-assisted catalyst design dramatically improves low-temperature nitrogen oxide removal
New review highlights overlooked role of soil erosion in the global nitrogen cycle
Biochar type shapes how water moves through phosphorus rich vegetable soils
Why does the body deem some foods safe and others unsafe?
Report examines cancer care access for Native patients
New book examines how COVID-19 crisis entrenched inequality for women around the world
Evolved robots are born to run and refuse to die
Study finds shared genetic roots of MS across diverse ancestries
Endocrine Society elects Wu as 2027-2028 President
Broad pay ranges in job postings linked to fewer female applicants
How to make magnets act like graphene
[Press-News.org] 500-year-old Transylvanian diaries show how the Little Ice Age completely changed life and death in the regionTapping into ‘society’s archive’, researchers have examined written sources from the 16th century that chronicle famine, excessive flooding, and plagues in what today is Romania