(Press-News.org) Yogurt, which contains live strains of bacteria, is thought to protect against many types of diseases, with some reports indicating it could reduce risk of colorectal cancer. A new study led by investigators from Mass General Brigham finds that yogurt consumption over time may protect against colorectal cancer through changes in the gut microbiome. Using data from studies that have followed participants for decades, researchers found that long-term consumption of two or more servings per week of yogurt was tied to lower rates of proximal colorectal cancer positive for Bifidobacterium, a bacterial species found in yogurt. The study showed that the bacterial species was quite common: about 30 percent of patients with colorectal cancer had detectable Bifidobacterium in their tumor tissue. Their results are published in Gut Microbes.
“Our study provides unique evidence about the potential benefit of yogurt,” said corresponding author Shuji Ogino, MD, PhD, the chief of the Program in Molecular Pathological Epidemiology in the Department of Pathology at Brigham and Women’s Hospital, a founding member of the Mass General Brigham healthcare system. Ogino is also an American Cancer Society Professor, a Professor at Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health, and an Affiliate Member of the Broad Institute of MIT and Harvard. “My lab’s approach is to try to link long-term diets and other exposures to a possible key difference in tissue, such as the presence or absence of a particular species of bacteria. This kind of detective work can increase the strength of evidence connecting diet to health outcomes.”
Ogino and colleagues – team OPTISTIMISTICC – are funded by Cancer Research UK through Cancer Grand Challenges, a research initiative co-founded by Cancer Research UK and the National Cancer Institute in the United States. OPTIMISTICC aims to transform the understanding of how the microbiome contributes to disease development, progression and response to treatment. As part of this, Ogino’s team aims to define the risk factors and environmental exposures that individuals encounter through life which are behind the rise of early-onset colorectal cancer and ultimately develop strategies to reduce the burden of this type of cancer.
To conduct their study, the researchers used data from two U.S.-wide prospective cohort studies known as the Nurses’ Health Study (NHS) and the Health Professionals Follow-up Study (HPFS). The studies have followed more than 100,000 female registered nurses and 51,000 male health professionals, respectively. Participants have been followed since 1976 for the NHS and 1986 for HFPS, answering repeated questionnaires about lifestyle factors and disease outcomes, including questions about average daily intake of plain and flavored yogurt, as well as other dairy products. The researchers also assessed tissue samples for participants with confirmed cases of colorectal cancer, measuring the amount of Bifidobacterium DNA in tumor tissue.
The researchers found 3,079 documented cases of colorectal cancer in the two study populations. Information on Bifidobacterium content was available in 1,121 colorectal cancer cases. Among those, 346 cases (31%) were Bifidobacterium-positive, and 775 cases (69%) were Bifidobacterium-negative. The researchers did not observe a significant association between long-term yogurt intake and overall colorectal cancer incidence, but they did see an association in Bifidobacterium-positive tumors, with a 20 percent lower rate of incidence for participants who consumed two or more servings of yogurt a week. This lower rate was driven by lower incidence of Bifidobacterium-positive proximal colon cancer—a type of colorectal cancer that occurs in the right side of the colon. Studies have found that patients with proximal colon cancer have worse survival outcomes than patients with distal cancers.
“It has long been believed that yogurt and other fermented milk products are beneficial for gastrointestinal health,” said co-senior author Tomotaka Ugai, MD, PhD, of the Department of Pathology at the Brigham and the Department of Epidemiology at the Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health. “Our new findings suggest that this protective effect may be specific for Bifidobacterium-positive tumors.”
The researchers hypothesize that long-term yogurt intake may reduce risk of proximal colon cancer by changing the gut microbiome, including Bifidobacterium, but they note that further research that brings together both basic science and population health studies is needed to draw a definitive conclusion.
“This paper adds to the growing evidence that illustrates the connection between diet, the gut microbiome, and risk of colorectal cancer,” said co-author Andrew T Chan, MD, chief of the Clinical and Translational Epidemiology Unit at Massachusetts General Hospital, a founding member of the Mass General Brigham healthcare system and co-lead for Cancer Grand Challenges team PROSPECT addressing causes of cancer in young adults. “It provides an additional avenue for us to investigate the specific role of these factors in the risk of colorectal cancer among young people.”
Authorship: In addition to Ogino, Ugai and Chan, Mass General Brigham authors include Satoko Ugai, Hidetaka Kawamura, Kota Arima, Kazuo Okadome, Qian Yao, Kosuke Matsuda, and Yuxue Zhong. Additional authors include Li Liu, Keisuke Kosumi, Tsuyoshi Hamada, Kosuke Mima, Hiroki Mizuno, Wendy S. Garrett, Mingyang Song, Marios Giannakis, Edward L. Giovannucci, and Xuehong Zhang.
END
Long-term yogurt consumption tied to decreased incidence of certain types of colorectal cancer
Mass General Brigham researchers found that higher yogurt intake was associated with lower rates of Bifidobacterium-positive proximal colon cancer
2025-02-12
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Ovarian cancer discovery could turn failed treatment into lifesaver
2025-02-12
University of Virginia Cancer Center researchers have explained the failure of immune checkpoint therapy for ovarian cancer by discovering how gut bacteria interfere with the treatment. Doctors may be able to use the findings to overcome this treatment failure and save the lives of thousands of women every year.
The new discovery, from the lab of UVA’s Melanie Rutkowski, PhD, speaks to the surprising ways that the microbiome – the collection of organisms that live on and inside our bodies – is vital not only to ...
DNA methylation clocks may require tissue-specific adjustments for accurate aging estimates
2025-02-12
“Our results suggest that forensic applications of DNAm clocks using non-blood tissue types will provide age estimates that are not as accurate as predictions based on blood, especially if using clocks algorithms trained on blood samples.”
BUFFALO, NY—February 12, 2025 — A new research paper was published in Aging (Aging-US) on January 3, 2025, in Volume 17, Issue 1, titled “Characterization of DNA methylation clock algorithms applied to diverse tissue types.”
Researchers ...
Tidal energy measurements help SwRI scientists understand Titan’s composition, orbital history
2025-02-12
SAN ANTONIO — February 12, 2025 —Southwest Research Institute (SwRI) scientists are studying Saturn’s moon Titan to assess its tidal dissipation rate, the energy lost as it orbits the ringed planet with its massive gravitational force. Understanding tidal dissipation helps scientists infer many other things about Titan, such as the makeup of its inner core and its orbital history.
“When most people think of tides they think of the movement of the oceans, in and out, with the passage of the Moon overhead, said Dr. Brynna Downey. “But that is just because water moves ...
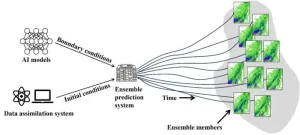
Data-driven networks influence convective-scale ensemble weather forecasts
2025-02-12
To effectively present the uncertainty of convective-scale weather forecasts, convective-scale ensemble prediction systems have been developed at major operational centers, whose lateral boundary conditions are usually provided by global numerical weather models. Recently, the emergence of AI weather models has provided a new approach to driving convective-scale ensemble prediction systems. AI weather models can produce forecasts for the next 7 to 10 days in just a few minutes, which is around 10,000 times faster than numerical weather models. However, the performance of using the ...
Endocrine Society awards Baxter Prize to innovator in endocrine cancer drug discovery
2025-02-12
WASHINGTON—Donald Patrick McDonnell, Ph.D., has been awarded the Endocrine Society’s John D. Baxter Prize for Entrepreneurship for discovering hormone therapies for treating breast and prostate cancer, the Society announced today.
The John D. Baxter Prize for Entrepreneurship was established to recognize the extraordinary achievement of bringing an idea, product, service, or process to market. This work ultimately elevates the field of endocrinology and positively impacts the health of patients.
McDonnell is a professor at Duke University School ...
Companies quietly switching out toxic product ingredients in response to California law
2025-02-12
A new study by Silent Spring Institute and University of California, Berkeley shows how laws that promote greater transparency around harmful chemicals in products can shift markets toward safer products.
The study, published in the journal Environmental Science & Technology, focused on California’s right-to-know law called Proposition 65, or Prop 65. Under the law, the state of California maintains a list of approximately 900 chemicals known to cause cancer, birth defects, or reproductive harm. Companies that sell products in California are required to warn people if their products could expose them to harmful ...
Can math save content creators? A new model proposes fairer revenue distribution methods for streaming services
2025-02-12
As more consumers turn to subscription-based platforms, the distribution of revenue in streaming services has become a crucial issue in the digital economy. Content creators and artists argue that the current models are opaque, frequently neglecting the needs of creators. In response, researchers at UMH have proposed a model based on three allocation rules that could be applied according to various fairness criteria.
"Our model is based on three main approaches: the equal division rule, which divides revenue equally among services; the proportional rule, which allocates revenue according ...
Study examines grief of zoo employees and volunteers across the US after animal losses
2025-02-12
A collaboration of researchers from Colorado State University and Denver Zoo Conservation Alliance surveyed zoo employees and volunteers across the US about their experiences of burnout and grief related to zoo animal losses.
Their latest study has found that poor grief support in some US zoos leaves staff feeling limited empathy from leadership, burned out, and unable to openly express their grief after the death of an animal to which they had formed a close emotional bond.
The research, published in the journal ...
National study underway to test new mechanical heart pump
2025-02-12
ANN ARBOR, Mich. — A cardiac surgery and heart failure team at the University of Michigan implanted a novel mechanical heart pump into a patient as part of a clinical trial that will compare it to the only device currently used to treat end-stage heart failure.
“This trial presents an opportunity to assess novel technology as we explore a potential new treatment for advanced heart failure — a life-threatening condition with extremely limited therapeutic opportunities available,” said Francis Pagani, M.D., Ph.D., national ...
Antarctica’s only native insect’s unique survival mechanism
2025-02-12
Picture an Antarctic animal and most people think of penguins, but there is a flightless midge, the only known insect native to Antarctica, that somehow survives the extreme climate. How the Antarctic midge (Belgica antarctica) copes with freezing temperatures could hold clues for humans about subjects like cryopreservation, but there remain many mysteries about the tiny insect.
One mystery appears to have been solved by an Osaka Metropolitan University-led international research team. Graduate School of Science Professor Shin G. Goto and Dr. Mizuki Yoshida, a graduate student at the time of the research who is now a postdoc at Ohio State University, found ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Ultrasound AI receives FDA De Novo clearance for delivery date AI technology
Amino acid residue-driven nanoparticle targeting of protein cavities beyond size complementarity
New AI algorithm enables scientific monitoring of "blue tears"
Insufficient sleep among US adolescents across behavioral risk groups
Long COVID and recovery among US adults
Trends in poverty and birth outcomes in the US
Heterogeneity of treatment effects of GLP-1 RAs for weight loss in adults
Within-person association between daily screen use and sleep in youth
Low-dose lithium for mild cognitive impairment
Catheter ablation and oral anticoagulation for secondary stroke prevention in atrial fibrillation
A new theory of brain development
Pilot clinical trial suggests low dose lithium may slow verbal memory decline
Bioprinting muscle that knows how to align its cells just as in the human body
A hair-thin fiber can read the chemistry of a single drop of body fluid
SwRI develops magnetostrictive probe for safer, more cost-effective storage tank inspections
National report supports measurement innovation to aid commercial fusion energy and enable new plasma technologies
Mount Sinai, Uniformed Services University join forces to predict and prevent diseases before they start
Science of fitting in: Do best friends or popular peers shape teen behavior?
USF study: Gag grouper are overfished in the Gulf; this new tool could help
New study from Jeonbuk National University finds current climate pledges may miss Paris targets
Theoretical principles of band structure manipulation in strongly correlated insulators with spin and charge perturbations
A CNIC study shows that the heart can be protected during chemotherapy without reducing antitumor efficacy
Mayo Clinic study finds single dose of non-prescribed Adderall raises blood pressure and heart rate in healthy young adults
Engineered immune cells show promise against brain metastases in preclinical study
Improved EV battery technology will outmatch degradation from climate change
AI cancer tools risk “shortcut learning” rather than detecting true biology
Painless skin patch offers new way to monitor immune health
Children with poor oral health more often develop cardiovascular disease as adults
GLP-1 drugs associated with reduced need for emergency care for migraine
New knowledge on heritability paves the way for better treatment of people with chronic inflammatory bowel disease
[Press-News.org] Long-term yogurt consumption tied to decreased incidence of certain types of colorectal cancerMass General Brigham researchers found that higher yogurt intake was associated with lower rates of Bifidobacterium-positive proximal colon cancer