(Press-News.org) Charles Martinez, assistant professor and Extension specialist in the Department of Agricultural and Resource Economics at the University of Tennessee Institute of Agriculture, recently received the Emerging Scholar Award from the Southern Agricultural Economics Association (SAEA). The award is presented to high-performing, early-career professionals with demonstrated research and resulting publication activity.
Martinez was chosen among peers nationwide for this distinguished honor. He received the award February 3 during the annual SAEA meeting in Irving, Texas.
“In a short time, Dr. Martinez has established himself as a trusted source of information across the nation on topics ranging from land use to beef cattle production,” said Chris Boyer, professor and head of the Department of Agricultural and Resource Economics. “He has accomplished this by listening to stakeholders’ needs and dedicating himself to find the answers they seek.”
Martinez’s research and outreach efforts focus on the fields of farm and financial management, experimental economics, livestock and meat market economics and policy.
Shortly after joining UTIA in 2020 as a statewide farm and financial specialist for UT Extension, his role expanded to supporting new and beginning farmers through the UT Farming Fundamentals and Master Farm Manager programs. Now, as director of the UT Center for Farm Management, he continues to support agricultural enterprises in Tennessee and the Southeast through research, Extension and education, offering data-driven solutions and hands-on farm management experiences.
“I am extremely honored to have received the 2025 SAEA Emerging Scholar Award,” Martinez said. “This award is the accumulation of all the publications, Extension programs, farm visits and projects that I’ve contributed to thanks to my great collaborators, students and colleagues at UTIA. I also thank my wonderful wife, Vanessa, and my two awesome kids, Henry and Remington, for their support throughout our time here at UTIA.”
The University of Tennessee Institute of Agriculture is comprised of the Herbert College of Agriculture, UT College of Veterinary Medicine, UT AgResearch and UT Extension. Through its land-grant mission of teaching, research and outreach, the Institute touches lives and provides Real. Life. Solutions. to Tennesseans and beyond. utia.tennessee.edu.
END
Tennessee professor receives SAEA Emerging Scholar Award
Charles Martinez recognized for dedicated efforts in agricultural and resource economics
2025-02-12
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Sea turtles’ secret GPS: researchers uncover how sea turtles learn locations using Earth's magnetic field
2025-02-12
A new study from researchers at the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill provides the first empirical evidence that loggerhead sea turtles can learn and remember the unique magnetic signatures of different geographic regions. This discovery offers new insights into how turtles and other migratory animals navigate vast distances to reach specific foraging and breeding grounds. The findings, published in the journal Nature, also suggest that sea turtles possess two distinct magnetic senses that function differently to detect the Earth’s magnetic field.
Loggerhead turtles are famous for their extraordinary ...
Mayo Clinic researchers and surgeons test virtual reality to calm presurgery jitters
2025-02-12
ROCHESTER, Minn. — Heart surgery is a serious and invasive medical procedure, and that can be intimidating for a patient. A new study published in Mayo Clinic Proceedings suggests that virtual reality (VR) can be an effective tool to reduce preoperative anxiety in older patients undergoing their first open-heart surgery. While much of the research to date using VR involved younger patient populations, these research findings suggest that immersive VR was effective and well tolerated in older ...
Mothers with incarcerated children shoulder emotional and financial burdens
2025-02-12
The financial and emotional toll borne by mothers whose adult children have experienced incarceration is often overlooked but can exacerbate financial burdens, especially for Black mothers, according to new research from Rice University sociologist Brielle Bryan.
The study, “Maternal Wealth Implications of Child Incarceration: Examining the Upstream Consequences of Children’s Incarceration for Women’s Assets, Homeownership and Home Equity,” appears in a recent edition of Demography and explores the wealth disparities and racial inequities that intensify these burdens.
The research focuses ...
Adults can learn absolute pitch: new research challenges long-held musical belief
2025-02-12
Under embargo until 12/02/25 12:00PM EST/17:00PM GMT
It’s been a long-held belief that absolute pitch - the ability to identify musical notes without reference - is a rare gift reserved for a select few with special genetic gifts or those who began musical training in early childhood. However, new research from the University of Surrey challenges this, demonstrating that adults can acquire this skill through rigorous training.
The study involved a diverse group of 12 adult musicians, with varying levels of musical experiences, who participated in an eight-week online training program. ...
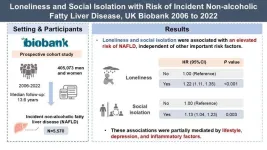
Loneliness and social isolation linked to increased risk of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease, study finds
2025-02-12
Loneliness and social isolation have been linked to an elevated risk of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), according to a groundbreaking study conducted by researchers from Central South University and the Army Medical University in China, in collaboration with the Karolinska Institutet in Sweden. Published in Health Data Science, the study analyzed data from over 400,000 participants in the UK Biobank, shedding light on the far-reaching impacts of social factors on liver health.
The research team, led by Professor Jiaqi Huang and Professor Jin Chai, sought to explore whether loneliness and social isolation—two ...
Exotic observations with neutrons at the ILL
2025-02-12
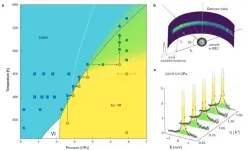
In everyday life, we typically encounter water in one of three familiar states – solid, liquid or gas. But there are in fact many more phases, some of which – predicted to exist at high temperature and pressure – are so strange they’re referred to as exotic. State-of-the-art neutron spectrometers and sample environment infrastructures at the Institut Laue-Langevin (ILL) have enabled the first experimental observation of one of these exotic phases – plastic ice VII.
Plastic ice VII was originally predicted more than 15 years ago by molecular dynamics ...
Scientists discover new gene-to-gene interaction increasing risk of alopecia
2025-02-12
Scientists have discovered an interaction between genes that increases the risk of developing a type of alopecia.
In a new JAMA Dermatology study, scientists at King’s College London found that changes in two parts of the genome work together to influence alopecia risk.
Frontal fibrosing alopecia (FFA) is a highly distressing dermatological disorder which is associated with inflammation, scarring and irreversible hair loss. The disease affects an increasing number of patients worldwide and is caused by genetic and environmental factors.
The study authors conducted a meta-analysis of four cohorts ...
Chinese scientists find key genes to fight against crop parasites
2025-02-12
Chinese scientists have identified two key genes responsible for sorghum's resistance to Striga, a parasitic plant that causes significant crop losses. The breakthrough, which also highlights the potential of AI to predict key amino acid sites in strigolactone (SL) transporters, could have wide-ranging applications in enhancing parasitic plant resistance across various crops.
This study, published in Cell, was conducted by Prof. XIE Qi's team at the Institute of Genetics and Developmental ...
Lung cancer cells can go ‘off grid’
2025-02-12
Francis Crick Institute press release
Under strict embargo: 16:00hrs GMT Wednesday 12 February 2025
Peer reviewed
Experimental study
Animals, people and cells
Researchers from the Francis Crick Institute have found that some particularly aggressive lung cancer cells can develop their own electric network, like that seen in the body’s nervous system.
This unique property could make them less dependent on the environment surrounding the tumour and even spread more easily.
Small cell lung cancer (SCLC) is one of the hardest types of cancer to ...
An RNA inhibitor may effectively reduce a high-risk type of cholesterol in patients with cardiovascular disease
2025-02-12
The RNA inhibitor olpasiran significantly reduces a type of “bad cholesterol” that’s associated with a high risk of cardiovascular events, according to results from an analysis by a Mount Sinai researcher of a phase 2 trial. The study reported that higher doses of olpasiran lowered the type of cholesterol called lipoprotein(a) [Lp(a)] by more than 95 percent in participants with atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease. Findings were published February 12, 2025, in JAMA Cardiology.
“Our study is the first clinical trial to investigate the association between oxidized phospholipids on lipoprotein(a) and inflammatory mediators,” says ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
New study from Jeonbuk National University finds current climate pledges may miss Paris targets
Theoretical principles of band structure manipulation in strongly correlated insulators with spin and charge perturbations
A CNIC study shows that the heart can be protected during chemotherapy without reducing antitumor efficacy
Mayo Clinic study finds single dose of non-prescribed Adderall raises blood pressure and heart rate in healthy young adults
Engineered immune cells show promise against brain metastases in preclinical study
Improved EV battery technology will outmatch degradation from climate change
AI cancer tools risk “shortcut learning” rather than detecting true biology
Painless skin patch offers new way to monitor immune health
Children with poor oral health more often develop cardiovascular disease as adults
GLP-1 drugs associated with reduced need for emergency care for migraine
New knowledge on heritability paves the way for better treatment of people with chronic inflammatory bowel disease
Under the Lens: Microbiologists Nicola Holden and Gil Domingue weigh in on the raw milk debate
Science reveals why you can’t resist a snack – even when you’re full
Kidney cancer study finds belzutifan plus pembrolizumab post-surgery helps patients at high risk for relapse stay cancer-free longer
Alkali cation effects in electrochemical carbon dioxide reduction
Test platforms for charging wireless cars now fit on a bench
$3 million NIH grant funds national study of Medicare Advantage’s benefit expansion into social supports
Amplified Sciences achieves CAP accreditation for cutting-edge diagnostic lab
Fred Hutch announces 12 recipients of the annual Harold M. Weintraub Graduate Student Award
Native forest litter helps rebuild soil life in post-mining landscapes
Mountain soils in arid regions may emit more greenhouse gas as climate shifts, new study finds
Pairing biochar with other soil amendments could unlock stronger gains in soil health
Why do we get a skip in our step when we’re happy? Thank dopamine
UC Irvine scientists uncover cellular mechanism behind muscle repair
Platform to map living brain noninvasively takes next big step
Stress-testing the Cascadia Subduction Zone reveals variability that could impact how earthquakes spread
We may be underestimating the true carbon cost of northern wildfires
Blood test predicts which bladder cancer patients may safely skip surgery
Kennesaw State's Vijay Anand honored as National Academy of Inventors Senior Member
Recovery from whaling reveals the role of age in Humpback reproduction
[Press-News.org] Tennessee professor receives SAEA Emerging Scholar AwardCharles Martinez recognized for dedicated efforts in agricultural and resource economics