(Press-News.org) Pancreatic cancer is fueled by connections to the nervous system. This is reported by scientists from the German Cancer Research Center (DKFZ) and the Heidelberg Institute for Stem Cell Technology and Experimental Medicine (HI-STEM)* in their current publication in Nature. The team discovered that the tumor specifically reprograms the neurons for its own benefit. In mice, blocking nerve function inhibited cancer growth and increased the sensitivity of tumor cells to certain chemotherapies and immunotherapies.
For several years, scientists have been discovering interactions with the nervous system in almost all types of cancer studied, interactions that in many cases promote tumor growth and survival. This also applies to pancreatic cancer, which is interwoven with a dense network of nerves. However, only the nerve fibers project into the tumor, while the nuclei of the nerve cells lie far outside, in the ganglia, the control centers of the peripheral nervous system. Therefore, it was previously unclear which molecular interactions they enter into with cancer cells.
Using a newly developed method, a team led by Andreas Trumpp, DKFZ and HI-STEM, has now succeeded for the first time in molecularly examining the nerve cells in both healthy tissue and pancreatic cancer in mice.
Pancreatic cancer reprograms nerve cells
In pancreatic tumors, the nerves are extremely well ramified and in contact with most of the tumor cells. Through the detailed molecular analysis of the individual neurons in the tumor, the researchers discovered that pancreatic cancer reprograms the gene activity of the nerves for its own benefit. The activity of many genes is increased or attenuated, resulting in a tumor-specific signature.
What is more, even after surgical removal of the primary tumor, the tumor nervous system retained its cancer-promoting properties: when the scientists reimplanted pancreatic cancer cells into the animals that had undergone surgery, the resulting secondary tumors were twice as large as those of mice that had been transplanted with pancreatic cancer cells for the first time.
In addition to their direct interaction with cancer cells, nerve cells influence in particular the fibroblasts of the tumor (CAF – cancer-associated fibroblasts), which make up a large part of the tumor mass. They are also stimulated to grow and contribute significantly to the suppression of the immune defense in the tumor environment.
Nerves cut – tumors shrink
When the sympathetic nerve connections to the pancreas were surgically severed or destroyed with special neurotoxins, tumor growth was significantly inhibited. At the same time, the activity of growth-promoting genes in the cancer cells as well as in the CAFs decreased. In the CAFs, the researchers observed a significant increase in pro-inflammatory gene activity after the nerves were destroyed. “Apparently, the neuronal connections in pancreatic cancer suppress the pro-inflammatory activity of the fibroblasts, thereby inhibiting the cancer defense by immune cells,” explains Vera Thiel, the first author of the paper.
Severed nerves increase the effectiveness of immunotherapies
If the interruption of nerve connections apparently has an inflammatory effect, i.e. activates the immune system, this could increase the effectiveness of an immunotherapy with so-called checkpoint inhibitors (ICI). Drugs in this group metaphorically speaking release the “brakes” of the immune system. However, they cannot combat pancreatic carcinomas on their own: the tumors are considered immunologically “cold”, meaning the therapeutically important T-cells simply cannot reach the tumor.
When the researchers blocked the neural connection to the pancreatic tumor in a mouse modell using a targeted neurotoxin, the tumor became sensitive to the checkpoint inhibitor nivolumab again and the tumor mass shrank to one-sixth of the mass in control animals. “By blocking the nerves, were able to convert an immunologically cold tumor into one that was sensitive to immunotherapy,” says Simon Renders, also first author of the publication, summarizing the result.
Severed nerves plus chemotherapy: synergistic effect
The drug nab-paclitaxel is a component of standard chemotherapy for pancreatic cancer. In addition to inhibiting cell division, it also affects sensory nerves, which is why peripheral neuropathy is one of the known severe side effects of this agent.
Trumpp's team showed that under repeated cycles of nab-paclitaxel, the sensory nerve fibers in the tumor decreased drastically. The tumor mass also decreased as expected. The effect on sensory nerves apparently seems to be part of the drug's effectiveness against pancreatic cancer. However, the remaining nerve fibers retained their cancer-promoting gene activity even under treatment.
But what happens when the tumor is completely cut off from its neuronal connections? The researchers achieved this by treating the mice with nab-paclitaxel (to block sensory nerves) and a neurotoxin to switch off the sympathetic neurons. This combination had a synergistic effect and reduced the tumor mass by more than 90 percent.
“The result underscores that both types of nerve cells have functional relevance for tumor growth,” explains Vera Thiel. ”Complete blockade of the communication between nerves and tumor in combination with chemotherapy and/or immune checkpoint inhibitors is a promising approach for combating pancreatic cancer more effectively in the future. For example, it is conceivable to reduce the size of the tumors to such an extent that they subsequently become resectable, Trumpp summarizes. His team, together with doctors from Heidelberg University Hospital, is already planning early clinical trials to test this strategy in pancreatic cancer patients.
The Heidelberg Institute for Stem Cell Research and Experimental Medicine (HI-STEM) gGmbH was founded in 2008 as a public-private partnership between the DKFZ and the Dietmar Hopp Foundation and has been funded by the foundation for 15 years now.
Why research in mice is necessary for this research project
To investigate which different types of peripheral nerves influence the development of pancreatic cancer, the fully developed nervous system of an intact organism is essential. In addition, the aim of the work was to examine the interaction between the nervous system and the tumor as a potential target for new therapeutic approaches. In order to discover possible synergies with the body's own defense system, the immune system with all its components is also needed. Both cannot be reproduced in cell or organ culture systems.
Vera Thiel*, Simon Renders*, Jasper Panten*, Nicolas Dross, Katharina Bauer, Daniel Azorin, Vanessa Henriques, Vanessa Vogel, Corinna Klein, Aino Maija Leppä, Isabel Barriuso Ortega, Jonas Schwickert, Iordanis Ourailidis, Julian Mochayedi, Jan-Phillip Malm, Carsten Müller-Tidow, Hannah Monyer, John Neoptolemeos, Thilo Hackert, Oliver Stege, Duncan T. Odom, Rienk Offringa, Albrecht Stenzinger, Frank Winkler, Martin Sprick, Andreas Trumpp: Characterization of single neurons reprogrammed by pancreatic cancer.
Nature 2025, DOI: 10.1038/s41586-025-08735-3
https://www.nature.com/articles/s41586-025-08735-3
With more than 3,000 employees, the German Cancer Research Center (Deutsches Krebsforschungszentrum, DKFZ) is Germany’s largest biomedical research institute. DKFZ scientists identify cancer risk factors, investigate how cancer progresses and develop new cancer prevention strategies. They are also developing new methods to diagnose tumors more precisely and treat cancer patients more successfully. The DKFZ's Cancer Information Service (KID) provides patients, interested citizens and experts with individual answers to questions relating to cancer.
To transfer promising approaches from cancer research to the clinic and thus improve the prognosis of cancer patients, the DKFZ cooperates with excellent research institutions and university hospitals throughout Germany:
National Center for Tumor Diseases (NCT, 6 sites)
German Cancer Consortium (DKTK, 8 sites)
Hopp Children's Cancer Center (KiTZ) Heidelberg
Helmholtz Institute for Translational Oncology (HI-TRON Mainz) - A Helmholtz Institute of the DKFZ
DKFZ-Hector Cancer Institute at the University Medical Center Mannheim
National Cancer Prevention Center (jointly with German Cancer Aid)
The DKFZ is 90 percent financed by the Federal Ministry of Education and Research and 10 percent by the state of Baden-Württemberg. The DKFZ is a member of the Helmholtz Association of German Research Centers.
Contact:
Dr. Sibylle Kohlstädt
Strategic Communication and Public Relations
German Cancer Research Center
Im Neuenheimer Feld 280
D-69120 Heidelberg
T: +49 6221 42 2843
Email: presse@dkfz.de
END
Pancreatic cancer: blocked nerves as a possible new treatment strategy
2025-02-17
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
This research is absolutely nuts – for better health care
2025-02-17
A nut used in herbal tea has become a hydrogel perfect for a variety of biomedical uses in new research from the University of Chicago Pritzker School of Engineering (UChicago PME) and UChicago Chemistry Department.
A paper published today in Matter created a malva nut hydrogel for medical uses ranging from wound care to ECG readings. The research doesn’t rely on the rumored health benefits of the nuts – in China, they’re known as the sore throat remedy Pangdahai (PDH) – but for their ability to swell in water.
“You never saw the fruit from a tree expand in that kind of volume,” said first ...
Genetic study links defects in sugar digestion to irritable bowel syndrome
2025-02-17
Sucrase-isomaltase (SI) is an intestinal enzyme critical for the digestion of dietary carbohydrates, particularly sucrose and starch. Previous studies from the Gastrointestinal Genetics team at CIC bioGUNE - BRTA and LUM University suggested a genetic link between SI defects and IBS, whereby certain DNA changes cause reduced enzymatic activity and inefficient digestion of carbohydrates, thus inducing symptoms like bloating, diarrhoea, and abdominal pain. As the name gives away, however, SI is a special case in that it encompasses two enzymes with different carbohydrate-digesting ...
Binghamton University, State University of New York retains top research ranking among elite universities
2025-02-17
BINGHAMTON, N.Y. -- Binghamton University maintains its status as an R1 institution for its prolific research activity, according to a new list from the Carnegie Classification of Institutions of Higher Education.
Every three years, the Carnegie Classification looks at schools’ research expenditures and graduate programs to evaluate which campuses can be considered an R1 institution for “very high spending and doctorate production.”
Schools with this designation must spend at least $50 million on research and development and award at least 70 research doctorates. Binghamton wrapped ...
Breaking the pattern: How disorder toughens materials
2025-02-17
Cut open a bone and you’ll see a subtly disordered structure. Tiny beams, called trabeculae, connect to one another in irregular patterns, distributing stress and lending bones an impressive toughness. What if human-made materials could exhibit similar properties?
In a new paper in Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences Nexus, researchers at Penn Engineering, Penn Arts & Sciences and Aarhus University found that adding just the right amount of disorder to the structure of certain materials can make them more than twice as resistant to cracking.
The finding opens the door to more widespread use of so-called “mechanical metamaterials,” ...
A geometric deep learning method for decoding brain dynamics
2025-02-17
In the parable of the blind men and the elephant, several blind men each describe a different part of an elephant they are touching – a sharp tusk, a flexible trunk, or a broad leg – and disagree about the animal’s true nature. The story illustrates the problem of understanding an unseen, or latent object based on incomplete individual perceptions. Likewise, when researchers study brain dynamics based on recordings of a limited number of neurons, they must infer the latent patterns of brain dynamics that generate these recordings.
“Suppose you and I both engage in a mental task, ...
Novel catalyst development for sustainable ammonia synthesis
2025-02-17
As the world moves toward sustainability, the demand for efficient alternatives across industries continues to grow. Ammonia, a key chemical used in fertilizers, explosives, and various other products, is primarily synthesized through the energy-intensive Haber-Bosch process. This process requires extremely high temperatures and pressures, contributing to global carbon dioxide emissions. Conventional catalysts, such as iron and ruthenium, rely on these harsh conditions to drive the reaction. However, a recent study by researchers from Institute of Science Tokyo, the National Institute for Materials Science, and Tohoku University, Japan, led by Professor Masaaki Kitano, explores ...
Researchers identify DNA changes, biological pathways associated with inherited cancer risk
2025-02-17
Thousands of single changes in the nucleotides that make up the human genome have been associated with an increased risk of developing cancer. But until now, it’s not been clear which are directly responsible for the uncontrolled cellular growth that is the hallmark of the disease and which are simply coincidences or minor players.
Stanford researchers have conducted the first large-scale screen of these inherited changes, called single nucleotide variants, and homed in on fewer than 400 that are essential to initiate and drive cancer growth. These variants control several common biological ...
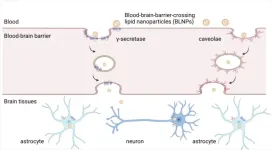
New lipid nanoparticle platform delivers mRNA to the brain through the blood-brain barrier
2025-02-17
New York, NY [February 17, 2025]—Scientists at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai have developed a lipid nanoparticle system capable of delivering messenger RNA (mRNA) to the brain via intravenous injection, a challenge that has long been limited by the protective nature of the blood-brain barrier.
The findings, in mouse models and isolated human brain tissue, were published in the February 17 online issue of Nature Materials [10.1038/s41563-024-02114-5]. They demonstrate the potential of this technology to pave the way for ...
Wildfires in the Andes cause severe soil degradation and hinder ecosystem recovery
2025-02-17
In September 2018, a wildfire burned nearly two thousand hectares of shrubland on the Pichu Pichu volcano, an ecologically significant area in the Peruvian Andes. Unlike Mediterranean ecosystems, where vegetation has evolved strategies to withstand fire, the volcanic soils of Arequipa—one of the driest regions in the world—are not adapted to wildfire disturbances. A Miguel Hernández University of Elche (UMH) research team collected and analyzed soil samples from the burned area at 3,700 meters above sea level to understand how these fragile ecosystems ...
Men and boys matter: Psychology professor reveals hidden issues we need to talk about
2025-02-17
These include those linked to body image, fatherhood and sexual relationships. His latest book - Current Issues Facing Men and Boys – also argues that men struggle to negotiate harmful notions of masculinity and are not included in conversations around gender.
Current Issues Facing Men and Boys urges the public, policymakers, practitioners and other key stakeholders to explore and support policies and practices that promote male wellbeing. This book comes as the UK government announces plans for the country's first men's health strategy, aiming ...