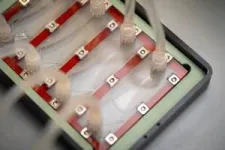
(Press-News.org) By assessing how “sticky” tumor cells are, researchers at the University of California San Diego have found a potential way to predict whether a patient’s early-stage breast cancer is likely to spread. The discovery, made possible by a specially designed microfluidic device, could help doctors identify high-risk patients and tailor their treatments accordingly.
The device, which was tested in an investigator-initiated trial, works by pushing tumor cells through fluid-filled chambers and sorting them based on how well they adhere to the chamber walls. When tested on tumor cells obtained from patients with different stages of breast cancer, researchers found a striking pattern: cells from patients with aggressive cancers were weakly adherent (less sticky), while cells from patients with less aggressive cancers were strongly adherent (more sticky).
The findings were published on Mar. 5 in Cell Reports.
“What we were able to show in this trial is that the physical property of how adhesive tumor cells are could be a key metric to sort patients into more or less aggressive cancers,” said study senior author Adam Engler, a professor in the Shu Chien-Gene Lay Department of Bioengineering at the UC San Diego Jacobs School of Engineering. “If we can improve diagnostic capabilities with this method, we could better personalize treatment plans based on the tumors that patients have.”
Previous research by Engler’s lab, in collaboration with Anne Wallace, director of the Comprehensive Breast Health Center at Moores Cancer Center at UC San Diego Health, had already established that weakly adherent cancer cells are more likely to migrate and invade other tissues compared to strongly adherent cells. Now with patient tumors, the team has taken this insight a step further, demonstrating that adhesion strength of tumor cells is variable and the next step will be to determine if adhesion can help forecast whether a patient’s cancer is likely to metastasize.
Their latest study examined cell adhesion in an early-stage breast cancer known as ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS). Often classified as stage zero breast cancer, DCIS can remain harmless, never progressing beyond the milk ducts where it forms. But in some cases, it develops into invasive breast cancer that could be potentially life-threatening. Scientists and doctors have spent years trying to determine which cases require aggressive treatment and which can be left alone, but the answers have remained elusive.
Current clinical decisions often rely on the size and grade of the DCIS lesion, but these factors do not always predict its behavior.
“Having a mechanism to better predict which DCIS is going to behave more aggressively, such as is seen with this adhesion model, could hold great promise to help us more aggressively treat this type of cancer,” Wallace said. “We don’t want to over-treat with aggressive surgery, medicines and radiation if not necessary, but we need to utilize those when the cancer has higher invasive potential. We want to continue to personalize therapy.”
“Right now, we don’t have a reliable way to identify which DCIS patients are at risk of developing more aggressive breast cancer,” Engler said. “Our device could change that.”
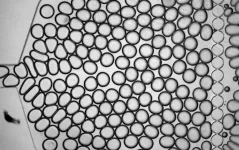
The team’s device, which is roughly the size of an index card, consists of microfluidic chambers coated with adhesive proteins found in breast tissue, such as fibronectin. When tumor cells are placed into the chambers, they adhere to the fibronectin coating. They are then subjected to increasing shear stress as fluid flows through the chambers. By observing where cells detach under specific stress levels, researchers classify them as weakly or strongly adherent.
The team tested the device on samples from 16 patients. These samples consisted of normal breast tissue, DCIS tumors, and aggressive breast cancer tumors obtained from patients with invasive ductal and lobular carcinomas. The experiments revealed that aggressive breast cancer samples contained weakly adherent cells, while normal breast tissue samples contained strongly adherent cells. DCIS samples showed intermediate adhesion levels, but with significant variability among patients.
“What’s interesting is that there is a lot of heterogeneity from patient to patient within a single disease subtype,” said study co-first author Madison Kane, a bioengineering Ph.D. student in Engler’s lab. “Among DCIS patients, for example, we found some with strongly adherent tumor cells and others with weakly adherent cells. We hypothesize that those with weakly adherent cells are at higher risk of developing invasive cancer, and they are likely being underdiagnosed at the beginning of their patient care plan.”
The team plans to track DCIS patients over the next five years to determine whether adhesion strength correlates with metastatic progression. If their hypothesis holds, the device could offer oncologists a powerful new tool to guide treatment strategies, recommending more aggressive interventions for patients whose tumor cells show weak adhesion.
“Our hope is that this device will allow us to prospectively identify those at highest risk, so that we can intervene before metastasis occurs,” Engler said.
This project highlights the importance of interdisciplinary collaboration. Engler’s bioengineering team worked closely with Wallace’s team at Moores Cancer Center, which provided patient samples and support. Funding from the National Institutes of Health (NIH), which includes grants that support shared resources and facilities at Moores Cancer Center, as well as training grants for student researchers working on the project, played a crucial role in the device’s development and the clinical study.
“It’s been a great partnership with Dr. Wallace and Moores Cancer Center,” Engler said. “Their support has been instrumental in advancing investigator-initiated trials like this. We are also extremely grateful for all the different funding mechanisms that support facilities, training and lab work, which make research like this possible.”
Full study: “Adhesion Strength of Tumor Cells Predicts Metastatic Disease in vivo.” Co-authors include Madison A. Kane*, Katherine G. Birmingham*, Benjamin Yeoman*, Neal Patel, Hayley Sperinde, Thomas Molley, Pranjali Beri, Jeremy Tuler, Aditya Kumar, Sarah Klein, Somaye Zare, Anne Wallace and Adam J. Engler, UC San Diego; and Parag Katira, San Diego State University.
*These authors contributed equally to this work
This work was supported by the National Institutes of Health (R01CA280279, R01CA206880 and R21CA217735), the National Science Foundation (CMMI-1763139, CMMI-1763132), Cy pres research awards from the Krueger v. Wyeth settlement fund, and the National Cancer Institute (T32CA009523).
END
A new way to predict cancer's spread? Scientists look at 'stickiness' of tumor cells
2025-03-05
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Prehistoric bone tool ‘factory’ hints at early development of abstract reasoning in human ancestors
2025-03-05
UCL Press Release
Under embargo until Wednesday 5 March 2025, 16:00 UK time / 11:00 US Eastern time
Prehistoric bone tool ‘factory’ hints at early development of abstract reasoning in human ancestors
The oldest collection of mass-produced prehistoric bone tools reveal that human ancestors were likely capable of more advanced abstract reasoning one million years earlier than thought, finds a new study involving researchers at UCL and CSIC- Spanish National Research Council.
The paper, published in Nature, describes a collection of 27 now-fossilised bones that had been shaped into hand tools 1.5 million years ago by human ancestors.
It’s ...
Study: Vaping does not help US tobacco smokers quit
2025-03-05
Researchers at the Herbert Wertheim School of Public Health and Human Longevity Science and Moores Cancer Center at University of California San Diego have found that, among smokers in the United States, e-cigarette use does not increase smoking cessation and is actually associated with reduced tobacco abstinence. The findings, published March 5 in JAMA, refute the notion that e-cigarettes can help people quit, a common misperception among tobacco users and e-cigarette proponents.
“Most smokers think vaping will help you quit ...
Insect populations are declining — and that is not a good thing
2025-03-05
Insect populations, foundational to food chains and pollination, have dramatically declined over the past 20 years due to rapid climate change
Scientists identify two ways fly species from different climates (high-altitude forest and hot desert) have adapted to temperature
Paper provides evidence that changes in brain wiring and heat sensitivity contributed to shifting preference to hot or cold conditions, respectively
Results may help predict the impact of ongoing climate change on insect distribution and behavior
EVANSTON, Ill. --- Tiny, cold-blooded animals like flies depend on their environment to regulate body temperature, ...
Scientists discover genes to grow bigger tomatoes and eggplants
2025-03-05
Bigger, tastier tomatoes and eggplants could soon grace our dinner plates thanks to Johns Hopkins scientists who have discovered genes that control how large the fruits will grow.
The research—led by teams at Johns Hopkins University and Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory—could lead to the development of new varieties of heirloom tomatoes and eggplants, including those that help support agriculture in areas around the world where local varieties are currently too small for large-scale production.
Findings were published in the journal Nature.
“Once ...
Effects of combining coronary calcium score with treatment on plaque progression in familial coronary artery disease
2025-03-05
About The Study: The combination of coronary artery calcium (CAC) score with a primary prevention strategy in intermediate-risk patients with a family history of coronary artery disease was associated with reduction of atherogenic lipids and slower plaque progression compared with usual care. These data support the use of CAC score to assist intensive preventive strategies in intermediate-risk patients.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Thomas H. Marwick, MBBS, PhD, MPH, email Tom.Marwick@bakeridi.edu.au.
To ...
Cancer screening 3 years after the onset of the COVID-19 pandemic
2025-03-05
About The Study: In 2023, reported breast and colorectal cancer screening rebounded from COVID-19 pandemic–related declines and surpassed pre-pandemic estimates. These findings are encouraging given larger-than-expected declines in early-stage breast and colorectal cancer diagnoses in 2020 and increases in distant-stage breast cancer diagnoses through 2021. Cervical cancer screening rates remained below pre-pandemic levels, a troubling trend as early-stage diagnoses continued to decrease in 2021. The persistent decline may in part reflect longer-term declines in patient knowledge and clinician recommendation of cervical cancer ...
Trajectories of sleep duration, sleep onset timing, and continuous glucose monitoring in adults
2025-03-05
About The Study: In this cohort study of middle-aged and older participants, persistent inadequate sleep duration and late sleep onset, whether alone or in combination, were associated with greater glycemic variability. These findings emphasize the importance of considering both sleep duration and timing for optimizing glycemic control in the general population.
Corresponding Authors: To contact the corresponding authors, email Ju-Sheng Zheng, PhD, (zhengjusheng@westlake.edu.cn) and Yu-ming Chen, PhD, (chenyum@mail.sysu.edu.cn).
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link ...
Sports gambling and drinking behaviors over time
2025-03-05
About The Study: This study found that over time, the trajectory of sports gambling frequency was associated with the trajectory of alcohol-related problems. Screening and treatment interventions are recommended for sport gamblers who also drink concurrently, especially because this group appears to be at an elevated risk for developing greater alcohol-related problems over time.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Joshua B. Grubbs, PhD, email joshuagrubbs12@unm.edu
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(10.1001/jamapsychiatry.2025.0024)
Editor’s Note: Please ...
For better quantum sensing, go with the flow
2025-03-05
Combine a garden-variety green laser, microwaves with roughly the energy of your wi-fi, and some diamond dust in drops of water, and what do you get? A precise chemical detection tool.
For the first time, researchers have combined nanodiamonds in microdroplets of liquid for quantum sensing. The new technique is precise, fast, sensitive, and requires only small amounts of the material to be studied – helpful when studying trace chemicals or individual cells. The results were published in the journal Science Advances in December.
“We weren’t even sure ...
Toxic environmental pollutants linked to faster aging and health risks in US adults
2025-03-05
“Environmental chemical exposures represent a key modifiable risk factor impacting human health and longevity, and our findings provide evidence for associations between several environmental exposures and epigenetic aging in a large sample representative of the US adult population.”
BUFFALO, NY — March 5, 2025 — A new research paper was published in Aging (Aging-US) on February 11, 2025, Volume 17, Issue 2, titled “Exposome-wide association study of environmental chemical exposures ...