(Press-News.org) Juveniles grow up hearing a multitude of adages about life, such as: “True friends are forever,” “Fake it ’til you make it,” and “Change is a good thing.”
However, these adages — and other life advice about behavior in society — are difficult to process for juveniles who were incarcerated at a young age and served long sentences, says J.Z. Bennett, a criminologist at the University of Cincinnati whose research focuses on prison reform.
“Spending decades in prison removes individuals from social structures and sources of informal social control, such as education, employment, marriage and parenting,” he writes in a new study published in the journal Criminology: “Thicker Than Blood: Exploring the Importance of Carceral Bonds for Those Formerly Serving Juvenile Life Without Parole Sentences.”
Juvenile life without parole (JLWOP) is a sentence that places a child 17 years old or younger in prison for life without the possibility of parole. The United States is the only nation that hands down such sentences for crimes committed before turning 18.
Bennett’s study draws from data and life-history interviews of JLWOP offenders, or “juvenile lifers,” who were subsequently released after Supreme Court rulings in 2012 and 2016 found that mandatory life sentences for juveniles were unconstitutional.
Since the Supreme Court rulings, more than 2,500 individuals have been resentenced, and more than 1,000 of those have been released, Bennett’s research team found.
The average age of the juvenile lifers interviewed was 53.
According to Bennett, the study’s key findings are:
Prison friendships matter more than people realize — Children sentenced to life without parole lose contact with family and friends on the outside but form deep, surrogate family bonds in prison. These relationships provide emotional and practical support throughout their incarceration. However, upon release, they face the difficult reality of rebuilding ties with family and society while also grieving the loss of connections that sustained them behind bars.
Long sentences throw lives out of sync — Serving decades in prison disconnects individuals from the world outside. While their family and peers move forward, they remain in a system that does not prepare them for release. Instead, their strongest relationships are with those they were incarcerated with, leading to an ongoing struggle to bridge the gap between their past in prison and their future in the community.
Freedom isn’t just about getting out, it’s an emotional rollercoaster — While release from a life sentence is often seen as a moment of triumph, it is also a time of deep emotional upheaval. Many experience loneliness, disorientation and difficulty adjusting to everyday life. Family members often expect them to simply move forward, but without an opportunity to process decades of incarceration, they may feel misunderstood and unsupported.
Parole rules can make reentry even harder — Many states prohibit individuals with felony records from associating with one another, despite the fact that these peer relationships are often the most valuable source of support. Those who have shared the experience of long-term incarceration understand the unique challenges of reentry in ways that others cannot. Preventing these connections removes a crucial support system and makes reintegration even more difficult.
“This study challenges the assumption that extreme sentences promote rehabilitation. Instead, the findings suggest that decades behind bars disrupt personal development, sever vital relationships and create barriers to successful reintegration,” Bennett says.
“Policymakers should consider alternative approaches that promote accountability,” he adds, “while also supporting rehabilitation and maintaining social connections that are critical for long-term success.”
Bennett is an assistant professor in UC’s School of Criminal Justice, in the College of Education, Criminal Justice, and Human Services. In addition to teaching corrections courses, he leads UC’s Inside-Out Prison Exchange Program, where UC students travel to corrections facilities to discuss criminal justice topics such as sentencing, parole, life after prison and recidivism with incarcerated individuals in a classroom setting. Bennett is an editor of a new book, “Black Freedom Struggle in Urban Appalachia,” available on Amazon.
END
UC Study: Long sentences for juveniles make reentry into society more difficult
Assimilating back into society severs ties made while incarcerated and hinders progress
2025-03-11
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Death by feral cat: DNA shows cats to be culprits in killing of native animals
2025-03-11
Conservation scientists from UNSW Sydney have used DNA technology to identify feral cats as the primary predators responsible for the deaths of reintroduced native animals at two conservation sites in South Australia.
The finding fits in with research data that suggests feral cats have killed more native animals than any other feral predators in Australia, and are believed to be responsible for two thirds of mammal extinctions since European settlement.
But in a study published recently in the ...
Plant Physiology is Searching for its Next Editor-in-Chief
2025-03-10
After taking the helm of Plant Physiology 2022, Yunde Zhao's celebrated term as Editor-in-Chief of the journal, during which he introduced changes that saw the journal flourish, will come to a close on December 31, 2026. The American Society of Plant Biologists (ASPB) is seeking a prominent plant scientist to assume the duties and responsibilities of Editor-in-Chief of Plant Physiology effective January 1, 2027. ASPB’s EIC Search Committee is charged with evaluating candidates for the position and invites members of the plant science community to participate in the process by nominating someone who they ...
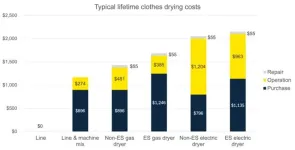
Clothes dryers and the bottom line: Switching to air drying can save hundreds
2025-03-10
Researchers from the University of Michigan are hoping their new study will inspire some Americans to rethink their relationship with laundry. Because, no matter how you spin it, clothes dryers use a lot of comparatively costly energy when air works for free.
Household dryers in the U.S. consume about 3% of our residential energy budget, about six times that used by washing machines. Collectively, dryers cost more than $7 billion to power each year in this country, and generating that energy emits the equivalent of more than ...
New insights into tRNA-derived small RNAs offer hope for digestive tract disease diagnosis and treatment
2025-03-10
This new article published in Genes & Diseases highlights the critical role of tRNA-derived small RNAs (tsRNAs) in digestive tract diseases, positioning these molecules as potential biomarkers for diagnosis, prognosis, and targeted therapies. The comprehensive review explores the biogenesis, classification, and biological functions of tsRNAs, shedding light on their influence over cellular processes such as translation regulation, epigenetic modification, and protein interactions.
Recent findings emphasize the significance of tsRNAs in both tumor and non-tumor digestive diseases, demonstrating their ability to regulate cell proliferation, ...
Emotive marketing for sustainable consumption?
2025-03-10
Does triggering certain emotions increase willingness to pay for sustainably produced food? In social media, emotional messages are often used to influence users' consumer behaviour. An international research team including the University of Göttingen investigated the short- and medium-term effects of such content on consumers' willingness to pay for bars of chocolate. They found that in the short term, provoking certain emotions increases willingness to pay, but the effect weakens after a very short time. The results were published in the journal Q Open.
Food ...
Prostate cancer is not a death knell, study shows
2025-03-10
Prostate cancer statistics can look scary: 34,250 U.S. deaths in 2024. 1.4 million new cases worldwide in 2022.
Dr. Bruce Montgomery, a UW Medicine oncologist, hopes that patients won’t see these numbers and just throw up their hands in fear or resignation.
“Being diagnosed with prostate cancer is not a death knell,” said Montgomery, senior author of a literature and trial review that appeared in JAMA today. Montgomery is the clinical director of Genitourinary Oncology at Fred Hutch Cancer ...
Unveiling the role of tumor-infiltrating immune cells in endometrial carcinoma
2025-03-10
A new review article published in Genes & Diseases sheds light on the complex molecular mechanisms through which tumor-infiltrating immune cells regulate endometrial carcinoma (EC). As one of the most prevalent gynecological cancers, EC continues to challenge researchers and clinicians due to its dynamic interaction with the immune microenvironment. This comprehensive review presents crucial insights into how immune cells influence tumor progression and how immune evasion strategies enable cancer cells to thrive.
The tumor microenvironment ...
Traditional Chinese medicine unlocks new potential in treating diseases through ferroptosis regulation
2025-03-10
Innovative insights into the role of ferroptosis, a unique form of programmed cell death, are reshaping the landscape of disease treatment. This growing field highlights how Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM) can effectively modulate ferroptosis, offering novel therapeutic approaches for various conditions, including cancer, cardiovascular diseases, neurodegenerative disorders, and organ injuries. The powerful bioactive compounds in TCM have demonstrated the ability to regulate iron metabolism, lipid peroxidation, and redox balance, positioning them as key players in advancing modern medicine.
With its rich history of holistic ...
MSU study pinpoints the impact of prenatal stress across 27 weeks of pregnancy
2025-03-10
MSU has a satellite uplink/LTN TV studio and Comrex line for radio interviews upon request.
EAST LANSING, Mich. – A team of researchers at Michigan State University and the University of Michigan found new insights on the timing of prenatal stress and its effect on infant stress reactivity and temperament — including differences between genders.
The study, published in Psychoneuroendocrinology, is the first to examine weekly stress across 27 weeks of pregnancy to pinpoint when it most affects a newborn’s stress response and temperament — two measures that indicate infant biobehavioral reactivity.
“Prenatal ...
Biochemist’s impact on science and students honored
2025-03-10
Kayunta Johnson-Winters, an associate professor of chemistry and biochemistry at The University of Texas at Arlington, has been named a 2025 fellow of the American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology.
The honor recognition recognizes her contributions to biochemistry and molecular biology and her efforts to support junior faculty, women in science and student mentorship.
“This is a tremendous honor and recognizes Kay’s important work in advancing our understanding of disease while mentoring junior faculty and student researchers,” said Morteza Khaledi, dean of UTA’s College of Science. “I’m pleased ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Study: Reported crop yield gains from breeding may be overstated
Stem cells from human baby teeth show promise for treating cerebral palsy
Chimps’ love for crystals could help us understand our own ancestors’ fascination with these stones
Vaginal estrogen therapy not linked to cancer recurrence in survivors of endometrial cancer
How estrogen helps protect women from high blood pressure
Breaking the efficiency barrier: Researchers propose multi-stage solar system to harness the full spectrum
A new name, a new beginning: Building a green energy future together
From algorithms to atoms: How artificial intelligence is accelerating the discovery of next-generation energy materials
Loneliness linked to fear of embarrassment: teen research
New MOH–NUS Fellowship launched to strengthen everyday ethics in Singapore’s healthcare sector
Sungkyunkwan University researchers develop next-generation transparent electrode without rare metal indium
What's going on inside quantum computers?: New method simplifies process tomography
This ancient plant-eater had a twisted jaw and sideways-facing teeth
Jackdaw chicks listen to adults to learn about predators
Toxic algal bloom has taken a heavy toll on mental health
Beyond silicon: SKKU team presents Indium Selenide roadmap for ultra-low-power AI and quantum computing
Sugar comforts newborn babies during painful procedures
Pollen exposure linked to poorer exam results taken at the end of secondary school
7 hours 18 mins may be optimal sleep length for avoiding type 2 diabetes precursor
Around 6 deaths a year linked to clubbing in the UK
Children’s development set back years by Covid lockdowns, study reveals
Four decades of data give unique insight into the Sun’s inner life
Urban trees can absorb more CO₂ than cars emit during summer
Fund for Science and Technology awards $15 million to Scripps Oceanography
New NIH grant advances Lupus protein research
New farm-scale biochar system could cut agricultural emissions by 75 percent while removing carbon from the atmosphere
From herbal waste to high performance clean water material: Turning traditional medicine residues into powerful biochar
New sulfur-iron biochar shows powerful ability to lock up arsenic and cadmium in contaminated soils
AI-driven chart review accurately identifies potential rare disease trial participants in new study
Paleontologist Stephen Chester and colleagues reveal new clues about early primate evolution
[Press-News.org] UC Study: Long sentences for juveniles make reentry into society more difficultAssimilating back into society severs ties made while incarcerated and hinders progress