(Press-News.org) Critically endangered hawksbill turtles migrate up to 1,000km from nesting to foraging grounds in the Western Caribbean, riding with and against ocean currents to congregate in popular feeding hotspots
Article URL: https://plos.io/41LfJZK
Article title: Inter-nesting area use, migratory routes, and foraging grounds for hawksbill turtles (Eretmochelys imbricata) in the Western Caribbean
Author countries: US, Honduras, Costa Rica
Funding: Funding for this project was provided by the Boyd Lyon Sea Turtle Fund to QDB, the Sonoma County Community Foundation to CED, the Fort Wayne Children's Zoo Conservation Fund and the Jack Schrey Distinguished Professor Funds to FVP, the USFWS Marine Turtle Conservation Fund Grant #611510 under the direction of Earl Possardt to SGD, the Department of Earth and Biological Sciences at Loma Linda University to SGD, as well as the California Turtle and Tortoise Club Inland Empire Chapter to SGD.
END
Critically endangered hawksbill turtles migrate up to 1,000km from nesting to foraging grounds in the Western Caribbean, riding with and against ocean currents to congregate in popular feeding hotspot
2025-03-12
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
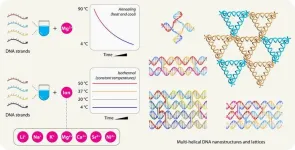
UAlbany researchers unlock new capabilities in DNA nanostructure self-assembly
2025-03-12
ALBANY, N.Y. (March 12, 2025) — University at Albany researchers at the RNA Institute are pioneering new methods for designing and assembling DNA nanostructures, enhancing their potential for real-world applications in medicine, materials science and data storage.
Their latest findings demonstrate a novel ability to assemble these structures without the need for extreme heat and controlled cooling. They also demonstrate successful assembly in unconventional “buffer” substances including nickel. These developments, published today in the journal Science Advances, unlock new possibilities in DNA nanotechnology.
DNA ...
PM2.5 exposure may be associated with increased skin redness in Taiwanese adults, suggesting that air pollution may contribute to skin health issues
2025-03-12
PM2.5 exposure may be associated with increased skin redness in Taiwanese adults, suggesting that air pollution may contribute to skin health issues.
####
Article URL: https://plos.io/4iDTuuo
Article Title: Association between PM2.5 and skin redness features in Taiwan
Author Countries: Taiwan, United States
Funding: The authors received no specific funding for this work. END ...
BD² announces four new sites to join landmark bipolar disorder research and clinical care network
2025-03-12
Today, Breakthrough Discoveries for thriving with Bipolar Disorder (BD²) announced four new national institutions to receive $2.3 million each to join the BD² Integrated Network, a collaborative research and clinical care model that will improve care, interventions, and outcomes for people living with bipolar disorder.
University of Cincinnati/Lindner Center of HOPE, University of California San Diego, The University of Texas at Austin, and The Feinstein Institutes for Medical Research join the six inaugural institutions in the network. Working in partnership with clinicians, researchers, and people living ...
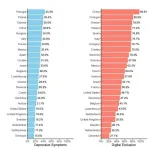
Digital Exclusion Increases Risk of Depression Among Older Adults Across 24 Countries
2025-03-12
Older adults who lack internet access are at a significantly higher risk of developing depressive symptoms, especially those with limited familial support or lower income levels, according to a new study published in Health Data Science. Conducted by an international team of researchers, this study analyzed data from five major aging cohort studies covering 24 countries, revealing a strong link between digital exclusion and mental health.
The researchers, led by Dr. Yinzi Jin from Peking University, investigated how digital exclusion—defined as the lack of internet access—affects the mental health of older adults. Using data from the Health and Retirement Study (HRS), ...
Quantum annealing processors achieve computational advantage in simulating problems on quantum entanglement
2025-03-12
Quantum annealing processors outperform classical supercomputers in solving real-world scientific simulations of quantum spin dynamics, researchers report in a new study, achieving results far beyond the capacity of conventional computational methods, which may require impossible time and energy to match. The results provide a challenge to classical computing, where method improvement has in the past tempered claims of quantum advantage. Only in recent years have quantum computers begun to live up to their lofty promises, with quantum processing units (QPUs) with diverse architectures – such as photonic, neutral-atom, and ...
How UV radiation triggers a cellular rescue mission
2025-03-12
How UV Radiation Triggers a Cellular Rescue Mission
Ultraviolet (UV) radiation from the sun is a well-known cause of DNA damage, which can lead to diseases like skin cancer. But how do our cells repair this damage to protect us? Researchers from Sabanci University, Veysel Oğulcan Kaya and Ogün Adebali, have uncovered a fascinating answer: when DNA is damaged by UV light, our cells reorganize their genetic material in 3D space to prioritize repair, in what might be called a “cellular rescue mission.”
A New Look at DNA Repair
DNA, the blueprint of ...
Hepatic stellate cells control liver function and regeneration
2025-03-12
Until now, doctors knew hepatic stellate cells mainly as drivers of liver fibrosis. The actual functions of this cell type have hardly been studied to date. Researchers from the German Cancer Research Center (DKFZ), the Mannheim Medical Faculty and Columbia University in New York have now published in the journal Nature that hepatic stellate cells control liver metabolism as well as liver regeneration and size. The results of the study could contribute to new therapeutic approaches for liver diseases.
The liver is a central organ for carbohydrate and protein metabolism as well as for the detoxification ...
The secret DNA circles fueling pancreatic cancer’s aggression
2025-03-12
Pancreatic cancer is one of the deadliest cancers worldwide, with a five-year survival rate of 13%. This poor prognosis stems from both late detection and the cancer’s notorious capacity to adapt and resist therapy. Now, a study led by researchers at the University of Verona, University of Glasgow, and the Botton-Champalimaud Pancreatic Cancer Centre uncovers a hidden driver of this adaptability: extrachromosomal DNA (ecDNA).
A New Player in Pancreatic Cancer
The team found that some pancreatic cancer cells gain a major survival edge by carrying copies of critical cancer genes—such as ...
2D metals: Chinese scientists achieve breakthrough in atomic manufacturing
2025-03-12
Since the groundbreaking discovery of graphene in 2004, the dizzying pace of progress in two-dimensional (2D) materials has ushered in a new era of fundamental research and technological innovation. Although nearly 2,000 2D materials have been theoretically predicted and hundreds have been created in laboratory settings, most of these 2D materials are limited to van der Waals (vdW) layered crystals.
Scientists have long been keen to develop atomically thin 2D metals, thereby expanding ...
Cause of post-COVID inflammatory shock in children identified
2025-03-12
MIS-C is a serious inflammatory shock that affects children. It can occur several weeks after a COVID infection and can be life-threatening. Until now, however, the precise cause of the condition was unknown. Researchers at Charité – Universitätsmedizin Berlin and the German Rheumatology Research Center (DRFZ), an institute of the Leibniz Association, have identified that reactivation of a pre-existing, dormant infection with the Epstein-Barr virus triggers an excessive inflammatory response. The researchers have detailed their findings in an article in Nature.* These insights open the door to new treatment methods, potentially not limited to MIS-C.
The majority of children ...