(Press-News.org) Diabetic ketoacidosis is a common severe complication of diabetes, which develops when the body can’t produce enough insulin.
During DKA the body starts breaking down fat, causing a buildup of acids in the bloodstream. The symptoms often include thirst, weakness, nausea and confusion.
Concerningly, this condition accounts for more than 500,000 hospital days per year, often in the intensive care unit, with an estimated cost of $2.4 billion.
In a study, published in CHEST Critical Care, University of Michigan researchers show that using continuous glucose monitors can help measure glucose accurately during DKA and potentially prevent ICUs from being overwhelmed.
“Although DKA is a condition with low mortality, patients often end up in the ICU, primarily due to the need for frequent glucose checks. There is a mismatch between relative risk of death from DKA compared to the other conditions we see in the ICU,” said Nate Haas, M.D., clinical assistant professor of emergency medicine.
Management of DKA requires frequent blood glucose measurements via fingerstick to guide treatment, typically performed once per hour, which can be burdensome for nurses and cause patient discomfort.
Although DKA is a condition with low mortality, patients often end up in the ICU, primarily due to the need for frequent glucose checks. There is a mismatch between relative risk of death from DKA compared to the other conditions we see in the ICU."
-Nate Haas, M.D.
In contrast, a continuous glucose monitor is a safe and cost-effective sensor that is temporarily placed on the skin of the patient’s abdomen or arm.
However, the benefit of using it during DKA was unknown.
“Prior to this study, there were concerns that continuous glucose monitors may not be as accurate during DKA because they rely on interstitial fluid, which surrounds your cells. Since patients with DKA are severely dehydrated, it was unclear whether the monitors would be as accurate,” Haas said.
The study, which was conducted from March to August 2023, focused on 20 patients. The team compared glucose readings taken simultaneously from continuous glucose monitors and standard, hourly fingerstick glucose checks.
Using 334 paired measurements, the study found that continuous glucose monitors remained accurate during DKA. Promisingly, they were able to more quickly identify drops in blood glucose levels and were clinically comparable to the glucose values obtained from hourly finger sticks.
“This is the first step in improving patient outcomes, patient experience, and reducing resource utilization for the common, costly condition of DKA. By using this tool, we can reduce the number of fingersticks needed, simplify management, and prevent the need for ICU admission for DKA in the future,” Haas said.
He is working to develop a clinical trial with collaborators from across the country to further assess the use of continuous glucose monitor-guided DKA management.
“This work required a large, multidisciplinary group from endocrinology, emergency medicine, nursing and biostatistics, and I’m hoping that our future work will help reduce ICU overcrowding and improve patient outcomes,” Haas said.
Additional authors: Lynn Ang, Nazanene H. Esfandiari, Ahsan M. Khan, James A. Cranford, Ashley Cohen, Jordan Sell, Mostafa Abdel-Hamid, Kevin E. Romanchik and Frederick K. Korley.
Funding/disclosures: The 2023 Society for Academic Emergency Medicine Foundation Advanced Research Methodology Evaluation and Design Pilot Grant with a cost share from the Department of Emergency Medicine at the University of Michigan.
Paper cited: “Analytical Accuracy of a Continuous Glucose Monitor in Adult Diabetic Ketoacidosis,” CHEST Critical Care. DOI: 10.1016/j.chstcc.2024.100109
END
Continuous glucose monitors can optimize diabetic ketoacidosis management
Novel use of instrument can improve patient comfort and intensive care unit capacity
2025-03-18
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Time is not the driving influence of forest carbon storage, U-M study finds
2025-03-18
Figures and photos
It is commonly assumed that as forest ecosystems age, they accumulate and store, or "sequester," more carbon.
A new study based at the University of Michigan Biological Station untangled carbon cycling over two centuries and found that it's more nuanced than that.
The synergistic effects of forest structure, the composition of the tree and fungal communities, and soil biogeochemical processes have more influence on how much carbon is being sequestered above and below ground than previously thought.
The ...
Adopting zero-emission trucks and buses could save lives, prevent asthma in Illinois
2025-03-18
Guided by the lived experiences of community partners, Northwestern University scientists have simulated the effects of zero-emission vehicle (ZEV) adoption on future air quality for the greater Chicago area.
The results were published today (March 18) in the journal Frontiers of Earth Science.
Motivated by California’s Advanced Clean Trucks (ACT) policy, Neighbors for an Equitable Transition to Zero-Emissions (NET-Z) Illinois members partnered with Northwestern researchers to explore how a similar strategy might play out in Cook County and the surrounding areas.
To develop a model that more realistically simulates ...
New fossil discovery reveals how volcanic deposits can preserve the microscopic details of animal tissues
2025-03-18
An analysis of a 30,000-year-old fossil vulture from Central Italy has revealed for the first time that volcanic rock can preserve microscopic details in feathers - the first ever record of such a preservation.
An international team, led by Dr Valentina Rossi (University College Cork, Ireland), discovered a new mode of preservation of soft tissues that can occur when animals are buried in ash-rich volcanic sediments.
The new research, published in the scientific journal Geology, reveals that the feathers ...
New chromosome barcode system unveils genetic secrets of alfalfa
2025-03-18
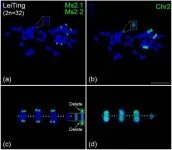
In a recent study, scientists have developed a revolutionary chromosome identification system for alfalfa, one of the world's most economically vital forage crops. Leveraging an advanced Oligo-fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH) barcode technique, researchers successfully mapped and identified all chromosomes in alfalfa, uncovering unexpected chromosomal anomalies, including aneuploidy and large segment deletions. This breakthrough not only enhances molecular cytogenetics but also sheds light on the genetic stability ...
Reusing old oil and gas wells may offer green energy storage solution
2025-03-18
UNIVERSITY PARK, Pa. — Moving from fossil fuels to renewable energy sources like wind and solar will require better ways to store energy for use when the sun is not shining or the wind is not blowing. A new study by researchers at Penn State found that taking advantage of natural geothermal heat in depleted oil and gas wells can improve the efficiency of one proposed energy storage solution: compressed-air energy storage (CAES).
The researchers recently published their findings in the Journal of Energy Storage.
CAES plants compress air and store it underground when energy demand is low and then extract the air to create electricity when demand ...
Natural insect predators may serve as allies in spotted lanternfly battle
2025-03-18
UNIVERSITY PARK, Pa. — Insect predators found in the United States could help keep spotted lanternfly populations in check while potentially reducing reliance on chemical control methods, according to a new study conducted by researchers at Penn State.
Led by entomologists in Penn State’s College of Agricultural Sciences and published in Arthropod-Plant Interactions, the study evaluated the effectiveness of various insects in potentially controlling spotted lanternfly populations. The invasive pest, first detected in the United States in 2014, has spread across at least 18 states, causing significant damage to vineyards, orchards ...
Rice research team creates universal RNA barcoding system for tracking gene transfer in bacteria
2025-03-18
In the microscopic world of bacteria, gene transfer is a powerful mechanism that can alter cellular function, drive antibiotic resistance and even shape entire ecosystems. Now an interdisciplinary group of researchers at Rice University has developed an innovative RNA “barcoding” method to track these genetic exchanges in microbial communities, providing new insights into how genes move across species. The findings were recently published in Nature Biotechnology.
“We’ve long known that bacteria swap genes in ways that impact human health, biotechnology and environmental stability,” said James Chappell, associate professor of biosciences ...
New genetic pathway unlocks drought-resistant cucumbers with fewer branches
2025-03-18
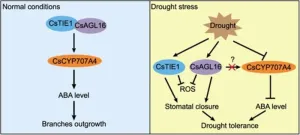
A new discovery has unveiled a genetic module, CsTIE1-CsAGL16, that simultaneously regulates lateral branch development and drought tolerance in cucumbers. This dual-function genetic pathway offers a promising new approach to breeding cucumber varieties that are both resilient to water scarcity and tailored to market preferences. By deciphering how these genes coordinate water conservation and branch growth, researchers have opened new doors for improving crop adaptability and productivity in the face of climate change.
Drought stress poses a major challenge to ...
New high-definition pictures of the baby universe
2025-03-18
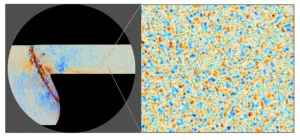
New research by the Atacama Cosmology Telescope (ACT) collaboration has produced the clearest images yet of the universe’s infancy – the earliest cosmic time yet accessible to humans. Measuring light that traveled for more than 13 billion years to reach a telescope high in the Chilean Andes, the new images reveal the universe when it was about 380,000 years old – the equivalent of hours-old baby pictures of a now middle-aged cosmos.
“We are seeing the first steps towards making the earliest stars and galaxies,” says Suzanne Staggs, director of ACT and Henry ...
Zhou conducting GPU modeling research
2025-03-18
Keren Zhou, Assistant Professor, Computer Science, College of Engineering and Computing (CEC), received funding for: “GPU Modeling Research of Smart Modeling and Simulation for HPC (SMASH).”
Zhou and his collaborators will complete research and development tasks.
Zhou received $65,648 from Brookhaven National Laboratory on a subaward from the U.S. Department of Energy for this research. Funding began in Feb. 2025 and will end in late Sept. 2025.
...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
attexis RCT shows clinically relevant reduction in adult ADHD symptoms and is published in Psychological Medicine
Cellular changes linked to depression related fatigue
First degree female relatives’ suicidal intentions may influence women’s suicide risk
Specific gut bacteria species (R inulinivorans) linked to muscle strength
Wegovy may have highest ‘eye stroke’ and sight loss risk of semaglutide GLP-1 agonists
New African species confirms evolutionary origin of magic mushrooms
Mining the dark transcriptome: University of Toronto Engineering researchers create the first potential drug molecules from long noncoding RNA
IU researchers identify clotting protein as potential target in pancreatic cancer
Human moral agency irreplaceable in the era of artificial intelligence
Racial, political cues on social media shape TV audiences’ choices
New model offers ‘clear path’ to keeping clean water flowing in rural Africa
Ochsner MD Anderson to be first in the southern U.S. to offer precision cancer radiation treatment
Newly transferred jumping genes drive lethal mutations
Where wells run deep, biodiversity runs thin
Q&A: Gassing up bioengineered materials for wound healing
From genetics to AI: Integrated approaches to decoding human language in the brain
Leora Westbrook appointed executive director of NR2F1 Foundation
Massive-scale spatial multiplexing with 3D-printed photonic lanterns achieved by researchers
Younger stroke survivors face greater concentration, mental health challenges — especially those not employed
From chatbots to assembly lines: the impact of AI on workplace safety
Low testosterone levels may be associated with increased risk of prostate cancer progression during surveillance
Analysis of ancient parrot DNA reveals sophisticated, long-distance animal trade network that pre-dates the Inca Empire
How does snow gather on a roof?
Modeling how pollen flows through urban areas
Blood test predicts dementia in women as many as 25 years before symptoms begin
Female reproductive cancers and the sex gap in survival
GLP-1RA switching and treatment persistence in adults without diabetes
Gnaw-y by nature: Researchers discover neural circuit that rewards gnawing behavior in rodents
Research alert: How one receptor can help — or hurt — your blood vessels
Lamprey-inspired amphibious suction disc with hybrid adhesion mechanism
[Press-News.org] Continuous glucose monitors can optimize diabetic ketoacidosis managementNovel use of instrument can improve patient comfort and intensive care unit capacity