(Press-News.org) A study in Neurology, led by Yue Leng, PhD, and Sasha Milton, followed the sleep patterns of 733 older female participants to see if specific patterns of change were associated with a higher risk of dementia. The participants, whose average age was 83, were monitored by wrist devices that track movement and time spent asleep. They had normal cognition at the start of the study.
What They Discovered
At the end of the study, five years later, 13% had developed dementia. This included 25 participants (8%) with stable sleep patterns, 39 (15%) with declining nighttime sleep patterns and 29 (19%) with increasing sleepiness. After adjusting for factors like age, education, diabetes and hypertension, those with increasing sleepiness had double the risk of the stable sleepers.
Why it Matters
This study is one of the first to look at how sleep patterns change over time and relate to dementia risk. It adds to a body of recent UCSF-led research that shows poor sleep quality in midlife, delayed dream phase and extended napping are linked to a higher risk of dementia.
Need to Know
It is unknown if worsening sleep increases the risk of dementia or if dementia leads to worsening sleep. Some scientists believe both theories may be correct.
Funding: National Institutes of Health, National Institute on Aging
About UCSF: The University of California, San Francisco (UCSF) is exclusively focused on the health sciences and is dedicated to promoting health worldwide through advanced biomedical research, graduate-level education in the life sciences and health professions, and excellence in patient care. UCSF Health, which serves as UCSF's primary academic medical center, includes top-ranked specialty hospitals and other clinical programs, and has affiliations throughout the Bay Area. UCSF School of Medicine also has a regional campus in Fresno. Learn more at ucsf.edu, or see our Fact Sheet.
###
Follow UCSF
ucsf.edu | Facebook.com/ucsf | YouTube.com/ucsf
END
Is increased sleepiness in our 80s tied to higher dementia risk?
2025-03-19
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
South Africa and China establish record-breaking 12,900 km ultra-secure quantum satellite link
2025-03-19
Scientists from South Africa and China have successfully established the world’s longest intercontinental ultra-secure quantum satellite link, spanning 12,900 km. Using the Chinese quantum microsatellite Jinan-1, launched into low Earth orbit, this milestone marks the first-ever quantum satellite communication link established in the Southern Hemisphere.
In this demonstration, quantum keys were generated in real-time through Quantum Key Distribution (QKD), enabling the secure encryption of images transmitted between ground stations in China and South Africa via one-time pad encryption—considered unbreakable. The results from this pioneering ...
A rule-changer for ceramic fuel cells
2025-03-19
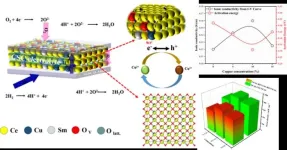
A joint research team from Southeast University and Shenzhen University has developed a novel function of semiconductor-ionic conductor (SIC) using a Cu-Sm co-doping ceria (SCDC). By enhancing ionic and electronic conductivity in the same time, the team is able to achieve superionic transport property and excellent fuel cell performance using the SIC electrolyte. It changes traditional pure ionic electrolyte to SIC with strong electron-ion coupling synergistic effect to obtain exceptional ionic conductivity and fuel cell performance. This study leads to a new way to develop advanced electrolytes and fuel cells in energy conversion technologies.
Ceramic ...
Good vibrations: Scientists discover a groundbreaking method for exciting phonon-polaritons
2025-03-19
NEW YORK, March 19, 2025 – Imagine a world where your phone stays cool no matter how long you use it, and it’s also equipped with tiny sensors that can identify dangerous chemicals or pollutants with unparalleled sensitivity and precision. Newly published research in the journal Nature demonstrates a new way of generating long-wave infrared and terahertz waves, which is an important step toward creating materials that can help realize these technological advances. The work, led by researchers at the Advanced Science Research Center at the CUNY Graduate Center (CUNY ASRC) paves the way for cheaper, smaller long-wave infrared light sources and more efficient device cooling.
Phonon-polaritons ...
CNIC scientists discover a type of immune cell that produces defensive "shields" in the skin
2025-03-19
A team at the Centro Nacional de Investigaciones Cardiovasculares (CNIC) led by Dr. Andrés Hidalgo has discovered a specialized population of neutrophils in the skin that produce extracellular matrix, helping to maintain the skin’s resistance and integrity. The study, published in Nature, demonstrates that the immune system not only targets pathogens, but also physically strengthens the skin to prevent them entering the body.
Neutrophils are an important type of circulating immune cell. The specialized neutrophils described ...
Science behind “Polly want a cracker” could guide future treatment design for speech disorders
2025-03-19
A new study explains how a parakeet’s brain helps it to mimic human words.
By recording for the first time the brain activity of parakeets as they made sounds, a research team at NYU Grossman School of Medicine found that their brains generate patterns seen before only in humans as they speak.
Published online March 19 in the journal Nature, the study mapped the activity of a group of nerve cells in the bird’s brain called the central nucleus of the anterior arcopallium (AAC), which is known to strongly influence the muscles in its vocal ...
Brain imaging reveals surprises about learning
2025-03-19
By revealing for the first time what happens in the brain when an animal makes a mistake, Johns Hopkins University researchers are shedding light on the holy grail of neuroscience: the mechanics of how we learn.
The team pinpointed the exact moment mice learned a new skill by observing the activity of individual neurons, confirming earlier work that suggested animals are fast learners that purposely test the boundaries of new knowledge.
The federally funded work, which upends assumptions about the speed of learning and the role of the sensory cortex, and which the researchers believe will hold true across animal ...
Scientists see the first steps of DNA unwinding
2025-03-19
For the first time, scientists have witnessed the very moment DNA begins to unravel, revealing a necessary molecular event for DNA to be the molecule that codes all life. A new study from King Abdullah University of Science and Technology (KAUST), published in Nature, captures the moment DNA begins to unwind, allowing for all the events that follow in DNA replication. This direct observation sheds light on the fundamental mechanisms that allow cells to faithfully duplicate their genetic material, a cornerstone for growth and reproduction.
Using cryo-electron microscopy and deep learning to observe the helicase ...
Earliest stages and possible new cause of stomach cancer revealed
2025-03-19
For the first time, scientists have systematically analysed somatic mutations in stomach lining tissue to unpick mutational processes, some of which can lead to cancer. The team also uncovered hints of a potential new cause of stomach cancer that needs further research.
Researchers at the Wellcome Sanger Institute, Broad Institute of MIT and Harvard, the University of Hong Kong, and their collaborators sequenced the whole genomes of normal stomach lining samples from people with and without gastric cancer.
The team ...
Unique cell shape keeps lymphatic vessels and plant leaves stable
2025-03-19
The cells that make up the walls of the finest of all lymphatic vessels have a lobate, oak leaf-like shape that makes them particularly resilient to changes in fluid volume. A similar cell shape also supports mechanical stability in plants. This has been shown by researchers from Uppsala University in a new article published in the journal Nature.
The lymphatic system consists of a network of lymph vessels that maintains the body’s fluid balance and supports the immune system. The finest of all these lymphatic vessels are called lymph capillaries. They have walls that are made up of just a single layer of lymphatic endothelial ...
New understanding of B cell mutation strategies could have implications for vaccines
2025-03-19
A vaccine's ability to generate long-lasting, high-affinity antibodies hinges on a delicate balance. Upon exposure to a vaccine or pathogen, B cells scramble to refine their defenses, rapidly mutating in hopes of generating the most effective antibodies. But each round of this process is a roll of the genetic dice—every mutation has the potential to improve affinity; far more often, however, it degrades or destroys a functional antibody. How do high-affinity B cells ever beat the odds?
New research now suggests that B cells avoid gambling away good mutations by strategically banking successful ones. As described in Nature, ...