(Press-News.org) Researchers at University of California San Diego School of Medicine, in collaboration with the Prevencasa free clinic in Tijuana, Mexico, have confirmed the presence of xylazine in the illicit drug supply at the U.S.-Mexico border. While xylazine remains less common in the Western U.S., border cities serve as key trafficking hubs and may have higher rates of emerging substances. The findings, published on March 20, 2025 in the Journal of Addiction Medicine, highlight the urgent need for public health intervention.
“Xylazine is a veterinary anesthetic that is not approved for human use and is increasingly detected alongside illicit fentanyl in parts of the United States and Canada,” said senior author Joseph R. Friedman, M.D., Ph.D., a resident physician in the Department of Psychiatry at UC San Diego School of Medicine. “Although xylazine has been most prevalent on the East Coast of the United States, this new evidence confirms its presence in Tijuana, on the U.S.-Mexico border, posing numerous health risks for people in this region.”
The study analyzed de-identified records of 23 users from Prevencasa, examining urine and paraphernalia samples from individuals who reported using illicit opioids within the past 24 hours. Researchers used test strips to screen for xylazine, along with other drugs such as fentanyl, opiates and methamphetamine. Paraphernalia samples were further analyzed using mass spectrometry.
Key findings include:
Xylazine was detected in 82.6% of participant urine samples using Wisebatch test strips and in 65.2% using SAFElife test strips.
Paraphernalia testing confirmed xylazine in 52.2% of samples via mass spectrometry, along with fentanyl (73.9%), fluorofentanyl (30.4%), tramadol (30.4%) and lidocaine (30.4%).
100% of participants’ urine tested positive for fentanyl.
Xylazine is associated with severe health risks, including profound sedation, more complex withdrawal syndromes, and a heightened risk of skin infections and wounds. Given Tijuana’s strategic location as a transit point for illicit drugs entering the U.S., researchers caution that xylazine prevalence could soon rise in Southern California and beyond.
“This study underscores the importance of expanding drug-checking efforts in border regions,” Friedman added. “Our findings also support the use of xylazine test strips as a harm reduction tool, providing people who use drugs and healthcare providers with critical information about exposure risks.”
A previous study published in the Harm Reduction Journal demonstrated that individuals can use fentanyl test strips to check their own drug supply before consumption. While further research is needed to standardize xylazine testing methods, the results highlight the rapidly evolving landscape of drug-checking technologies and the need for public health agencies to adapt accordingly.
Additionally, researchers noted a high prevalence of lidocaine in Tijuana’s illicit fentanyl supply, which may interfere with xylazine test strip accuracy. More studies are needed to understand why lidocaine is being added and how it affects drug-checking reliability.
Larger studies are required to further assess xylazine’s spread and refine testing methods. Researchers advocate for increased surveillance, harm reduction strategies, and clinical awareness to mitigate the emerging risks posed by xylazine in the illicit drug supply.
Additional co-authors on the study include: Alejandro G. Montoya, M.D., Carmina Ruiz, Mariana A. Gonzalez Tejeda, R.N., Luis A. Segovia, B.S. and Lilia Pacheco Bufanda from Prevencasa A.C. in Tijuana. Morgan E. Godvin, B.A. and Chelsea L. Shover, Ph.D. from UCLA Department of Internal Medicine. Edward Sisco, Ph.D., Elise M. Pyfrom, B.S. and Meghan G. Appley, Ph.D. from the National Institute of Standards and Technology.
The study was funded, in part, by the National Institute on Drug Abuse (DA049644) and (K01DA050771) as well as the National Institute of Mental Health (MH101072).
# # #
END
Xylazine detected in U.S.-Mexico border drug supply, study finds
Presence of xylazine in Tijuana raises concerns about health impacts and increased spread into Southern California
2025-03-20
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Producing nuclear fusion fuel is banned in the US for being too toxic, but these researchers found an alternative
2025-03-20
Lithium-6 is essential for producing nuclear fusion fuel, but isolating it from the much more common isotope, lithium-7, usually requires liquid mercury, which is extremely toxic. Now, researchers have developed a mercury-free method to isolate lithium-6 that is as effective as the conventional method. The new method is presented March 20 in the Cell Press journal Chem.
“This is a step towards addressing a major roadblock to nuclear energy,” says chemist and senior author Sarbajit Banerjee of ETH Zürich and Texas A&M University. “Lithium-6 is a critical material for the renaissance of nuclear energy, ...
Adaptive defenses against malicious jumping genes
2025-03-20
Adverse genetic mutations can cause harm and are due to various circumstances. “Jumping genes” are one cause of mutations, but cells try and combat them with a specialized RNA called piRNA. For the first time, researchers from the University of Tokyo and their collaborators have identified how the sites responsible for piRNA production evolve effective behaviors against jumping genes. This research could lead to downstream diagnostic or therapeutic applications.
The word mutation can mean different things in different situations. ...
Cancer antigen 125 levels at time of ovarian cancer diagnosis by race and ethnicity
2025-03-20
About The Study: In this cohort study of patients with ovarian cancer, American Indian and Black patients were 23% less likely to have an elevated cancer antigen (CA)-125 level at diagnosis. Current CA-125 thresholds may miss racially and ethnically diverse patients with ovarian cancer. International guidelines use CA-125 thresholds to recommend which patients with pelvic masses should undergo evaluation by gynecologic oncologists for ovarian cancer. However, CA-125 thresholds were developed from white populations. Work is needed to develop inclusive CA-125 thresholds and ...
Prevalence and severity of astigmatism in children after COVID-19
2025-03-20
About The Study: In this study, lifestyle changes after the pandemic were associated with an increase in the prevalence and severity of child astigmatisms, likely associated with changes in the developing cornea. The potential impact of higher degrees of astigmatism may warrant dedicated efforts to elucidate the relationship between environmental and/or lifestyle factors, as well as the pathophysiology of astigmatism.
Corresponding Authors: To contact the corresponding authors, email Jason C. Yam, MD (yamcheuksing@cuhk.edu.hk) and Li ...
Study: new guidelines expanded access to lung cancer screening, but gaps remain in reaching rural and uninsured populations
2025-03-20
MIAMI, FLORIDA (STRICTLY EMBARGOED UNTIL MARCH 20, 2025, AT 11 A.M. EDT) – Since 2021, when lung cancer screening guidelines began to include younger people and those with a lower smoking history, the number of screenings climbed, but significant gaps remain, especially among people with limited access to healthcare, according to a new study led by researchers at Sylvester Comprehensive Cancer Center, part of the University of Miami Miller School of Medicine.
"The updated guidelines substantially increased lung cancer screenings overall, even as ...
Analysis of new colorectal cancer immunotherapy shows more treatment options
2025-03-20
A team of researchers from Cleveland Clinic Genomic Medicine share insights from an early set of 19,000 patients to receive immune checkpoint inhibitor treatments for colorectal cancer in the U.S.
The report comes from the laboratory of Stephanie Schmit, PhD, MPH, and was published in JAMA Network Open. It serves as an opportunity to better understand how immune checkpoint inhibitor treatments, including PD-1 and PD-L1 inhibitors, work in a larger population that reflects real-world settings. Dr. Schmit collaborated with a team of ...
Scientists use cellular programming to mimic first days of embryonic development
2025-03-20
The earliest days after fertilization, once a sperm cell meets an egg, are shrouded in scientific mystery.
The process of how a humble single cell becomes an organism fascinates scientists across disciplines. For some animals, the entire process of cellular multiplication, generation of specialized cells, and their organization into an ordered multicellular embryo takes place in the protective environment of the uterus, making direct observation and studies challenging. This makes it difficult for scientists to understand what can go wrong during that process, and how specific risk factors and the surrounding environment may prevent ...
Potential targeted therapy for pediatric brain cancer identified by Dana-Farber team
2025-03-20
Boston – An international team of clinical collaborators, led by physician scientists from Dana-Farber Cancer Institute, performed a first-ever clinical test of the targeted therapy avapritinib in pediatric and young patients with a form of high-grade glioma. They found that the drug, already FDA-approved for certain adult cancers, was generally safe and resulted in tumor reduction visible on brain scans, as well as clinical improvement, in 3 out of 7 patients.
The study was published in Cancer Cell.
Pediatric-type high-grade gliomas are currently incurable brain tumors with median survival times less than 18 months after initial diagnosis.
Avapritinib ...
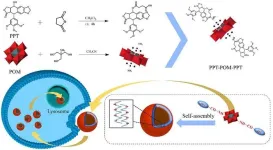
Self-assembled vesicles containing podophyllotoxin covalently modified with polyoxometalates for antitumor therapy
2025-03-20
POMs are a class of inorganic metal-oxygen cluster compounds with broad-spectrum antitumor potential. However, their strong hydrophilicity and poor lipophilicity result in insufficient cell membrane permeability, and high doses are required to achieve therapeutic effects, which severely limits their clinical application. To address this challenge, the research team proposes a covalent modification strategy: the construction of an amphipathic drug molecule PPT-POM-PPT by linking the hydrophobic anti-tumor drug Podophyllotoxin (PPT) with hydrophilic POMs. This molecule ...
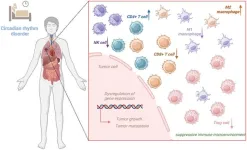
Circadian rhythms in tumor regulation: Impacts on tumor progression and the immune microenvironment
2025-03-20
Circadian rhythms are endogenous time-keeping mechanisms that regulate physiological processes in response to external light-dark cycles. These rhythms are orchestrated by the suprachiasmatic nucleus (SCN) in the hypothalamus and involve a network of genes, including CLOCK and BMAL1, that influence metabolism, immune responses, and cell proliferation. Recent research has highlighted the crucial role of circadian rhythms in tumor biology, demonstrating that their dysregulation contributes to tumorigenesis, progression, and metastasis. Additionally, circadian rhythms influence the tumor immune microenvironment and the ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
How boron helps to produce key proteins for new cancer therapies
Writing the catalog of plasma membrane repair proteins
A comprehensive review charts how psychiatry could finally diagnose what it actually treats
Thousands of genetic variants shape epilepsy risk, and most remain hidden
First comprehensive sex-specific atlas of GLP-1 in the mouse brain reveals why blockbuster weight-loss drugs may work differently in females and males
When rats run, their gut bacteria rewrite the chemical conversation with the brain
Movies reconstructed from mouse brain activity
Subglacial weathering may have slowed Earth's escape from snowball Earth
Simple test could transform time to endometriosis diagnosis
Why ‘being squeezed’ helps breast cancer cells to thrive
Mpox immune test validated during Rwandan outbreak
Scientists pinpoint protein shapes that track Alzheimer’s progression
Researchers achieve efficient bicarbonate-mediated integrated capture and electrolysis of carbon dioxide
Study reveals ancient needles and awls served many purposes
Key protein SYFO2 enables 'self-fertilization’ of leguminous plants
AI tool streamlines drug synthesis
Turning orchard waste into climate solutions: A simple method boosts biochar carbon storage
New ACP papers say health care must be more accessible and inclusive for patients and physicians with disabilities
Moisture powered materials could make cleaning CO₂ from air more efficient
Scientists identify the gatekeeper of retinal progenitor cell identity
American Indian and Alaska native peoples experience higher rates of fatal police violence in and around reservations
Research alert: Long-read genome sequencing uncovers new autism gene variants
Genetic mapping of Baltic Sea herring important for sustainable fishing
In the ocean’s marine ‘snow,’ a scientist seeks clues to future climate
Understanding how “marine snow” acts as a carbon sink
In search of the room temperature superconductor: international team formulates research agenda
Index provides flu risk for each state
Altered brain networks in newborns with congenital heart disease
Can people distinguish between AI-generated and human speech?
New robotic microfluidic platform brings ai to lipid nanoparticle design
[Press-News.org] Xylazine detected in U.S.-Mexico border drug supply, study findsPresence of xylazine in Tijuana raises concerns about health impacts and increased spread into Southern California