NRL's narrow field imager launches on NASA's PUNCH mission
2025-03-20
(Press-News.org) WASHINGTON, D.C. — The U.S. Naval Research Laboratory’s (NRL) Narrow Field Imager (NFI) was launched into space aboard a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket as a part of NASA’s Polarimeter to Unify the Corona and Heliosphere (PUNCH) mission on March 11 and deployed from Falcon 9 on March 12.
PUNCH is a four-satellite constellation, collecting observations in low Earth orbit. It will conduct global, 3D observations of the inner heliosphere to investigate the solar corona's evolution into the solar wind. The mission is scheduled to conduct science for the next two years, following a 90-day commissioning period.
The NRL-developed NFI, sponsored by NASA, is a compact, externally occulted coronagraph. The external occulter blocks direct sunlight from entering the main optical aperture, which views the corona and starfield around the Sun using a compound lens system. Polarization is resolved using a polarizing filter wheel and the image is digitized using a CCD camera with a 2K x 2K active detector area.
NFI will image the transition of the Sun’s atmosphere to the solar wind to understand how the Sun generates the space plasma environment.
"The launch and deployment of NRL's Narrow Field Imager aboard the PUNCH mission marks a significant step forward in our ability to understand the dynamic processes that drive space weather," said NRL Coronal and Heliospheric Physics Section Head Robin Colaninno, Ph.D. "By imaging the transition of the Sun's atmosphere to the solar wind, we're gaining crucial insights that will ultimately improve our ability to predict and mitigate the impacts of these powerful events on Earth and in space."
Predicting the impact of space weather, from minor fluctuations to major coronal mass ejections (CMEs) and corotating interaction regions (CIRs), requires a comprehensive understanding of the solar wind. While originating at the Sun, these events evolve significantly on their journey to Earth, especially within the sparsely imaged region between the solar corona and inner heliosphere, posing a significant scientific challenge.
By capturing the evolution of coronal mass ejections (CMEs), PUNCH will provide scientists new data on their formation and propagation. This is essential for understanding and predicting these events, which can cause significant disruptions on Earth, including satellite damage, radio communication blackouts, and power grid failures. Enhanced predictions will also safeguard robotic explorers operating in interplanetary space.
About the U.S. Naval Research Laboratory
NRL is a scientific and engineering command dedicated to research that drives innovative advances for the U.S. Navy and Marine Corps from the seafloor to space and in the information domain. NRL, located in Washington, D.C. with major field sites in Stennis Space Center, Mississippi; Key West, Florida; Monterey, California, and employs approximately 3,000 civilian scientists, engineers and support personnel.
For more information, contact NRL Corporate Communications at (202) 480-3746 or nrlpao@nrl.navy.mil. Please reference package number at top of press release.
###
END
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2025-03-20
A new study has discovered that birds in the Galápagos Islands are changing their behaviour due to traffic noise, with those frequently exposed to vehicles showing heightened levels of aggression.
Published in the journal Animal Behaviour and led by experts from Anglia Ruskin University (ARU) and the Konrad Lorenz Research Centre at the University of Vienna, the research examined the impact of vehicle noise pollution on Galápagos yellow warblers (Setophaga petechia aureola), a songbird widespread on the archipelago.
The Galápagos Islands, ...
2025-03-20
Groundbreaking Study Finds AI-Driven Interviews with Children May Boost Accuracy in Witness Accounts
In a first-of-its-kind study published in the journal PLOS ONE, an international team of researchers led by scholars from New York University Shanghai and Åbo Akademi University in Turku, Finland explored the potential of artificial intelligence to assist in sensitive child investigative interviews. The study compared how effectively a Large Language Model (LLM), specifically ChatGPT, and untrained human interviewers were able to interview children about a mock event ...
2025-03-20
Welfare measurement is among the most fundamental questions in economics. Policymakers and others use gross domestic product (GDP) as a proxy for welfare, but this application does not reflect the benefits of introducing new and free goods and services, such as digital goods, and may result in misunderstanding the economy.
In a new study, researchers developed a framework to measure the welfare contributions of new and free goods and services and quantify their benefits. By applying the framework to several examples (e.g., Facebook, Smartphone cameras), the study found that these goods and services significantly increase welfare.
The study ...
2025-03-20
March 20, 2025 — Placing an external ventricular drain (EVD) at bedside using augmented reality (AR) guidance is more precise than freehand placement and is associated with fewer reinterventions and complications, according to a clinical pilot study of a novel system. Frederick Van Gestel, MD, a neurosurgery resident at Universitair Ziekenhuis Brussel and PhD researcher at Vrije Universiteit Brussel in Brussels, Belgium, and colleagues report first-in-human results in Neurosurgery, the official publication of the Congress ...
2025-03-20
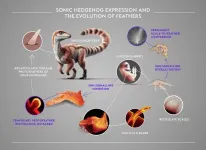
Inhibiting the sonic hedgehog (Shh) pathway strongly perturbs feather development in chickens by restricting feather bud outgrowth, invagination and branching, according to a study published March 20th, in the open-access journal PLOS Biology by Rory Cooper and Michel Milinkovitch from the University of Geneva, Switzerland.
Avian feathers are intricate appendages whose forms vary substantially across species and body areas, and between juvenile and adult stages. Understanding both the developmental and evolutionary mechanisms underpinning this morphological diversity has long fascinated biologists. The morphological intricacies ...
2025-03-20
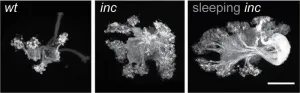
Fruit fly mutants that have severe sleep deficits perform better at olfactory learning and memory tasks, according to a study published March 20th in the open-access journal PLOS Biology by Sheng Huang and Stephan Sigrist from Freie Universität Berlin, Germany, and colleagues. The paradox of enhanced memory despite sleep loss could be explained by protein kinase A (PKA) signaling in the mushroom body of the fly brain.
Sleep is a dynamic process conserved from invertebrates to mammals and humans. Although sleep is thought to serve many purposes, it is often studied for its restorative roles, which ...
2025-03-20
Marine mammals may have a secret weapon to survive long dives – an ability to directly sense their own circulating blood-oxygen levels that most mammals lack – allowing them to stay submerged longer and resurface before hypoxia leads to drowning, researchers report. Air-breathing marine mammals have developed a range of physiological adaptations to survive in aquatic environments, including thermoregulation to endure the pressures of the deep. However, one of the most critical evolutionary challenges for diving mammals is avoiding drowning. Despite adaptations for larger oxygen storage and tolerance to low oxygen levels, these animals still risk drowning if they ...
2025-03-20
Challenging assumptions about infant memory, a novel functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) study shows that babies as young as 12 months old can encode memories, researchers report. The findings suggest that infantile amnesia – the inability to remember our first few years of life – is more likely caused by memory retrieval failures rather than an inability to form memories in the first place. Despite infancy being a period of rapid learning, memories from this time do not persist into later childhood or adulthood. In ...
2025-03-20
Rising mountains do more than reshape the landscape – they also drive evolutionary change, according to a new study. By simulating millions of years of tectonic uplift, researchers have uncovered a link between mountain building and biodiversity, shedding light on how Earth’s dynamic topography shapes biodiversity over deep time. Mountain ranges are widely recognized as global hotspots of terrestrial biodiversity yet only cover a relatively small proportion of the Earth’s surface, suggesting a strong connection between topographic evolution and species diversity. Mountainous terrain can promote speciation by isolating populations, ...
2025-03-20
Challenging long-held assumptions about global terrestrial carbon storage, a new study finds that the majority of carbon dioxide (CO2) absorbed by ecosystems has been locked away in dead plant material, soils, and sediments, rather than living biomass, researchers report. These new insights, which suggest that terrestrial carbon stocks are more resilient and stable than previously appreciated, are crucial for shaping future climate mitigation strategies and optimizing carbon sequestration efforts. Recent studies have shown that terrestrial carbon stocks are increasing, offsetting ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] NRL's narrow field imager launches on NASA's PUNCH mission