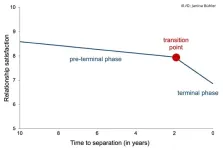
(Press-News.org) The end of a romantic relationship usually does not come out of the blue but is indicated one or two years before the breakup. As the results of a psychological study have demonstrated, the terminal stage of a relationship consists of two phases. First, there is a gradual decline in relationship satisfaction, reaching a transition point one to two years before the dissolution of the relationship. "From this transition point onwards, there is a rapid deterioration in relationship satisfaction. Couples in question then move towards separation," said Professor Janina Bühler from the Institute of Psychology at Johannes Gutenberg University Mainz (JGU). She conducted the corresponding investigation in collaboration with Professor Ulrich Orth of the University of Bern. Their paper was recently published in the Journal of Personality and Social Psychology.
Analysis built on national studies from Germany, Australia, the United Kingdom, and the Netherlands
It is a common fact that satisfaction in a romantic relationship declines over time. This reduction in satisfaction is particularly marked in the first years of a relationship, and a distinctive low point is often reached after a period of ten years. Instead of considering the processes that occur in the time-since-beginning of a romantic relationship, Janina Bühler and Ulrich Orth decided to look at the time-to-separation of relationships for the purposes of their research.
With this in view, they used data from four representative studies conducted in Germany, Australia, the United Kingdom, and the Netherlands. All these countries are WEIRD, i.e., Western, Educated, Industrialized, Educated, Rich, Democratic, and their individuals are free – by law – to decide about their relationship status. For each of the four data sets covering a total of 11,295 individuals there was a control group roughly the same size consisting of couples that had not separated. The surveys in the four countries were conducted over different periods of time, ranging from 12 to 21 years. In the case of Germany, the researchers employed the data of the Panel Analysis of Intimate Relationships and Family Dynamics (pairfam), a multidisciplinary longitudinal study. In all countries, the subjects were asked to specify how satisfied they were right then with their existing romantic relationship.
Using the available data, Bühler and Orth assessed the extent to which the satisfaction with the relationship developed in the light of their subsequent separation. "In order to better understand dissolving relationships, we examined them from the point of view of time-to-separation. To do this, we applied a concept that is in general use in other fields of psychology," said Janina Bühler. Based on the data of the four national representative studies, the researchers were able to determine that relationships can be subjected to what is known as terminal decline. This decline in relationship satisfaction occurs in two phases. The initial preterminal phase, which can have a duration of several years, is characterized by a minor decline in satisfaction. However, this is followed by a transition or tipping point from which there is an accelerated decline in satisfaction. The terminal phase of a relationship after this transition point lasts 7 to 28 months, one to two years on average. "Once this terminal phase is reached, the relationship is doomed to come to an end. This is apparent from the fact that only the individuals in the separation group go through this terminal phase, not the control group," explained Bühler.
Partners assess the terminal phase of a relationship differently
At the same time, the two partners do not experience the transition phase in the same way. The partner who initiates the separation has already become dissatisfied with the relationship at an earlier point in time. For the recipient of the separation, the transition point arrives relatively shortly before the actual separation. They experience a very rapid decline in relationship satisfaction.
"Partners pass through various phases. They do not normally separate from one day to the next, and the way these phases impact on the two partners differs," added Bühler. In many cases, couples seek help too late, i.e., when the transition point has already been reached. "It is thus important to be aware of these relationship patterns. Initiating measures in the preterminal phase of a relationship, i.e., before it begins to go rapidly downhill, may thus be more effective and even contribute to preserving the relationship," concluded Bühler, who also works as a couples therapist.
Recognition by the APS for innovative contributions to the subject
Janina Bühler has been Junior Professor of Personality Psychology and Diagnostics at Mainz University since January 2022. From January 2024, she has headed an Emmy Noether Research Group that investigates the interactions between relationship events and the personalities of partners in a relationship. In February 2025, she was nominated a Rising Star by the Association for Psychological Science (APS). This designation is given to early career researchers whose innovative work has already advanced their field and signals great potential for future contributions.
Related links:
https://www.psychologicalscience.org/members/awards-and-honors/aps-rising-stars/... – New APS Rising Stars
:
https://press.uni-mainz.de/adolescents-today-are-more-satisfied-with-being-singl... – press release "Adolescents today are more satisfied with being single" (25 June 2024)
https://press.uni-mainz.de/new-emmy-noether-junior-research-group-focuses-on-cou... – press release "New Emmy Noether junior research group focuses on couple relationships" (4 Oct. 2023) END
Transition point in romantic relationships signals the beginning of their end
Dissatisfaction in a relationship will inevitably lead to separation at some point / Recent study is based on the concept of terminal decline
2025-03-21
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Scientists witness living plant cells generate cellulose and form cell walls for the first time
2025-03-21
In a groundbreaking study on the synthesis of cellulose – a major constituent of all plant cell walls – a team of Rutgers University-New Brunswick researchers has captured images of the microscopic process of cell-wall building continuously over 24 hours with living plant cells, providing critical insights that may lead to the development of more robust plants for increased food and lower-cost biofuels production.
The discovery, published in the journal Science Advances, reveals a dynamic process never seen before and may provide practical applications for everyday products derived from plants including ...
Mount Sinai-led team identifies cellular mechanisms that may lead to onset of inflammatory bowel disease
2025-03-21
A research team led by Mount Sinai has uncovered mechanisms of abnormal immune cell function that may lead to Crohn’s disease, according to findings published in Science Immunology on March 21. The researchers said their discovery provides better understanding of disease development and could inform the development and design of new therapies to prevent inflammation before it starts in the chronic disorder.
Crohn’s disease is an inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) that causes chronic inflammation of the gastrointestinal (GI) tract, and symptoms can include abdominal ...
SNU-GU researchers jointly develop a liquid robot capable of transformation, separation, and fusion like living cells
2025-03-21
A liquid robot capable of transforming, separating, and fusing freely like living cells has been developed.
Seoul National University College of Engineering announced that a joint research team led by Professor Ho-Young Kim from the Department of Mechanical Engineering, Professor Jeong-Yun Sun from the Department of Materials Science and Engineering, and Professor Keunhwan Park from the Department of Mechanical, Smart, and Industrial Engineering at Gachon University has successfully developed a next-generation ...
Climate warming and heatwaves accelerate global lake deoxygenation, study reveals
2025-03-21
Freshwater ecosystems require adequate oxygen levels to sustain aerobic life and maintain healthy biological communities. However, both long-term climate warming and the increasing frequency and intensity of short-term heatwaves are significantly reducing surface dissolved oxygen (DO) levels in lakes worldwide, according to a new study published in Science Advances.
Led by Prof. SHI Kun and Prof. ZHANG Yunlin from the Nanjing Institute of Geography and Limnology of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, in collaboration with researchers from the Nanjing University and the UK’s ...
Unlocking dopamine’s hidden role: Protective modification of Tau revealed
2025-03-21
Peking University, March 19, 2025: The research group led by Prof. Wang Chu from the College of Chemistry and Molecular Engineering at Peking University published a research article entitled “Quantitative Chemoproteomics Reveals Dopamine’s Protective Modification of Tau” in Nature Chemical Biology (DOI:10.1038/s41589-025-01849-9). Using a novel quantitative chemoproteomic strategy, the team uncovered a protective role of dopamine (DA) in regulating the function of the microtubule-associated protein Tau. This discovery deepens our understanding of dopamine’s physiological and pathological roles in the human brain.
Why it matters:
1. Dopamine, ...
New drug therapy combination shows promise for advanced melanoma patients
2025-03-21
A federally funded research team led by Sheri Holmen, PhD, investigator at Huntsman Cancer Institute and professor in the Department of Surgery at the University of Utah (the U), is testing a new combination drug therapy that could both treat and prevent melanoma metastasis, or spreading from its original site, to the brain.
“Once melanoma has spread to the brain, it’s very hard to treat. Metastasis to the brain is one of the main causes of death from melanoma,” says Holmen. “We wanted to find a solution to an unmet clinical need for those patients who had no other treatment options ...
Nature’s warriors: How rice plants detect and defend against viral invaders
2025-03-21
Peking University, March 20, 2025: A groundbreaking study led by Li Yi, professor at the School of Life Sciences, was published in Nature on March 12, titled “Perception of viral infections and initiation of antiviral defence in rice”, uncovering a molecular mechanism by which rice cells perceive viral infections and initiate antiviral response, which significantly contributes to understanding of virus-host interactions for further disease resistance breeding.
Why it matters:
Viruses affecting rice, a staple food for more than half of the world population, pose ...
How the brain responds to prices: Scientists discover neural marker for price perception
2025-03-21
Russian scientists have discovered how the brain makes purchasing decisions. Using electroencephalography (EEG) and magnetoencephalography (MEG), researchers found that the brain responds almost instantly when a product's price deviates from expectations. This response engages brain regions involved in evaluating rewards and learning from past decisions. Thus, perceiving a product's value is not merely a conscious choice but also a function of automatic cognitive mechanisms. The results have been published in Frontiers in Human Neuroscience.
Every day, people are faced with prices of food, technology, and services. Sometimes, a product seems overpriced, ...
Boosting brain’s waste removal system improves memory in old mice
2025-03-21
As aging bodies decline, the brain loses the ability to cleanse itself of waste, a scenario that scientists think could be contributing to neurodegenerative conditions such as Alzheimer’s disease and Parkinson’s disease, among others. Now, researchers at Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis report they have found a way around that problem by targeting the network of vessels that drain waste from the brain. Rejuvenating those vessels, they have shown, improves memory in old mice.
The study, published online March 21 in the journal Cell, lays the groundwork to develop therapies for age-related cognitive decline that overcome ...
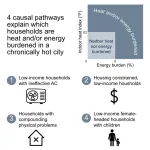
New study sheds light on risks from residential heat and energy burdens in Miami
2025-03-21
A new study on indoor extreme heat connects these two burdens to reveal how the co-occurrence of escalating energy bills and dangerously hot homes in Miami-Dade County exacerbates health and well-being risks for vulnerable households across months of the year.
“Our findings help us understand which types of households are struggling with high indoor heat and high energy bills in a place like Miami, which is hot for many months of the year,” said Lynée Turek-Hankins, the lead author of the study that was conducted during her doctoral studies at the University of Miami Rosenstiel School of Marine, Atmospheric, and Earth Science and the Abess Center for Ecosystem ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Scientists discover why we know when to stop scratching an itch
A hidden reason inner ear cells die – and what it means for preventing hearing loss
Researchers discover how tuberculosis bacteria use a “stealth” mechanism to evade the immune system
New microscopy technique lets scientists see cells in unprecedented detail and color
Sometimes less is more: Scientists rethink how to pack medicine into tiny delivery capsules
Scientists build low-cost microscope to study living cells in zero gravity
The Biophysical Journal names Denis V. Titov the 2025 Paper of the Year-Early Career Investigator awardee
Scientists show how your body senses cold—and why menthol feels cool
Scientists deliver new molecule for getting DNA into cells
Study reveals insights about brain regions linked to OCD, informing potential treatments
Does ocean saltiness influence El Niño?
2026 Young Investigators: ONR celebrates new talent tackling warfighter challenges
Genetics help explain who gets the ‘telltale tingle’ from music, art and literature
Many Americans misunderstand medical aid in dying laws
Researchers publish landmark infectious disease study in ‘Science’
New NSF award supports innovative role-playing game approach to strengthening research security in academia
Kumar named to ACMA Emerging Leaders Program for 2026
AI language models could transform aquatic environmental risk assessment
New isotope tools reveal hidden pathways reshaping the global nitrogen cycle
Study reveals how antibiotic structure controls removal from water using biochar
Why chronic pain lasts longer in women: Immune cells offer clues
Toxic exposure creates epigenetic disease risk over 20 generations
More time spent on social media linked to steroid use intentions among boys and men
New study suggests a “kick it while it’s down” approach to cancer treatment could improve cure rates
Milken Institute, Ann Theodore Foundation launch new grant to support clinical trial for potential sarcoidosis treatment
New strategies boost effectiveness of CAR-NK therapy against cancer
Study: Adolescent cannabis use linked to doubling risk of psychotic and bipolar disorders
Invisible harms: drug-related deaths spike after hurricanes and tropical storms
Adolescent cannabis use and risk of psychotic, bipolar, depressive, and anxiety disorders
Anxiety, depression, and care barriers in adults with intellectual and developmental disabilities
[Press-News.org] Transition point in romantic relationships signals the beginning of their endDissatisfaction in a relationship will inevitably lead to separation at some point / Recent study is based on the concept of terminal decline