(Press-News.org)
A study in Alzheimer’s & Dementia, a leading journal in dementia research, has demonstrated the high accuracy of plasma p-tau217 as a blood-based biomarker for detecting abnormal brain beta-amyloid (Aβ) pathology, a hallmark of Alzheimer’s disease (AD). More significantly, the study validates its effectiveness even in individuals with cerebrovascular disease (CeVD), which is highly prevalent in Asian populations. This finding can enhance early diagnosis, improve patient risk stratification, and facilitate better clinical management of AD in diverse populations.
The study was led by Dr Mitchell Lai, Senior Lecturer at the Department of Pharmacology, Yong Loo Lin School of Medicine, National University of Singapore (NUS Medicine), in collaboration with local and international experts from the National University Health System (NUHS), University of Gothenburg, Institute of Neurology at University College London, and Banner Sun Health Research Institute.
Bridging gaps in Alzheimer’s research for Asia
While blood biomarkers like p-tau217 have been extensively studied in Western populations—where CeVD is less common—this study uniquely focuses on a Singapore-based cohort, reflective of broader Asian demographics with a high CeVD burden. The results confirm that higher plasma p-tau217 levels correlate with faster cognitive decline, reinforcing its role not just as a diagnostic tool but also as a potential predictor of disease progression.
Transforming Alzheimer’s diagnosis: A potential game-changer for clinical practice
Potential clinical applications include:
Earlier and more precise detection: Plasma p-tau217 provides a highly sensitive and specific method for identifying Alzheimer’s pathology before severe cognitive decline occurs, potentially enabling earlier intervention and monitoring.
A simpler, minimally invasive diagnostic tool: Unlike costly and invasive positron emission tomography (PET) scans and cerebrospinal fluid tests, a blood-based biomarker could be easily integrated into routine clinical practice, making Alzheimer’s screening more accessible and scalable.
Patient risk stratification for optimised, personalised care: Adding plasma p-tau217 to routine clinical assessments allows doctors to efficiently categorise individuals into low, intermediate, and high-risk groups for Aβ pathology, enabling tailored follow-up strategies and potential early therapeutic interventions for patients.
Professor Christopher Chen, Director of the Memory, Ageing and Cognition Centre at NUHS and co-author of the study, said “This study provides strong evidence that plasma p-tau217 could be a game-changer for early detection of AD brain changes in Asian populations with high CeVD burden. A blood-based biomarker like p-tau217 brings us closer to a more accessible approach to diagnosing and managing AD in Singapore and beyond”.
Dr Joyce Chong, a Research Fellow with the Department of Pharmacology, NUS Medicine, and first author of the study, added “Although blood biomarkers are not expected to replace the current gold standard in clinical measures such as amyloid PET, their greatest value may lie in providing a cost-effective, minimally-invasive screening and risk-stratification tool to help reduce the proportion of individuals requiring confirmatory PET scans.”
Looking forward, the team hopes to expand the study both in the length of follow-up, as well as the diversity of investigated biomarkers. Dr Lai said, “There is increasing awareness that dementia is a chronic condition arising from complex, interacting processes, especially in our population where CeVD is likely to be an important contributor to the cognitive impairments associated with AD. Our long-term goal is to be able to produce a panel of multi-modal, clinically useful biomarkers which can both suggest novel therapeutic targets as well as help in the diagnosis and prognosis of this debilitating condition.”
END
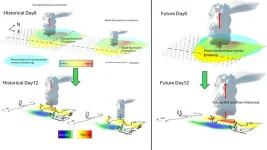
The monsoon rains have long remained the lifeblood of India, providing the lion’s share of the water used for drinking and irrigation. The yearly arrival of the rains, which quenches the thirst of the harsh summers, is caused by the movement of cloud bands from the equator towards the north.
A recent study from the Indian Institute of Science (IISc) has shown that contrary to previous understanding, the strength of the cloud band plays a key role in its movement as well as the density of rains that the Indian subcontinent receives during the wet spells of the monsoon.
India receives 80% ...
Two researchers from the Keck School of Medicine of USC have been elected as senior members of the National Academy of Inventors (NAI), an organization that recognizes inventors holding US patents and promotes academic technology and innovation to benefit society.
The newly elected senior members are Preet Chaudhary, MD, PhD, professor of medicine and the Ronald H. Bloom Family Chair in Lymphoma Research, and Michael Selsted, MD, PhD, professor of pathology.
“Professors Chaudhary and Selsted are nationally known for their entrepreneurial research, and I’m thrilled to see them acknowledged with this ...
● Records of more than 170,000 lung cancer patients combined with chest x-ray rates from 7,400 GP practices were analysed in the new research led by the University of Sheffield
● The study, published in the British Journal of General Practice, shows link between the frequency of chest x-rays and earlier diagnosis and improved survival
● Lung cancer is the leading cause of cancer deaths globally
A groundbreaking study has revealed a significant link between the frequency of chest x-ray referrals from GPs ...
Polarisation in lower-income countries largely flows from economic and material issues, while social topics and identity-related debates are the most polarising subjects in richer nations, new research reveals.
The study from City St George’s, University of London analysed 40 years of global data to explore how modernisation influences ideological divides, shedding light on the factors driving ideological polarisation across different nations around the world.
As political divisions deepen in many countries, the study clarifies the complex, multifaceted implications ...
Abu Dhabi, UAE, March 24, 2025: Researchers from NYU Abu Dhabi’s Advanced Microfluidics and Microdevices Laboratory (AMMLab) have developed an innovative sensing system that restores the missing tactile feedback in minimally invasive surgery (MIS), enhancing precision, ease of use, and safety. The new "off-the-jaw" system integrates force and angle sensors into the handle of laparoscopic tools, providing surgeons with real-time measurements of grasping forces and insights into tissue stiffness and thickness.
Minimally invasive surgery (MIS) involves small incisions, reducing ...
BACKGROUND
Urinary tract infections (UTIs) rank among the most prevalent bacterial infections globally. Traditional urine culture methods have significant limitations in detection time and sensitivity, prompting the need to evaluate targeted next-generation sequencing (tNGS) as a potential diagnostic tool.
METHODS
The study included a discovery cohort of 400 suspected UTI patients (202 analyzed) and a validation cohort of 200 patients (110 analyzed). The study assessed detection time, concordance rates, ability to identify polymicrobial infections, and antibiotic resistance genes (ARGs). Both clear and turbid ...
Embargoed for release until 5:00 p.m. ET on Monday 24 March 2025
Follow @Annalsofim on X, Facebook, Instagram, threads, and Linkedin
Below please find summaries of new articles that will be published in the next issue of Annals of Internal Medicine. The summaries are not intended to substitute for the full articles as a source of information. This information is under strict embargo and by taking it into possession, media representatives are committing to the terms of the embargo not only on their own behalf, but also on behalf of the ...
Original Research
Family-Based Lifestyle Intervention Improves Weight Management and Cardiovascular Health Among High-Risk Patients
Background and Goal: The PROgramme of Lifestyle Intervention in Families for Cardiovascular risk reduction (PROLIFIC) Study, conducted in India, aimed to assess whether a family-based approach to lifestyle interventions could improve weight management and obesity-related health outcomes among individuals with a family history of premature coronary heart disease.
Study Approach: In this cluster ...
Original Research
Background and Goal: Regular follow-up visits are critical for managing chronic conditions, yet some primary care clinics achieve higher visit regularity than others. This study aimed to identify specific strategies used by high-performing clinics to promote consistent follow-up visits for adults with chronic conditions.
Study Approach: This qualitative study used semi-structured interviews with 15 primary care physicians, 12 nurses, 15 administrative staff, and 4 pharmacists from 12 clinics—half with high temporal regularity (patients attending follow-ups consistently) and half with low temporal regularity, identifying strategies that helped high–temporal ...
Original Research
Background and Goal: This study focuses on how primary care patients balance the trade-off between continuity of care and access to timely appointments. It examines whether patients prefer to wait longer to see their own primary care physician (PCP) or prefer to see another clinician for faster care.
Study Approach: Researchers analyzed data from a cross-sectional online survey of adult primary care patients in Michigan. Patients were presented with scenarios in the survey for different visit types—annual checkups, chronic and mental health follow-ups, ...