(Press-News.org) The MIT Press is proud to release our 2025 Impact Report for Direct to Open (D2O), our sustainable framework for open access monographs that shifts publishing from a solely market-based purchase model where individuals and libraries buy single eBooks, to a collaborative, library-supported open access model.
The continued growth in the reach of open access publishing couldn’t be more timely. In 2025, access to truth and facts are under attack, and democratizing access to trustworthy, peer-reviewed information has never been more important. In the face of so many forces working against the spread of knowledge, Direct to Open continues to be a critical tool.
To date, Direct to Open has funded the open publication of 320 books. On average, our open access Humanities and Social Sciences books are used 2.26 times more and receive 8% more citations than their non-open counterparts. Our open access STEAM books are used 1.6 times more and receive 5% more citations than their non-open counterparts. Our Direct to Open titles are immediately accessible around the world upon publication, and drastically lower barriers to access for global readers—reaching the communities that need this scholarship most.
“At a time when access to reliable, peer-reviewed knowledge is more critical than ever, Direct to Open continues to prove that collaboration can drive meaningful change in scholarly publishing,” said Amy Harris, senior manager of library relations and sales at the MIT Press. “We are grateful to the hundreds of libraries that have joined us in expanding the public knowledge commons, ensuring that groundbreaking ideas reach the widest possible audience and make a lasting impact.”
Our 2025 Direct to Open Impact Report reveals some key additional statistics on our open access monographs and the Direct to Open program:
As of February 2025, Direct to Open titles have received 705,000 total reads.
D2O titles have two times the amount of use as compared to our non-open access books.
13 library consortia and 407 libraries have participated in the program.
Read the full 2025 Impact Report for more information, including testimonials from authors and library partners. For details on how your institution might participate in or support Direct to Open, please visit mitpress.mit.edu/D2O or contact the MIT Press library relations team at mitp-library-relations@mit.edu.
Media Contact
Rachel Aldrich
Marketing Manager
The MIT Press
raldrich@mit.edu
About the MIT Press
Established in 1962, The MIT Press is one of the largest and most distinguished university presses in the world and a leading publisher of books and journals at the intersection of science, technology, art, social science, and design.
END
The MIT Press releases 2025 Direct to Open (D2O) Impact Report
This year’s Direct to Open (D2O) Impact Report reveals the global reach of open access publishing at a time when the academy itself faces unprecedented challenges
2025-03-27
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
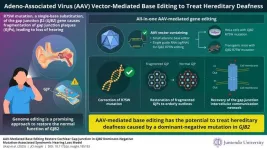
New study reveals the curative potential of genome editing approach for genetic deafness
2025-03-27
Congenital hearing loss refers to impaired auditory function that occurs due to genetic causes. GJB2 is the gene responsible for approximately half of all cases of hereditary hearing loss. Connexin 26 (CX26), which is encoded by GJB2, helps in the formation of intercellular gap junctions—channels that allow for the movement of ions and chemical messenger molecules between adjacent cells, where it regulates auditory function.
GJB2 mutations often lead to fragmentation of gap junctions and gap junction plaques (GJPs) which are composed ...
AAAS elects Keck School of Medicine of USC molecular biologist Yali Dou as 2025 fellow
2025-03-27
Molecular biologist Yali Dou, PhD, holder of the Marion and Harry Keiper Chair in Cancer Research and professor of medicine and cancer biology at the Keck School of Medicine of USC, has been elected a fellow of the American Association for the Advancement of Science (AAAS). She is one of seven USC faculty members in the 2025 cohort of new fellows.
The AAAS is the world’s oldest and largest general science organization and the publisher of Science, a top peer-reviewed academic journal. Election as a fellow is a lifetime honor — one of the AAAS’s ...
Damaging cluster of UK winter storms driven by swirling polar vortex miles above Earth
2025-03-27
University of Leeds news
Embargoed until 10:00 GMT, 27 March
Damaging cluster of UK winter storms driven by swirling polar vortex miles above Earth
Powerful winter storms which led to deaths and power outages in the UK and Ireland were made more likely by an intense swirling vortex of winds miles above the Arctic, say scientists.
A team of researchers led by the University of Leeds has pinpointed a new reason for winter storm clusters such as the trio named Dudley, Eunice and Franklin, which hit the nation within the space of a week in February 2022.
The findings which are published today in the journal ...
Losing forest carbon stocks could put climate goals out of reach
2025-03-27
In the past, intact forests absorbed 7.8 billion tonnes of CO₂ annually – about a fifth of all human emissions – but their carbon storage is increasingly at risk from climate change and human activities such as deforestation. A new study from the Potsdam Institute for Climate Impact Research (PIK) shows that failing to account for the potentially decreasing ability of forests to absorb CO₂ could make reaching the Paris agreement targets significantly harder, if not impossible, and much more costly.
“Delaying action leads to disproportionately higher costs,” explains Michael Windisch, ...
From weight to wellness: New database transforms obesity research
2025-03-27
A new medical database automatically compiles the medical records of obese patients and those suffering from obesity-related diseases in a uniquely comprehensive and reliable manner. The initiative, led by Kobe University, offers valuable insights for health promotion and drug development.
“Obesity is at the root of many diseases,” says OGAWA Wataru, an endocrinologist at Kobe University. Obesity has been linked to the development of diabetes, hypertension, gout, coronary heart disease, stroke and many other diseases. Monitoring, treating and preventing obesity and the diseases it can cause is therefore not only good for ...
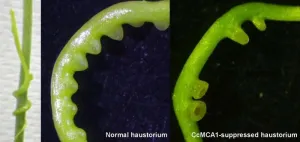
Nature’s viny vampire: Discovering what drives parasitic Cuscuta campestris
2025-03-27
The parasitic vine Cuscuta campestris grows by latching onto the stems and leaves of plants and inserting organs called haustorium into the host plant tissues to draw nutrients. The haustorium is formed when ion channels in the cell membrane are stimulated during coiling and induce a reaction within the cell.
Further, Cuscuta campestris has many types of ion channels, but which ones were linked to the development of haustorium were previously unknown.
“For the first time, the genes involved in sensing ...
How calcium may have unlocked the origins of life’s molecular asymmetry
2025-03-27
A new study led by researchers at the Earth-Life Science Institute (ELSI) at Institute of Science Tokyo has uncovered a surprising role for calcium in shaping life’s earliest molecular structures. Their findings suggest that calcium ions can selectively influence how primitive polymers form, shedding light on a long-standing mystery: how life’s molecules came to prefer a single “handedness” (chirality).
Like our left and right hands, many molecules exist in two mirror-image forms. Yet life on Earth has a striking preference: ...
Study finds long Covid patients feel pressure to prove their illness is real
2025-03-27
People living with Long Covid often feel dismissed, disbelieved and unsupported by their healthcare providers, according to a new study from the University of Surrey.
The study, which was published in the Journal of Health Psychology, looked at how patients with Long Covid experience their illness. The study found that many patients feel they have to prove their illness is physical to be taken seriously and, as a result, often reject psychological support, fearing it implies their symptoms are "all in the mind".
Professor ...
Smartwatches may help control diabetes through exercise
2025-03-27
Wearable mobile health technology could help people with Type 2 Diabetes (T2D) to stick to exercise regimes that help them to keep the condition under control, a new study reveals.
Researchers studied the behaviour of recently-diagnosed T2D patients in Canada and the UK as they followed a home-based physical activity programme – some of whom wore a smartwatch paired with a health app on their smartphone.
They discovered that MOTIVATE-T2D participants were more likely to start and maintain purposeful exercise at if they had the support of wearable technology- the study successfully recruited 125 participants with an 82% ...
Fossils: Ancient parasitic ‘Venus flytrap’ wasp preserved in amber
2025-03-27
An extinct lineage of parasitic wasps dating from the mid-Cretaceous period and preserved in amber may have used their Venus flytrap-like abdomen to capture and immobilise their prey. Research, published in BMC Biology, finds that the specimens of Sirenobethylus charybdis — named for the sea monster in Greek mythology which swallowed and disgorged water three times a day — date from almost 99 million years ago and may represent a new family of insects.
The morphology of S. charybdis indicates the wasps were ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
When safety starts with a text message
CSIC develops an antibody that protects immune system cells in vitro from a dangerous hospital-acquired bacterium
New study challenges assumptions behind Africa’s Green Revolution efforts and calls for farmer-centered development models
Immune cells link lactation to long-lasting health
Evolution: Ancient mosquitoes developed a taste for early hominins
Pickleball players’ reported use of protective eyewear
Changes in organ donation after circulatory death in the US
Fertility preservation in people with cancer
A universal 'instruction manual' helps immune cells protect our organs
Fifteen-year results from SWOG S0016 trial suggest follicular lymphoma is curable
The breasts of a breastfeeding mother may protect a newborn from the cold – researchers offer a new perspective on breast evolution
More organ donations now come from people who die after their heart stops beating
How stepping into nature affects the brain
Study: Cancer’s clues in the bloodstream reveal the role androgen receptor alterations play in metastatic prostate cancer
FAU Harbor Branch awarded $900,000 for Gulf of America sea-level research
Terminal ileum intubation and biopsy in routine colonoscopy practice
Researchers find important clue to healthy heartbeats
Characteristic genomic and clinicopathologic landscape of DNA polymerase epsilon mutant colorectal adenocarcinomas
Start school later, sleep longer, learn better
Many nations underestimate greenhouse emissions from wastewater systems, but the lapse is fixable
The Lancet: New weight loss pill leads to greater blood sugar control and weight loss for people with diabetes than current oral GLP-1, phase 3 trial finds
Pediatric investigation study highlights two-way association between teen fitness and confidence
Researchers develop cognitive tool kit enabling early Alzheimer's detection in Mandarin Chinese
New book captures hidden toll of immigration enforcement on families
New record: Laser cuts bone deeper than before
Heart attack deaths rose between 2011 and 2022 among adults younger than age 55
Will melting glaciers slow climate change? A prevailing theory is on shaky ground
New treatment may dramatically improve survival for those with deadly brain cancer
Here we grow: chondrocytes’ behavior reveals novel targets for bone growth disorders
Leaping puddles create new rules for water physics
[Press-News.org] The MIT Press releases 2025 Direct to Open (D2O) Impact ReportThis year’s Direct to Open (D2O) Impact Report reveals the global reach of open access publishing at a time when the academy itself faces unprecedented challenges