(Press-News.org) Mpox has the potential to become a significant global health threat if taken too lightly, according to scientists at the University of Surrey.
In a letter published in Nature Medicine, researchers highlight how mpox – traditionally spread from animals to humans – is now showing clear signs of sustained human-to-human transmission.
Mpox is a viral infection caused by a virus that belongs to the same family as smallpox. The virus can cause a painful rash, fever, and swollen glands and, in some cases, lead to more serious illness. Mpox usually spreads through close contact with an infected person or animal.
Carlos Maluquer de Motes, Reader in Molecular Virology at the University of Surrey, said:
“The most recent outbreaks show that intimate contact is now a significant way the virus spreads. That shift in how it’s transmitted is leading to longer transmission chains and lasting outbreaks.”
The article notes that this change coincided with the rapid spread of clade IIb (a clade is a group of viruses that share a common ancestor) mpox viruses, but different clade I variants are now on the rise too. Researchers are also concerned because clade I viruses are thought to be more aggressive. These viruses appear to be accumulating specific genetic mutations – driven by enzymes in the human body – that may be changing viral properties, so the longer these viruses circulate amongst us, the higher the chances these mutations help mpox adapt to humans.
Although mpox was once mainly seen in Central Africa, the virus caused an outbreak worldwide in 2022 and is now causing outbreaks in multiple sub-Saharan countries. While it currently affects adults the most, the researchers stress that it has the potential to spread among other groups, including children, a group at greater risk of serious illness – although sustained transmission in children has not yet been reported.
Dr Maluquer de Motes added:
“Mpox control has to climb up the global health agenda. We have limited diagnostic tools and even fewer antiviral treatments. We urgently need better surveillance and local or regional capacity to produce what we need – otherwise, we are at risk of future epidemics.”
Unlike smallpox, mpox has an animal reservoir, meaning it can’t be fully eradicated. The authors warn that unless international action is taken now – including investment in point-of-care testing and new treatments – mpox will continue to re-emerge and threaten global health.
END
Mpox could become a serious global threat, scientists warn
2025-04-01
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Combination immunotherapy shrank a variety of metastatic gastrointestinal cancers
2025-04-01
A new form of tumor infiltrating lymphocyte (TIL) therapy, a form of personalized cancer immunotherapy, dramatically improved the treatment’s effectiveness in patients with metastatic gastrointestinal cancers, according to results of a clinical trial led by researchers at the National Institutes of Health (NIH). The findings, published April 1, 2025 in Nature Medicine, offer hope that this therapy could be used to treat a variety of solid tumors, which has so far eluded researchers developing cell-based ...
Newborn warty birch caterpillars defend the world’s smallest territory
2025-04-01
Real estate is precious. Some creatures defend territories extending over several kilometres, but when Jayne Yack (Carleton University, Canada) encountered miniature newborn warty birch caterpillars (Falcaria bilineata) she wondered if she might have discovered one of the world’s smallest, and youngest, territorial critters. ‘We had noticed that tiny warty birch caterpillars produced vibrations’, says Yack, who first encountered the feisty little creatures in 2008. She also noticed that the tiny caterpillars – 1 to 2 mm long – reside in solitude on birch leaves, making her speculate whether they ...
Exposure to air pollution in childhood is associated with reduced brain connectivity
2025-04-01
A new study led by the Barcelona Institute for Global Health (ISGlobal), a centre supported by the "la Caixa" Foundation, has found that children exposed to higher levels of air pollution in early and mid childhood have weaker connections between key brain regions. The findings, published in Environment International, highlight the potential impact of early exposure to air pollution on brain development.
The research showed reduced functional connectivity within and between certain cortical and subcortical brain networks. These networks are systems of interconnected brain structures that work together to perform different cognitive functions, such as thinking, perceiving and controlling ...
Researchers develop test using machine learning to help predict immunotherapy response in lymphoma patients
2025-04-01
LOS ANGELES — Researchers with City of Hope, one of the largest and most advanced cancer research and treatment organizations in the United States, with its National Medical Center in Los Angeles ranked among the nation’s top 5 cancer centers by U.S. News & World Report, and MSK have created a tool that uses machine learning to assess a non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL) patient’s likely response to chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T cell therapy before starting the treatment, according to study results published today in Nature Medicine.
CAR T cell therapy ...
New UNSW research reveals dramatically higher loss of GDP under 4°C warming
2025-04-01
New projections by the UNSW Institute for Climate Risk & Response (ICRR) reveal a 4°C rise in global temperatures would cut world GDP by around 40% by 2100 – a stark increase from previous estimates of around 11%.
The recently-published analysis fixes an oversight in the current economic model underpinning global climate policy, toppling previous carbon benchmarks.
The results support limiting global warming to 1.7 °C, which is in line with significantly faster decarbonisation goals like the Paris Agreement, and far lower than the 2.7°C supported ...
Discovery of Quina technology challenges view of ancient human development in East Asia
2025-03-31
While the Middle Paleolithic period is viewed as a dynamic time in European and African history, it is commonly considered a static period in East Asia. New research from the University of Washington challenges that perception.
Researchers discovered a complete Quina technological system — a method for making a set of tools — in the Longtan site in southwest China, which has been dated to about 50,000 to 60,000 years ago. Quina technology was found in Europe decades ago but has never before been found in East Asia.
The team published its findings March ...
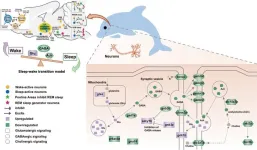
Whales and dolphins sleep by turning off one half of their brains at a time; scientists discover more about the genes and pathways that enable this phenomenon
2025-03-31
Whales and dolphins sleep by turning off one half of their brains at a time; scientists discover more about the genes and pathways that enable this phenomenon.
####
Article URL: https://plos.io/4c9g5gm
Article Title: Evolution of canonical circadian clock genes underlies unique sleep strategies of marine mammals for secondary aquatic adaptation
Author Countries: China
Funding: This work was supported by the National Key Research and Development (R&D) Program of China (grant no. 2022YFF1301600) to G.Y. & S.X., the Key Project ...
A new clue to how multicellular life may have evolved
2025-03-31
Life emerged on Earth some 3.8 billion years ago. The “primordial soup theory” proposes that chemicals floating in pools of water, in the presence of sunlight and electrical discharge, spontaneously formed organic molecules. These building blocks of life underwent chemical reactions, likely driven by RNA, eventually leading to the formation of single cells.
But what sparked single cells to assemble into more complex, multicellular life forms?
Nature Physics published a new insight about a possible driver of this key step in evolution — the fluid ...
ALL ALS consortium launches website to advance ALS research
2025-03-31
ALL ALS Consortium Launches Website to Advance ALS Research
The Access for All in ALS (ALL ALS) Consortium announced the launch of its official website, creating a central hub for information about its initiatives and clinical research studies. ALL-ALS.org is designed to inform and engage researchers, clinicians, and current and prospective study participants.
The ALL ALS Consortium formed in fall 2023 with funding from the National Institutes of Health (NIH). The consortium consists of 35 clinical sites in the United States and Puerto Rico, led by researchers at Barrow Neurological Institute in Phoenix, Arizona and Massachusetts ...
Many TB cases may have gone undetected in prisons in Europe and the Americas during COVID-19
2025-03-31
EMBARGOED UNTIL 6:30 P.M. EST on Monday, March 31, 2025
Contact:
Jillian McKoy, jpmckoy@bu.edu
Michael Saunders, msaunder@bu.edu
##
Many TB Cases May Have Gone Undetected in Prisons in Europe and the Americas During COVID-19
A new study found that reported diagnoses for tuberculosis were consistently lower than expected throughout the pandemic, even though incarceration rates remained largely consistent and TB detection among the general population managed to reverse after an early-pandemic decline.
Incarcerated populations have a high risk of developing tuberculosis ...