(Press-News.org) DALLAS, April 1, 2025 — A New York City-based physician scientist who explores ways to improve health by looking at the ways in which cells and molecules impact disease and an epidemiologist from Baltimore who has devoted her career to identifying ways to improve screening, diagnosis and patient care for people with diabetes are the most recent American Heart Association Merit Award recipients. Over the next five years, each researcher will receive a total of $1 million in funding from the Association, a global force changing the future of health for all.
The American Heart Association’s Merit Award is one of the most prestigious competitive research awards given by the Association, the largest non-government funder of cardiovascular research in the United States. The Merit Award supports scientists who have consistently performed highly promising, novel research with the potential to move cardiovascular science forward quickly, with high impact. The recipients of the 2025 award are:
Ann Marie Schmidt, M.D., the Dr. Iven Young Professor of Endocrinology in the Department of Medicine, the Holman Division of Endocrinology, Diabetes and Metabolism and a professor in the Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Pharmacology and the Department of Pathology at NYU Grossman School of Medicine in New York City; and
Elizabeth (Liz) Selvin, Ph.D., M.P.H., FAHA, Director of the Welch Center for Prevention, Epidemiology and Clinical Research and a professor of epidemiology at the Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health in Baltimore. She holds a joint appointment in the Division of General Internal Medicine, Department of Medicine at the Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine.
“Each year, the American Heart Association recognizes recipients of the Merit Awards as investigators with established track records of success in major research challenges in the areas of cardiovascular and cerebrovascular health. Their scientific exploration has the potential to produce unusually high impact toward the Association’s mission to be a relentless force for a world of longer, healthier lives,” said Keith Churchwell, M.D., FAHA, American Heart Association volunteer president, an associate clinical Professor of Medicine at Yale School of Medicine in New Haven, Connecticut and adjunct Associate Professor of Medicine at the Vanderbilt School of Medicine, Nashville, Tennessee. “Diabetes is one of the major controllable risk factors for cardiovascular disease and as prevalence of both conditions rise, it’s become imperative that we learn all we can about the ways they’re connected. This year’s recipients are already renowned for their work in identifying the important connections between cardiovascular disease and diabetes and I’m excited to see where their future exploration will take us in learning how to better manage these chronic conditions that take the lives of too many people each year.”
Schmidt’s research will focus on the large white blood cells that are part of the body's immune system and are known to contribute to diabetic complications. Her research team will expand on their discovery of a protein molecule called the ‘receptor for advanced glycation end products’ (RAGE) that may be one of the ways that diabetic white blood cells damage the body. Studying diabetic and non-diabetic mouse and human white blood cells, the team will look for ways to disrupt this damaging molecular process and, in turn, potentially develop new treatment therapies.
“Diabetes damages the body head-to-toe and this happens slowly over many years. We know people with diabetes have more strokes, heart attacks, heart failure, blindness and kidney problems, yet the reasons for this connection are not fully known,” Schmidt said. “We surmise that learning how large white blood cells in diabetes cause damage will show us new ways to stop their bad actions and decrease harm to the body. As diabetes robs people of good health and years of life, our work may help to fulfill the American Heart Association mission to improve health, especially for people with diabetes.”
Selvin’s research will focus on improving cardiovascular health in people with diabetes. Her seminal studies on the association between hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c) and diabetes complications helped establish the scientific foundation and clinical criteria for using HbA1c to diagnose diabetes. This Merit Award will support new research focusing on wearable continuous glucose monitors and their association with cardiometabolic risk in people with type 1 and type 2 diabetes.
“An important part of our work will be providing opportunities for trainees to engage in research with direct implications for policy and clinical practice,” Selvin said. “Helping to grow the next generation of scientists is critical to our ongoing work to save lives through improvements in the screening, diagnosis and treatment of diabetes and cardiovascular disease.”
Funding scientific research and discovery through initiatives like the annual merit awards is a cornerstone of the century-old American Heart Association’s lifesaving mission. The Association has now funded more than $5.9 billion of scientific research since 1949, making it the single largest non-government supporter of heart and brain health research in the U.S. New knowledge resulting from this funding continues to save lives and directly impact millions of people in every corner of the U.S. and around the world.
About the American Heart Association
The American Heart Association is a relentless force for a world of longer, healthier lives. Dedicated to ensuring equitable health in all communities, the organization has been a leading source of health information for more than one hundred years. Supported by more than 35 million volunteers globally, we fund groundbreaking research, advocate for the public’s health, and provide critical resources to save and improve lives affected by cardiovascular disease and stroke. By driving breakthroughs and implementing proven solutions in science, policy, and care, we work tirelessly to advance health and transform lives every day. Connect with us on heart.org, Facebook, X or by calling 1-800-AHA-USA1.
END
NYC, Baltimore research scientists receive grants to study cardiovascular/diabetes connection
The American Heart Association’s 2025 Merit Award winners each receive $1 million research grants to expand their scientific exploration of the connections and complications of cardiovascular disease and diabetes
2025-04-01
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
AI propaganda: prolific and persuasive
2025-04-01
A study of the use of AI by a Russian-backed propaganda outlet shows how AI allows propagandists to increase their production capacity without any loss in persuasive power. In December 2023, journalists at the BBC and Clemson University’s Media Forensics Hub published an investigation revealing that the site DCWeekly.org was a Russian propaganda outlet, part of a broader network disseminating pro-Kremlin and anti-Ukrainian narratives. Morgan Wack and colleagues found that prior to September 20, 2023, much of the content on the site was simply lifted from other right-leaning outlets. After that date, however, the stories were generally rewritten by AI, allowing the site to use a broader ...
An efficient self-assembly process for advanced self-healing materials
2025-04-01
Polysiloxane materials, such as polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS)-based elastomers, exhibit a self-healing capability by the introduction of silanolate (Si–O–) groups. This ability stems from their dynamic siloxane (Si–O–Si) bonds, which can break and reform to repair damage. Their self-healing properties could make them valuable in applications like protective coatings for use in various fields, such as optics, electronics, and aerospace.
To improve the properties of PDMS-based materials, they have been combined with inorganic fillers such as nanoparticles or nanosheets. Generally, the introduction of nanosheets into polymers leads to the formation of ...
Study reveals stark racial disparities in IBD care across the united states
2025-04-01
New York, NY – April 1, 2025- A study published today in the American Journal of Gastroenterology reveals significant disparities in healthcare utilization among racial and ethnic groups with inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) in the United States. The research, funded by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), led by investigators from the University of Pennsylvania, the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, and the Crohn's & Colitis Foundation provides crucial insights into the challenges faced by underrepresented communities ...
Break the sedentary cycle: National Walking Day can kickstart healthier routines
2025-04-01
DALLAS, April 1, 2025 — Sedentary behavior has become a national health crisis, with 1 in 4 U.S. adults sitting for more than eight hours a day, increasing their risk for heart disease, stroke, and mental health challenges, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. To help people move more, the American Heart Association, a global force changing the future of health of all, invites communities nationwide to walk together on Wednesday, April 2.
Adopting healthier routines doesn’t have to be intimidating or overwhelming according to Eduardo Sanchez MD, MPH, FAHA, the ...
Researchers develop new way to match young cancer patients with the right drugs
2025-04-01
A pan-Canadian team has developed a new way to quickly find personalized treatments for young cancer patients, by growing their tumours in chicken eggs and analyzing their proteins.
The team, led by researchers from the University of British Columbia and BC Children’s Hospital Research Institute, is the first in Canada to combine these two techniques to identify and test a drug for a young patient's tumour in time for their treatment.
Their success in finding a new drug for the patient, described today in EMBO Molecular Medicine, shows how the study of proteins, known as proteomics, ...
New 3D technology paves way for next-generation eye-tracking
2025-04-01
Eye tracking plays a critical role in the latest virtual and augmented reality headsets and is an important technology in the entertainment industry, scientific research, medical and behavioral sciences, automotive driving assistance and industrial engineering. Tracking the movements of the human eye with high accuracy, however, is a daunting challenge.
Researchers at the University of Arizona Wyant College of Optical Sciences have now demonstrated an innovative approach that could revolutionize eye-tracking ...
Diagnosing a dud may lead to a better battery
2025-04-01
It’s (going to be) electric.
But how soon? How quickly our society can maximize the benefit of electrification hinges on finding cheaper, higher performance batteries — a reality closer to hand through new research from Virginia Tech.
A team of chemists led by Feng Lin and Louis Madsen found a way to see into battery interfaces, which are tight, tricky spots buried deep inside the cell. The research findings were published on April 1 in the journal Nature Nanotechnology.
“There are major, longstanding challenges at the interfaces,” ...
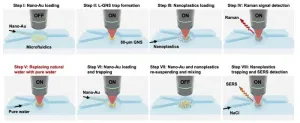
We know nanoplastics are a threat—this new tool can help us figure out just how bad they are
2025-04-01
April 1, 2025
AMHERST, Mass. – While the threat that microplastics pose to human and ecological health has been richly documented and is well known, nanoplastics, which are smaller than one micrometer (1/50th the thickness of an average human hair), are far more reactive, far more mobile and vastly more capable of crossing biological membranes. Yet, because they are so tiny and so mobile, researchers don’t yet have an accurate understanding of just how toxic these particles are. The first step to understanding the toxicology of nanoplastics is to build a reliable, ...
Mpox could become a serious global threat, scientists warn
2025-04-01
Mpox has the potential to become a significant global health threat if taken too lightly, according to scientists at the University of Surrey.
In a letter published in Nature Medicine, researchers highlight how mpox – traditionally spread from animals to humans – is now showing clear signs of sustained human-to-human transmission.
Mpox is a viral infection caused by a virus that belongs to the same family as smallpox. The virus can cause a painful rash, fever, and swollen glands and, in some cases, lead to more serious illness. Mpox usually spreads through ...
Combination immunotherapy shrank a variety of metastatic gastrointestinal cancers
2025-04-01
A new form of tumor infiltrating lymphocyte (TIL) therapy, a form of personalized cancer immunotherapy, dramatically improved the treatment’s effectiveness in patients with metastatic gastrointestinal cancers, according to results of a clinical trial led by researchers at the National Institutes of Health (NIH). The findings, published April 1, 2025 in Nature Medicine, offer hope that this therapy could be used to treat a variety of solid tumors, which has so far eluded researchers developing cell-based ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
GLP-1 drugs associated with reduced need for emergency care for migraine
New knowledge on heritability paves the way for better treatment of people with chronic inflammatory bowel disease
Under the Lens: Microbiologists Nicola Holden and Gil Domingue weigh in on the raw milk debate
Science reveals why you can’t resist a snack – even when you’re full
Kidney cancer study finds belzutifan plus pembrolizumab post-surgery helps patients at high risk for relapse stay cancer-free longer
Alkali cation effects in electrochemical carbon dioxide reduction
Test platforms for charging wireless cars now fit on a bench
$3 million NIH grant funds national study of Medicare Advantage’s benefit expansion into social supports
Amplified Sciences achieves CAP accreditation for cutting-edge diagnostic lab
Fred Hutch announces 12 recipients of the annual Harold M. Weintraub Graduate Student Award
Native forest litter helps rebuild soil life in post-mining landscapes
Mountain soils in arid regions may emit more greenhouse gas as climate shifts, new study finds
Pairing biochar with other soil amendments could unlock stronger gains in soil health
Why do we get a skip in our step when we’re happy? Thank dopamine
UC Irvine scientists uncover cellular mechanism behind muscle repair
Platform to map living brain noninvasively takes next big step
Stress-testing the Cascadia Subduction Zone reveals variability that could impact how earthquakes spread
We may be underestimating the true carbon cost of northern wildfires
Blood test predicts which bladder cancer patients may safely skip surgery
Kennesaw State's Vijay Anand honored as National Academy of Inventors Senior Member
Recovery from whaling reveals the role of age in Humpback reproduction
Can the canny tick help prevent disease like MS and cancer?
Newcomer children show lower rates of emergency department use for non‑urgent conditions, study finds
Cognitive and neuropsychiatric function in former American football players
From trash to climate tech: rubber gloves find new life as carbon capturers materials
A step towards needed treatments for hantaviruses in new molecular map
Boys are more motivated, while girls are more compassionate?
Study identifies opposing roles for IL6 and IL6R in long-term mortality
AI accurately spots medical disorder from privacy-conscious hand images
Transient Pauli blocking for broadband ultrafast optical switching
[Press-News.org] NYC, Baltimore research scientists receive grants to study cardiovascular/diabetes connectionThe American Heart Association’s 2025 Merit Award winners each receive $1 million research grants to expand their scientific exploration of the connections and complications of cardiovascular disease and diabetes