(Press-News.org)
Urban trees and plants do more than just beautify city landscapes. They purify the air, reduce urban heat islands, provide recreational spaces, and even boost property values. As essential components of sustainable urban ecosystems, plants silently contribute to our well-being. However, urban trees face many threats, including pests, diseases, and climate change, making it essential to keep their health in check.
Urban greenery monitoring has traditionally been a very labor-intensive process, requiring botanical expertise and considerable resources. With cities expanding worldwide and urban environments becoming more complex, keeping track of plant health has also become more difficult. Could artificial intelligence (AI) hold the key to addressing this challenge?
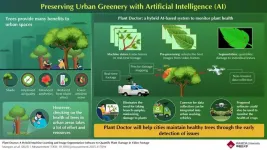
In a recent study, a joint research team led by Professor Umezu's Laboratory from the Department of Life Science and Medical Bioscience at Waseda University and Professor Shiojiri's Laboratory from the Faculty of Agriculture at Ryukoku University developed an innovative AI-driven solution for monitoring plant health. Their paper was published online in the journal Measurement on February 22, 2025, and will be published in Volume 249, on May 31, 2025. This study introduces ‘Plant Doctor,’ a hybrid AI system that automatically diagnoses urban tree health through video footage captured by ordinary cameras. “Machine vision techniques such as segmentation have great applications in the medical field. We wanted to extrapolate this technology to other areas, such as plant health,” says first author Marques, explaining their motivation.
Plant Doctor combines two cutting-edge machine vision algorithms—YOLOv8 and DeepSORT—to identify and track individual leaves across video frames. The goal of these algorithms is to ensure that only the best images for each leaf are selected for further processing. Then, a third algorithm, called DeepLabV3Plus, performs detailed image segmentation to precisely quantify leaf damage. The proposed system can automatically detect diseased areas on individual leaves, such as spots caused by bacteria, pests, and fungi.
One of the most attractive aspects of this approach is its scalability and cost efficiency. The system can process video footage collected by cameras mounted not only on drones but also on city maintenance vehicles like garbage trucks, turning routine services into opportunities to gather data without investing substantial resources. Moreover, by using images rather than actual branches and leaves, Plant Doctor minimizes stress on city plants. “We have provided a tool for botanical experts to assess plant health in one solution without the need to gather samples and damage the plants in the process,” remarks Marques. The research team validated the proposed system using footage of urban plants in Tokyo, obtaining favorable results and remarkably accurate leaf health diagnoses across various urban flora.
By combining plant health data with accurate location information, Plant Doctor enables both a micro-level analysis of individual plants and macro-level insights into disease patterns across urban areas. Worth noting, beyond urban applications, Plant Doctor could also be adapted for agricultural use, helping farmers monitor crop health and identify diseases before they spread.
Overall, the proposed technology represents a significant step toward more sustainable urban and rural plant health monitoring, allowing botanical experts to focus more on strategic interventions rather than routine monitoring. Let us hope these efforts lead to cities and fields with healthier plants!
***
Reference
DOI: 10.1016/j.measurement.2025.117094
Authors: Marc Josep Montagut Marques1, Liu Mingxin2, Kuri Thomas Shiojiri3, Tomika Hagiwara4, Kayo Hirose5, Kaori Shiojiri6, and Shinjiro Umezu1,7
Affiliations
1Department of Integrative Bioengineering, Waseda University
2Department of Modern Mechanical Engineering, Waseda University
3Kyoto Prefecture Momoyama High School
4Department of Biology, Faculty of Science, Kyushu University
5Department of Anesthesiology and Pain Relief Center, The University of Tokyo Hospital
6Department of Agriculture, Ryukoku University
7Space neo Inc.
About Waseda University
Located in the heart of Tokyo, Waseda University is a leading private research university that has long been dedicated to academic excellence, innovative research, and civic engagement at both the local and global levels since 1882. The University has produced many changemakers in its history, including nine prime ministers and many leaders in business, science and technology, literature, sports, and film. Waseda has strong collaborations with overseas research institutions and is committed to advancing cutting-edge research and developing leaders who can contribute to the resolution of complex, global social issues. The University has set a target of achieving a zero-carbon campus by 2032, in line with the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) adopted by the United Nations in 2015.
To learn more about Waseda University, visit https://www.waseda.jp/top/en
About Mr. Marc Josep Montagut Marques
Marc Josep Montagut Marques is a PhD student and currently working as a Laboratory Research Assistant at Waseda University. He currently specializes in perovskite solar cells, cyborg insects, and medical sensors; his previous line of research also included opto engineering, sensor integration, and nanofabrication.
END
UPTON, N.Y. — High temperatures and ionizing radiation create extremely corrosive environments inside a nuclear reactor. To design long-lasting reactors, scientists must understand how radiation-induced chemical reactions impact structural materials. Chemists at the U.S. Department of Energy’s (DOE) Brookhaven National Laboratory and Idaho National Laboratory recently performed experiments showing that radiation-induced reactions may help mitigate the corrosion of reactor metals in a new type of reactor cooled by molten salts. Their findings are published in the journal Physical ...
Danish researchers, in collaboration with the Danish Football Association, have released a White Paper that describes football as an effective recipe in the prevention and treatment of lifestyle-related diseases.
The White Paper entitled Football as Prevention and Treatment - A White Paper Focusing on 10 Non-Communicable Diseases and Risk Factors – compiles and presents research and practical experience from over 20 years of implementing recreational football training in Denmark and several other countries.
The authors also provide best practice ...
Research Highlights:
New research suggests that participating in at least 150 minutes of moderate to vigorous physical activity in just two days had similar health benefits as distributing the activity throughout the week.
People who followed the “weekend warrior” approach, condensing physical activity into one or two days each week, had a significantly lower risk of death from all causes, cardiovascular disease and cancer, similar to those who engaged in activity throughout the week.
The study ...
CNIO researchers discover that, in mice that eat a lot of fat, cancer cells travelling through the blood surround themselves with platelets, which act as an armor-like protection as they spread.
In addition, in animals with a fatty diet it is easier for tumor cells to 'nest' in other organs and give rise to metastasis of the primary tumor.
“These results anticipate a future in which dietary changes, together with the control of platelet activity, will complement antitumor treatments,” says Héctor Peinado, of the Spanish National Cancer Research Center (CNIO).
The study is published ...
Applied physicists at the Harvard John A. Paulson School of Engineering and Applied Sciences (SEAS) have created a photon router that could plug into quantum networks to create robust optical interfaces for noise-sensitive microwave quantum computers.
The breakthrough is a crucial step toward someday realizing modular, distributed quantum computing networks that leverage existing telecommunications infrastructure. Comprising millions of miles of optical fiber, today’s fiber-optic networks send information between computing clusters as pulses ...
NEW YORK, NY (April 2, 2025)--
April 2, 2025—An AI tool that analyzes nurses’ data and notes detected when patients in the hospital were deteriorating nearly two days earlier than traditional methods and reduced the risk of death by over 35%, found a year-long clinical trial of more than 60,000 patients led by researchers at Columbia University.
The new AI tool, CONCERN Early Warning System, uses machine learning to analyze nursing documentation patterns to predict when a hospitalized patient is deteriorating before the change is reflected in vital signs, allowing for timely, life-saving ...
An AI model trained on large amounts of genetic data can predict whether bacteria will become antibiotic-resistant. The new study shows that antibiotic resistance is more easily transmitted between genetically similar bacteria and mainly occurs in wastewater treatment plants and inside the human body.
"By understanding how resistance in bacteria arises, we can better combat its spread. This is crucial to protect public health and the healthcare system's ability to treat infections," says Erik Kristiansson, Professor at the Department of Mathematical Sciences at Chalmers University of Technology and the University of Gothenburg in Sweden.
Antibiotic ...
EMBARGOED UNTIL 09:00 BST WEDNESDAY 2 APRIL
Tinker Tots: A Citizen Science Project to Explore Ethical Dilemmas in Embryo Selection
Researchers at the University of Oxford, University of Exeter, and the National University of Singapore Yong Loo Lin School of Medicine present a new, interactive study.
Oxford, 2 April 2025: When choosing an embryo for implantation during in vitro fertilization (IVF), would you consider its chances of developing a health condition? What about traits like creativity, intelligence, ...
Beekeepers in the United States lost more than 55 percent of managed colonies last year—the highest loss rate since the Apiary Inspectors of America began determining them in 2011. A new study from University of Vermont scientists and international collaborators supports a novel method for testing hygienic behavior in honey bees that could promote breeding more disease resistant colonies in the future.
“Beekeepers are losing bees at a rate that they say is unsustainable,” says Samantha Alger, director of the Vermont Bee Lab at the UVM and lead author of the study. “In the ‘80s, beekeepers lost colonies ...
Building multifamily housing in California is more than twice as expensive as it is in Texas, with much of the difference driven by state and local policies that contribute to long permitting and construction timelines, and higher local development fees, according to a new RAND report based on cost information from more than 100 completed apartment projects.
The high cost of housing and its associated effect on homelessness is a defining policy issue in California.
The cost of building multifamily housing is 2.3 times higher in California than Texas and 1.5 times higher than in Colorado, ...