Development of a novel modified selective medium cefixime–tellurite-phosphate-xylose-rhamnose MacConkey agar for isolation of Escherichia albertii and its evaluation with food samples
2025-04-11
(Press-News.org)
Since cefixime and tellurite are known to inhibit most bacteria belonging to Enterobacterales, we found that addition of tellurite inhibited E. albertii growth in Luria Bertani broth but not in tryptic soy broth (TSB), and addition of phosphate and soy peptone enhanced E. albertii growth in TSB in presence of tellurite.
Subsequently, to find the positive factor present in TSB, E. albertii growth was examined in tryptone, soy peptone, glucose, or phosphate deficient tryptic soy agar plates. Phosphate, soy peptone, and/or glucose deficiency indeed decreased E. albertii growth. However, none of the substances are specifically present in xylose-rhamnose-melibiose (XRM)-MacConkey agar and thus, not affecting E. albertii growth.
Altogether, a novel E. albertii selective differential medium, XRM-MacConkey medium containing cefixime (C), tellurite (T), phosphate (P), and soy peptone (S) (named CT-PS-XR-MacConkey medium), which differentiate E. albertii (colorless) from E. coli (red) by colony color, has been developed.
The CT-PS-XR-MacConkey agar was evaluated with 156 bacterial strains including 65 E. albertii. While all E. albertii strains grew as colorless colonies, 54 strains of 9 different genera belonging to 19 different species were unable to grow on this medium. However, the rest of these bacterial strains grew either as colorless or as red colonies.
Furthermore, spiking experiments using chicken meat as food samples showed that the CT-PS-XR-MacConkey medium is highly selective for E. albertii than XRM-MacConkey agar.
Altogether, the results suggest that the CT-PS-XR-MacConkey agar is indeed a useful selective medium for isolation of E. albertii from food samples.
###
About OMU
Established in Osaka as one of the largest public universities in Japan, Osaka Metropolitan University is committed to shaping the future of society through “Convergence of Knowledge” and the promotion of world-class research. For more research news, visit https://www.omu.ac.jp/en/ and follow us on social media: X, Facebook, Instagram, LinkedIn.
END
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2025-04-11
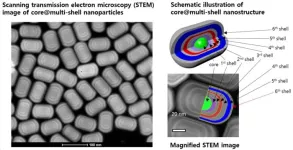
Dr. Ho Seong Jang and colleagues at the Extreme Materials Research Center at the Korea Institute of Science and Technology (KIST) have developed an upconversion nanoparticle technology that introduces a core@multi-shell nanostructure, a multilayer structure in which multiple layers of shells surround a central core particle, and enables high color purity RGB light emission from a single nanoparticle by adjusting the infrared wavelength.
Luminescent materials are materials that light up on their own and are used in a variety of display devices, including TVs, tablets, monitors, and smartphones, to allow us to view a variety of images ...
2025-04-11
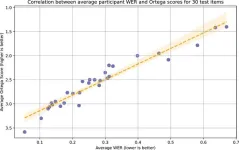
In today’s increasingly interconnected world, language learning has become essential for education, business, and cultural exchange. However, accurately measuring proficiency in language learners is a complex matter. One particularly valuable approach involves asking learners to listen to sentences and then repeat them back as accurately as possible. Known as elicited imitation (EI), this method reveals much more than mere memory and mimicking abilities. When sentences exceed our working memory capacity—typically beyond 8 to 10 syllables—successful repetition requires learners to quickly process and ...
2025-04-10
The persistent higher rate of alcohol deaths in England since the pandemic in 2020 is an “acute crisis” requiring urgent action from government, according to a new study led by researchers at UCL and the University of Sheffield.
For the study, published in Lancet Public Health, researchers analysed Office for National Statistics (ONS) figures of deaths caused solely by alcohol in England. They found that death rates were stable between 2009 and 2019, but increased by a fifth in 2020, rising by a further 13.5% between 2020 and 2022.
The team estimated that 3,911 more people had died solely because of alcohol in England ...
2025-04-10
Decarbonisation in the automotive and housing sectors is paramount if the UK’s legally binding commitment to achieving net zero by 2050 is to succeed, say researchers at University of Sheffield
Exploring the presence of socioeconomic inequalities in the uptake of low-carbon technologies (LCTs), such as solar panels and electric vehicles, has important policy implications for the decarbonisation in the UK
The new report advocates for interventions at an individual, as well as community-level, to help those from more disadvantaged backgrounds adopt technologies that ...
2025-04-10
TAMPA, Fla. (Apr. 10, 2025) — A multi-institutional study led by Moffitt Cancer Center found that percutaneous hepatic perfusion using a melphalan hepatic delivery system may help patients with a rare eye cancer that has spread to their liver. This disease, known as metastatic uveal melanoma, is traditionally very hard to treat and usually has poor outcomes.
The phase 3 FOCUS trial, published in the Annals of Surgical Oncology, compared two treatments for metastatic uveal melanoma. One group of patients received the melphalan hepatic delivery system treatment, while the other group received standard of care treatment. Patients treated with the melphalan hepatic delivery ...
2025-04-10
MINNEAPOLIS —The American Academy of Neurology (AAN), the world’s largest association of neurologists and neuroscience professionals, has elected Natalia S. Rost, MD, MPH, FAAN, FAHA, as its 39th president. Rost is professor of neurology at Harvard Medical School in Boston, and the C. Miller Fisher Endowed Chair in Stroke Research and former chief of the stroke division at Massachusetts General Hospital. Rost succeeds Carlayne E. Jackson, MD, FAAN, who completed her two-year term as president during the recent AAN Annual Meeting.
“I applaud Dr. Jackson for her leadership, and I am thrilled to take the helm at the American Academy of Neurology ...
2025-04-10
Charlottesville, VA — The Center for Open Science (COS) has announced the launch of the Replicability Project: Health Behavior (RPHB), a collaborative initiative that aims to strengthen the evidence base and advance scientific integrity in health-related research. The project will examine the replicability of a diverse sample of quantitative health studies published over the past decade (2015–2024).
Assessing the credibility of research is essential to advancing scientific integrity and maintaining public trust in science. The RPHB initiative aims to perform up to 60+ replications of empirical health behavior studies, providing crucial ...
2025-04-10
CHICAGO – The American Association for Cancer Research (AACR)-Cancer Research Institute (CRI) Lloyd J. Old Award in Cancer Immunology will be presented to Crystal L. Mackall, MD, Fellow of the AACR Academy, during the AACR Annual Meeting 2025, to be held April 25-30 at the McCormick Place Convention Center in Chicago, Illinois.
Mackall is the Ernest and Amelia Gallo Family Professor and Professor of Pediatrics and Medicine at Stanford University, the founding director of the Stanford Center for Cancer Cell Therapy, and director of the Parker Institute for Cancer Immunotherapy at Stanford. She is being honored for her illustrious contributions to cancer immunotherapy, including ...
2025-04-10
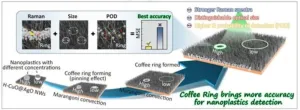
A new publication from Opto-Electronic Advances; DOI 10.29026/oea.2025.240260 discusses a novel strategy for detecting trace-level nanoplastics in aquatic environments.
Plastic materials have revolutionized human lifestyles through their versatile applications, yet their environmental legacy now presents critical challenges to global ecosystems and public health. Current models estimate annual plastic influx into aquatic systems at 4.8-12.7 million metric tonnes, with projections suggesting cumulative marine plastic accumulation ...
2025-04-10
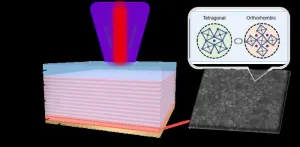
A new publication from Opto-Electronic Advances; DOI 10.29026/oea.2025.240220, discusses how phase-change perovskite enables traditional VCSEL to achieve low-threshold, tunable single-mode lasers.
As an important light source, lasers are widely used in many fields such as communications, medical treatment, display technology and scientific research. However, with the continuous advancement of technology, people have put forward higher requirements on the performance of lasers, especially in terms of integration and tunability. Traditional lasers typically rely on fixed gain media and external microcavity structures (such as Fabry-Perot cavities, ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Development of a novel modified selective medium cefixime–tellurite-phosphate-xylose-rhamnose MacConkey agar for isolation of Escherichia albertii and its evaluation with food samples