Learning about social interaction by studying dancing
Brain activity that enables people to align their movements with others is present only when dancers move to the beat of the same song and can see each other.
2025-04-14
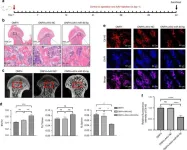
(Press-News.org) Dancing fluidly with another involves social coordination. This skill entails aligning movements with others while also processing dynamic sensory information, like sounds and visuals. In a new JNeurosci paper, Félix Bigand and Giacomo Novembre, from the Italian Institute of Technology, Rome, and colleagues report their findings on how the brain drives social coordination during dance.
The researchers recruited pairs of inexperienced dancers and recorded their brain activity, whole-body movements, and muscle activity as they danced to the same or different songs. The researchers also manipulated whether dancers could or could not see each other. These methods unveiled distinct neural signals for music processing, self-generated movements, movements generated by following a partner, and social coordination. Neural signals for social coordination that enabled synchronized movements between people occurred only when dancers were moving to the same song and could see each other. Says Bigand, “What was perhaps most peculiar was we found that out of the 15 different movements we recorded, the brain was most sensitive to bouncing or flexing of the knees [during social coordination]. This was strange because bouncing had relatively weak amplitudes [or strength] compared to most of the other movements. For the brain to respond more to a weaker movement, like bounce, suggests it has a unique role in social coordination.”
According to the authors, this work advances our understanding of social interaction beyond dancing because it sheds light on how the brain supports socially engaging activities while integrating dynamic sensory information. Bigand also emphasizes that the methods used to unravel distinct neural signals for different kinds of sensory information processing may improve the applicability of future preclinical work to reality.
###
Please contact media@sfn.org for full-text PDF.
About JNeurosci
JNeurosci was launched in 1981 as a means to communicate the findings of the highest quality neuroscience research to the growing field. Today, the journal remains committed to publishing cutting-edge neuroscience that will have an immediate and lasting scientific impact, while responding to authors' changing publishing needs, representing breadth of the field and diversity in authorship.
About The Society for Neuroscience
The Society for Neuroscience is the world's largest organization of scientists and physicians devoted to understanding the brain and nervous system. The nonprofit organization, founded in 1969, now has nearly 35,000 members in more than 95 countries.
END
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2025-04-14
A recent study has uncovered a potential breakthrough in treating osteonecrosis of the femoral head (ONFH), a debilitating bone disease that causes severe pain and joint collapse. Researchers have discovered that exosomes derived from M2 macrophages-derived exosomes (M2-Exos) can significantly improve bone regeneration by modulating neutrophil extracellular traps (NETs) and endothelial cell function. These tiny vesicles, packed with miR-93-5p, were shown to reduce harmful NETs formation and enhance ...
2025-04-14
New DNA probes allow for efficient surveying of the hidden lives of squids and octopuses in the deep sea. This development by Kobe University provides an effective tool for marine ecological research and conservation efforts.
Squids and octopuses eat and are eaten, and in between that they move around a lot. “Cephalopods play an important role in marine ecosystems, contributing to the distribution of energy and nutrients in the food web,” explains Kobe University marine ecologist WU Qianqian. And while for ecological research it is therefore essential to know about the distribution ...
2025-04-14
Patients with depression who received the Moodivate app saw clinically meaningful reductions in their symptoms that were twice those achieved with standard-of-care therapy in a clinical trial conducted at 22 primary care practices in Charleston, South Carolina. App users were also 3 times more likely to achieve a clinically meaningful improvement in their depression and 2.3 times more likely to attain depression remission. Moodivate (available on both iOS and Android) is a digital version of behavioral activation, a type of behavioral therapy that has proved effective against depression. Jennifer Dahne, Ph.D., professor in the Department of Psychiatry and Behavioral ...
2025-04-14
Ottawa, ON, April 14, 2025 – Individuals with an emergency department (ED) visit or hospitalization due to cannabis were at 23% and 72% greater risk of a new dementia diagnosis within five years compared to individuals with an ED visit or hospitalization for any other reason or the general population, according to a new study published in JAMA Neurology.
“Long-term and heavy cannabis use has been associated with memory problems in midlife along with changes in brain structure associated with dementia,” says Dr. Daniel Myran, a Canada Research Chair in Social ...
2025-04-14
The immune system must be able to quickly attack invaders like viruses, while also ignoring harmless stimuli, or allergies can result. Immune cells are known to ignore or “tolerate” molecules found on the body’s own healthy cells, for instance, as well as nonthreatening substances from outside the body like food. How the system achieves the latter has been unclear.
Now, a new study led by researchers at NYU Langone Health has revealed that a special group of cells in the intestines tamp down the immune responses caused by exposure to food proteins. ...
2025-04-14
About The Study: This study found that at current utilization and radiation dose levels, computed tomography examinations in 2023 were projected to result in approximately 103,000 future cancers over the course of the lifetime of exposed patients. If current practices persist, computed tomography-associated cancer could eventually account for 5% of all new cancer diagnoses annually.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Rebecca Smith-Bindman, MD, email rebecca.smith-bindman@ucsf.edu.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamainternmed.2025.0505)
Editor’s ...
2025-04-14
About The Study: The findings of this cohort study suggest that the incidence of pancreatic adenocarcinoma has increased among all age groups, whereas that of colorectal adenocarcinoma has increased among younger age groups. Clinicians should be aware of this trend when evaluating younger patients with relevant symptoms.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Arvind J. Trindade, MD, email arvind.trindade@gmail.com.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2025.4682)
Editor’s Note: Please see the article for additional ...
2025-04-14
About The Study: In this cross-sectional study of children ages 9 to 10, moderately preterm birth was associated with long-term cognitive problems independent of socioeconomic status, genetics, and other risk factors. These findings underscore the need for continued follow-up of all preterm children, with particular focus on those born before 34 weeks’ gestational age, because they may face greater developmental challenges over time.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Samson Nivins, PhD, email samson.nivins@ki.se.
To ...
2025-04-14
New York, NY [April 14, 2025]—A new multicenter study by researchers at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, in collaboration with the National Cancer Institute-funded Clinical Proteomic Tumor Analysis Consortium (CPTAC) and colleagues around the world, has discovered that the genes we are born with—known as germline genetic variants—play a powerful, underappreciated role in how cancer develops and behaves.
Published in the April 14 online issue of Cell [https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2025.03.026], the study is the first to detail how millions of inherited genetic differences influence the activity of thousands of proteins within tumors. Drawing on data ...
2025-04-14
The number of California teens who have been treated for self-harm has ballooned in recent years, with an especially concerning increase among multiracial girls, according to new research from the University of California, Berkeley, published today (Monday, April 14) in JAMA Pediatrics.
Using data from California emergency departments and inpatient care facilities from 2005 to 2021 — 231,232 reports in total — researchers examined both how the rate of annual nonfatal self-harm incidents has changed, as well as rate differences based on age, sex, and race and ethnicity.
The study ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Learning about social interaction by studying dancing
Brain activity that enables people to align their movements with others is present only when dancers move to the beat of the same song and can see each other.