(Press-News.org) Herndon, VA, March 25, 2025 -- About two million people in the United States lack access to running water or indoor plumbing in their homes. Another 30 million people live where drinking water systems violate safety rules. Water privatization -- the transfer of public water systems ownership and/or management to private companies -- has been proposed as a potential solution to provide more Americans with safe, clean drinking water. But opponents argue that private companies may prioritize profits over public needs.
To investigate how private vs. public water systems affect water quality and equal access to safe, clean water, researchers mapped the distribution of water system ownership, water system violations, and water injustice nationwide. Their findings are published in the journal Risk Analysis.
The study is the first to integrate geospatial mapping of water violations, social vulnerability, and, importantly, perceptions of water access in relation to public versus private ownership of water systems on a national scale.
“Policymakers can use our findings to identify and prioritize enforcement efforts in hotspots, make improvements in infrastructure, and implement policies that ensure affordable and safe drinking water - particularly for socially vulnerable communities,” says lead author Alex Segrè Cohen, assistant professor of science and risk communication at the University of Oregon. “We found that violations and risks of water injustice tend to cluster in specific areas or hotspots across the country.”
Here are some of the key findings:
• The top 10 counties with the highest ranking for water violations were in West Virginia, Pennsylvania, North Carolina, and Oklahoma.
• The highest number of violations reported by a single water system was a public system owned by a local government in Wyoming county, West Virginia.
• The top 10 counties with the highest ranking for water injustice were in Mississippi (8 out of the 10), South Dakota, and Texas.
• Hotspots of water injustice were more often located in areas with lower private system ownership. (This suggests that public water systems are not necessarily better at preventing violations, according to the authors).
• Living in a county with both high water injustice and a higher proportion of privatized water systems was associated with a greater concern or perception of vulnerability around water access and security - with concerns about water accessibility, safety, and reliability.
Water system violations include failures to comply with regulations under the Safe Drinking Water Act, including health-based violations such as exceeding maximum levels of contaminants, non-compliance with mandated water treatment techniques, and failure to follow monitoring schedules and communicate required information to customers.
The researchers define water injustice as the unequal access to safe and clean drinking water that disproportionately impacts low-income households and people of color.
They devised a county-level score based on the performance of local drinking water systems (based on data from the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency’s (EPA’s) Safe Drinking Water Information System (SDWIS) and community social vulnerability (using the U.S. Center for Disease Control’s (CDC’s) Environmental Justice Index). These data were merged with a nationally representative survey of U.S. residents (collected in 2019) that measured how people rated their access to drinking water and the quality and reliability of water systems in their area, among other water injustice indicators.
“Our results suggest that privatization alone is not a solution,” says Segrè Cohen. “The local context, such as regulatory enforcement, community vulnerability, and community priorities, matters in determining outcomes.”
About SRA
The Society for Risk Analysis is a multidisciplinary, interdisciplinary, scholarly, international society that provides an open forum for all those interested in risk analysis. SRA was established in 1980. Since 1982, it has continuously published Risk Analysis: An International Journal, the leading scholarly journal in the field. For more information, visit www.sra.org.
###
END
Study identifies U.S. hotspots for drinking water quality violations and lack of access to safe, clean water
Counties in West Virginia, North Carolina, Oklahoma and Pennsylvania ranked among the top 10 for violations
2025-04-15
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Busted! Researchers revolutionize fraud detection with machine learning
2025-04-15
Fraud is widespread in the United States and increasingly driven by technology. For example, 93% of credit card fraud now involves remote account access, not physical theft. In 2023, fraud losses surpassed $10 billion for the first time. The financial toll is staggering: credit card fraud costs $5 billion annually, affecting 60% of U.S. cardholders, while identity theft resulted in $16.4 billion in losses in 2021. Medicare fraud costs $60 billion each year, and government losses range from $233 billion to $521 billion annually, with improper payments totaling $2.7 trillion since 2003.
Machine learning plays a critical ...
Earthworm-inspired multimodal pneumatic continuous soft robot enhanced by winding transmission
2025-04-15
A research paper by scientists at Tianjin University presented an earthworm-inspired multimodal pneumatic continuous soft robot enhanced by wire-winding transmission.
The research paper, published on Mar. 19, 2025 in the journal Cyborg and Bionic Systems, proposes an earthworm-inspired multimodal pneumatic continuous soft robot to simultaneously achieve multimodal motion and good motion performance. Using the derived overlapped continuous control law (DOCCL) and wire-winding transmission, the robot can achieve a maximum planar crawling speed that surpasses that of other robots of the same type by an order of magnitude.
With ...
Coastal heritage threatened by climate change
2025-04-15
Humans have always lived by coasts and waterways, and thus these locations are rich with archeological sites. Natural and cultural resource management are conducted separately, despite the fact that climate change, sea level rise, and extreme weather threaten them both. Jayur Mehta and colleagues argue a synergy of both approaches is required to protect coastal archaeological landscapes. The authors used LiDAR digital elevation models, site location data, and NOAA sea level rise models to define ...
A tale of two hummingbird bills
2025-04-15
There are two species of streamertail hummingbirds on the island of Jamaica, West Indies—one with red-billed males (Trochilus polytmus) and the other with black-billed males (T. scitulus). This is a puzzling situation, as many evolutionary biologists have argued that avian speciation is unlikely to occur on small oceanic islands. Caroline Duffie Judy and colleagues investigated the hybrid zone that separates the two species, which is as narrow as 3.2 km. The authors analyzed 186 Trochilus specimens from 12 ...
Corn leads to improved performance in lithium-sulfur batteries
2025-04-15
PULLMAN, Wash. -- Researchers at Washington State University have demonstrated a way to use corn protein to improve the performance of lithium-sulfur batteries, a finding that holds promise for expanding the use of the high-energy, lighter-weight batteries in electric vehicles, renewable energy storage and other applications.
Lithium-sulfur batteries are lighter for the same amount of energy and more environmentally friendly than commonly used lithium-ion batteries, but their commercial adoption has been limited by technological hurdles that shorten their lifespan.
The WSU team’s research, published in the Journal of Power Sources, ...
SynGAP Research Fund (SRF), dba Cure SYNGAP1, announces Board of Trustees Update 2025
2025-04-15
Mill Valley, CA – April 15, 2025 – SynGAP Research Fund (SRF), dba Cure SYNGAP1, the leading patient advocacy group dedicated to improving the lives of those affected by SYNGAP1-related disorders (SRD), today announced the appointment of Jaime Aranda, Steve Gore, Heather Mestemaker, and Brian Smith to its Board of Trustees, effective April 15, 2025. They will succeed outgoing Trustees Emily Barnes, Sydney Stelmaszek, and Stella Tavilla, whose terms conclude on April 14, 2025. Additionally, a seat previously held by Pavel Gerovich, who stepped ...
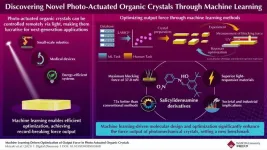
Machine learning unlocks superior performance in light-driven organic crystals
2025-04-15
Materials that convert external stimuli into mechanical motion, known as actuators, play a crucial role in robotics, medical devices, and other advanced applications. Among them, photomechanical crystals deform in response to light, making them promising for lightweight and remotely controllable actuation. Their performance depends on factors such as molecular structures, crystal properties, and experimental conditions.
A key performance indicator of these materials is the blocking force—the maximum force exerted when deformation is completely ...
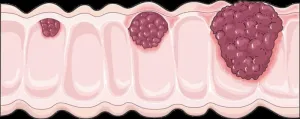
Exploring the mutational landscape of colorectal cancer
2025-04-15
Colorectal cancer (CRC), a type of cancer that affects the large intestine and rectum, is one of the leading causes of cancer-related deaths worldwide. The mutational landscape of CRC is well characterized, revealing key pathogenic genetic abnormalities that drive carcinogenesis (cancer development) and disease progression. Moreover, a step-wise colorectal carcinogenesis model has been proposed wherein normal epithelial cells transition to adenoma (non-cancerous tumor) and then to carcinoma (cancerous tumor) as they sequentially acquire genetic mutations.
Mutations ...
Researchers have mapped the hidden control system of vision
2025-04-15
Vision is one of the most complex functions of our brain and requires a seamless interaction between many different brain structures to decode shapes, colours, depths, and movements and turn them into a meaningful whole. Just like other brain functions, vision also depends on a balanced and controlled interaction between the chemical signals that "activate" and "brake" activity in the eye's cells – much like the accelerator and brake of a car. In research, the "brake" is known as GABA, which stands for gamma-aminobutyric ...
Key to the high aggressiveness of pancreatic cancer identified
2025-04-15
Barcelona, 15th April 2025. – Pancreatic cancer is one of the most aggressive cancers and has one of the lowest survival rates—only 10% after five years. One of the factors contributing to its aggressiveness is its tumor microenvironment, known as the stroma, which makes up the majority of the tumor mass and consists of a network of proteins and different non-tumor cells. Among these, fibroblasts play a key role, helping tumor cells to grow and increasing their resistance to drugs. Now, a study led by researchers from the Hospital del Mar Research Institute, IIBB-CSIC-IDIBAPS, ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Predicting brain health with a smartwatch
How boron helps to produce key proteins for new cancer therapies
Writing the catalog of plasma membrane repair proteins
A comprehensive review charts how psychiatry could finally diagnose what it actually treats
Thousands of genetic variants shape epilepsy risk, and most remain hidden
First comprehensive sex-specific atlas of GLP-1 in the mouse brain reveals why blockbuster weight-loss drugs may work differently in females and males
When rats run, their gut bacteria rewrite the chemical conversation with the brain
Movies reconstructed from mouse brain activity
Subglacial weathering may have slowed Earth's escape from snowball Earth
Simple test could transform time to endometriosis diagnosis
Why ‘being squeezed’ helps breast cancer cells to thrive
Mpox immune test validated during Rwandan outbreak
Scientists pinpoint protein shapes that track Alzheimer’s progression
Researchers achieve efficient bicarbonate-mediated integrated capture and electrolysis of carbon dioxide
Study reveals ancient needles and awls served many purposes
Key protein SYFO2 enables 'self-fertilization’ of leguminous plants
AI tool streamlines drug synthesis
Turning orchard waste into climate solutions: A simple method boosts biochar carbon storage
New ACP papers say health care must be more accessible and inclusive for patients and physicians with disabilities
Moisture powered materials could make cleaning CO₂ from air more efficient
Scientists identify the gatekeeper of retinal progenitor cell identity
American Indian and Alaska native peoples experience higher rates of fatal police violence in and around reservations
Research alert: Long-read genome sequencing uncovers new autism gene variants
Genetic mapping of Baltic Sea herring important for sustainable fishing
In the ocean’s marine ‘snow,’ a scientist seeks clues to future climate
Understanding how “marine snow” acts as a carbon sink
In search of the room temperature superconductor: international team formulates research agenda
Index provides flu risk for each state
Altered brain networks in newborns with congenital heart disease
Can people distinguish between AI-generated and human speech?
[Press-News.org] Study identifies U.S. hotspots for drinking water quality violations and lack of access to safe, clean waterCounties in West Virginia, North Carolina, Oklahoma and Pennsylvania ranked among the top 10 for violations