(Press-News.org) A new study from University of California San Diego suggests that climate trauma — such as experiencing a devastating wildfire — can have lasting effects on cognitive function. The research, which focused on survivors of the 2018 Camp Fire in Northern California, found that individuals directly exposed to the disaster had difficulty making decisions that prioritize long-term benefits. The findings were recently published in Scientific Reports, part of the Nature portfolio of journals.
“Our previous research has shown that survivors of California’s 2018 Camp Fire experience prolonged symptoms of post-traumatic stress disorder, anxiety and depression alongside hyper-distractibility,” said Jyoti Mishra, Ph.D., senior author and an associate professor at UC San Diego’s School of Medicine and co-director of the University of California Climate Resilience Initiative. “This new study suggests that climate trauma may also impact important cognitive abilities of decision-making and underlying brain function.”
Wildfires, which have become increasingly frequent due to climate change, are known to affect both physical and mental health. This study provides new evidence that cognitive function — particularly decision-making — is also impacted.
The study involved 75 participants, divided into three groups:
Directly exposed to the fire (n=27)
Indirectly exposed (witnessed the fire but were not directly affected, n=21)
Non-exposed controls (n=27)
All participants completed a decision-making task with monetary rewards while undergoing Electroencephalogram (EEG) brain recordings. Researchers evaluated their Win-Stay behavior, measuring how often they continued selecting the option with the highest long-term rewards.
Researchers found that wildfire survivors were significantly less likely to stick with choices that offered long-term rewards, a behavior they tracked with a choice metric known as “Win-Stay.” Brain recordings revealed a possible reason why. EEG brain scans taken while participants engaged in the decision-making tasks showed heightened activity in the parietal brain region, and localized to the posterior cingulate cortex (PCC) — a brain region associated with deep thought and rumination.
“It was clear that brains of study participants directly exposed to wildfires — as opposed to those not exposed — became significantly hyper-aroused when trying to make proper decision choices but they were still unable to execute the task well,” said Jason Nan, a UC San Diego bioengineering graduate student and study first author. “We interpret this to mean that their brain was attempting to focus on making sound decisions, but they were unable to.”
Understanding how climate trauma affects decision-making could lead to new diagnostic tools and personalized treatments for those impacted. One potential intervention is mindfulness and compassion training, which has shown promise in suppressing ruminating thoughts and thereby, mitigating the effects of trauma. Mobilizing early post-disaster intervention resources is a key priority of the California Climate Resilience Initiative.
As climate disasters become more frequent and more severe, researchers emphasize the need to: study pre- vs. post-disaster cognitive changes, investigate long-term effects of repeated exposure to climate trauma and develop scalable mental health interventions for affected communities.
Co-authors include: Satish Jaiswal and Dhakshin Ramanathan from UC San Diego, and Mathew C. Withers from Utah Valley University.
The study was funded, in part, by the Tang Prize Foundation, the Hope for Depression Research Foundation and the CA CARES (Climate Action, Resilience, and Environmental Sustainability) proof of concept funds.
# # #
END
Climate-related trauma can have lasting effects on decision-making, study finds
Researchers found that wildfire survivors were less likely to stick with choices that offered greater long-term rewards.
2025-04-16
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Your cells can hear
2025-04-16
Kyoto, Japan -- There's a sensation that you experience -- near a plane taking off or a speaker bank at a concert -- from a sound so total that you feel it in your very being. When this happens, not only do your brain and ears perceive it, but your cells may also.
Technically speaking, sound is a simple phenomenon, consisting of compressional mechanical waves transmitted through substances, which exists universally in the non-equilibrated material world. Sound is also a vital source of environmental information for living beings, while its capacity to induce physiological responses at the cell ...
Farm robot autonomously navigates, harvests among raised beds
2025-04-16
Strawberry fields forever will exist for the in-demand fruit, but the laborers who do the backbreaking work of harvesting them might continue to dwindle. While raised, high-bed cultivation somewhat eases the manual labor, the need for robots to help harvest strawberries, tomatoes, and other such produce is apparent.
As a first step, Osaka Metropolitan University Assistant Professor Takuya Fujinaga has developed an algorithm for robots to autonomously drive in two modes: moving to a pre-designated destination and moving alongside ...
The bear in the (court)room: who decides on removing grizzly bears from the endangered species list?
2025-04-16
By Dr Kelly Dunning
The Endangered Species Act (ESA), now 50 years old, was once a rare beacon of bipartisan unity, signed into law by President Richard Nixon with near-unanimous political support. Its purpose was clear: protect imperiled species and enable their recovery using the best available science to do so. Yet, as our case study on the grizzly bear in the Greater Yellowstone Ecosystem reveals, wildlife management under the ESA has changed, becoming a political battleground where science is increasingly drowned out by partisan ideology, bureaucratic delays, power struggles, and competing political interests. ...
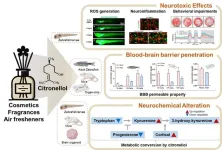
First study reveals neurotoxic potential of rose-scented citronellol at high exposure levels
2025-04-16
Citronellol, a rose-scented compound commonly found in cosmetics and household products, has long been considered safe. However, a Korean research team has, for the first time, identified its potential to cause neurotoxicity when excessively exposed.
A collaborative research team led by Dr. Myung Ae Bae at the Korea Research Institute of Chemical Technology (KRICT) and Professors Hae-Chul Park and Suhyun Kim at Korea University has discovered that high concentrations of citronellol can trigger neurological and behavioral toxicity. The study, published in the Journal ...
For a while, crocodile
2025-04-16
Most people think of crocodylians as living fossils— stubbornly unchanged, prehistoric relics that have ruled the world’s swampiest corners for millions of years. But their evolutionary history tells a different story, according to new research led by the University of Central Oklahoma (UCO) and the University of Utah.
Crocodylians are surviving members of a 230-million-year lineage called crocodylomorphs, a group that includes living crocodylians (i.e. crocodiles, alligators and gharials) and their many extinct ...
Scientists find evidence that overturns theories of the origin of water on Earth
2025-04-16
Images available via link in the notes section
University of Oxford researchers have helped overturn the popular theory that water on Earth originated from asteroids bombarding its surface;
Scientists have analysed a meteorite analogous to the early Earth to understand the origin of hydrogen on our planet.
The research team demonstrated that the material which built our planet was far richer in hydrogen than previously thought.
The findings, which support the theory that the formation of habitable conditions on Earth did not rely on asteroids ...
Foraging on the wing: How can ecologically similar birds live together?
2025-04-16
UNIVERSITY PARK, Pa. — A spat between birds at your backyard birdfeeder highlights the sometimes fierce competition for resources that animals face in the natural world, but some ecologically similar species appear to coexist peacefully. A classic study in songbirds by Robert MacArthur, one of the founders of modern ecology, suggested that similar wood warblers — insect-eating, colorful forest songbirds — can live in the same trees because they actually occupy slightly different locations in the tree and presumably eat different insects. Now, a new study is using modern techniques to revisit MacArthur’s ...
Little birds’ personalities shine through their song – and may help find a mate
2025-04-16
In birds, singing behaviours play a critical role in mating and territory defence.
Although birdsong can signal individual quality and personality, very few studies have explored the relationship between individual personality and song complexity, and none has investigated this in females, say Flinders University animal behaviour experts.
They have examined the relationships between song complexity and two personality traits (exploration and aggressiveness) in wild superb fairy-wrens (Malurus cyaneus) in Australia, a species in which both sexes learn to produce complex songs.
“Regardless of their sex ...
Primate mothers display different bereavement response to humans
2025-04-16
Macaque mothers experience a short period of physical restlessness after the death of an infant, but do not show typical human signs of grief, such as lethargy and appetite loss, finds a new study by UCL anthropologists.
Published in Biology Letters, the researchers found that bereaved macaque mothers spent less time resting (sleep, restful posture, relaxing) than the non-bereaved females in the first two weeks after their infants’ deaths.
Researchers believe this physical restlessness could represent an initial period of ‘protest’ among the bereaved macaque mothers, similar ...
New pollen-replacing food for honey bees brings new hope for survival
2025-04-16
PULLMAN, Wash., -- Scientists have unveiled a new food source designed to sustain honey bee colonies indefinitely without natural pollen.
Published April 16 in the journal Proceedings of the Royal Society B, the research from Washington State University and APIX Biosciences NV in Wingene, Belgium details successful trials where nutritionally stressed colonies, deployed for commercial crop pollination in Washington state, thrived on the new food source.
This innovation, which resembles the man-made diets ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
USF study: Gag grouper are overfished in the Gulf; this new tool could help
New study from Jeonbuk National University finds current climate pledges may miss Paris targets
Theoretical principles of band structure manipulation in strongly correlated insulators with spin and charge perturbations
A CNIC study shows that the heart can be protected during chemotherapy without reducing antitumor efficacy
Mayo Clinic study finds single dose of non-prescribed Adderall raises blood pressure and heart rate in healthy young adults
Engineered immune cells show promise against brain metastases in preclinical study
Improved EV battery technology will outmatch degradation from climate change
AI cancer tools risk “shortcut learning” rather than detecting true biology
Painless skin patch offers new way to monitor immune health
Children with poor oral health more often develop cardiovascular disease as adults
GLP-1 drugs associated with reduced need for emergency care for migraine
New knowledge on heritability paves the way for better treatment of people with chronic inflammatory bowel disease
Under the Lens: Microbiologists Nicola Holden and Gil Domingue weigh in on the raw milk debate
Science reveals why you can’t resist a snack – even when you’re full
Kidney cancer study finds belzutifan plus pembrolizumab post-surgery helps patients at high risk for relapse stay cancer-free longer
Alkali cation effects in electrochemical carbon dioxide reduction
Test platforms for charging wireless cars now fit on a bench
$3 million NIH grant funds national study of Medicare Advantage’s benefit expansion into social supports
Amplified Sciences achieves CAP accreditation for cutting-edge diagnostic lab
Fred Hutch announces 12 recipients of the annual Harold M. Weintraub Graduate Student Award
Native forest litter helps rebuild soil life in post-mining landscapes
Mountain soils in arid regions may emit more greenhouse gas as climate shifts, new study finds
Pairing biochar with other soil amendments could unlock stronger gains in soil health
Why do we get a skip in our step when we’re happy? Thank dopamine
UC Irvine scientists uncover cellular mechanism behind muscle repair
Platform to map living brain noninvasively takes next big step
Stress-testing the Cascadia Subduction Zone reveals variability that could impact how earthquakes spread
We may be underestimating the true carbon cost of northern wildfires
Blood test predicts which bladder cancer patients may safely skip surgery
Kennesaw State's Vijay Anand honored as National Academy of Inventors Senior Member
[Press-News.org] Climate-related trauma can have lasting effects on decision-making, study findsResearchers found that wildfire survivors were less likely to stick with choices that offered greater long-term rewards.