(Press-News.org) Researchers at the Center for Injury Research and Policy of The Research Institute at Nationwide Children's Hospital examined running-related injuries among children and adolescents 6 to 18 years old and found that an estimated 225,344 cases were treated in U.S. emergency departments from 1994 through 2007, for an average of more than 16,000 each year. During the 14-year study period, the annual number of running-related injuries increased 34 percent.
According to the study, appearing in the February 2011 issue of Clinical Pediatrics, the majority of running-related injuries were sprains and strains to the lower extremities. One third of the injuries involved a fall and more than one half of running-related injuries occurred at school.
The injuries, however, varied by age. Younger children (6 to 14 years old) were more likely to be injured as the result of a fall and while running at school. Adolescents 15 to 18 years old, on the other hand, were more likely to sustain injuries while running in the street or at a sports and recreation facility.
"Encouraging children and adolescents to run for exercise is a great way to ensure that they remain physically active," said Lara McKenzie, PhD, and principle investigator at the Center for Injury Research and Policy at Nationwide Children's Hospital. "However, the findings from our study show that formal, evidenced-based and age-specific guidelines are needed for pediatric runners so that parents, coaches and physical education teachers can teach children the proper way to run in order to reduce the risk of injury."
This is the first study to examine a nationally representative sample of running-related injuries treated in U.S. emergency departments. Further research in necessary to thoroughly understand pediatric running-related injuries and the role injury prevention intervention can play in reducing them.
INFORMATION:
Data for this study were collected from the National Electronic Injury Surveillance System (NEISS), which is operated by the U.S. Consumer Product Safety Commission. The NEISS dataset provides information on consumer product-related and sports and recreation-related injuries treated in hospital emergency departments across the country.
The Center for Injury Research and Policy (CIRP) of The Research Institute at Nationwide Children's Hospital works globally to reduce injury-related pediatric death and disabilities. With innovative research as its core, CIRP works to continually improve the scientific understanding of the epidemiology, biomechanics, prevention, acute treatment and rehabilitation of injuries. CIRP serves as a pioneer by translating cutting edge injury research into education, policy and advances in clinical care. For related injury prevention materials or to learn more about CIRP visit http://www.injurycenter.org.
New national study finds 34 percent increase in running-related injuries among children
2011-01-28
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Current violent juvenile treatment methods costly, ineffective, MU researcher finds
2011-01-28
COLUMBIA, Mo. – In a time of shrinking budgets, one University of Missouri professor believes that the current approach to juvenile crime is much too expensive to continue – and he has the numbers to prove it.
Charles Borduin, a professor of psychological sciences in the MU College of Arts and Science finds that multisystemic therapy (MST) is more effective in the lives of troubled youth and costs less.
Borduin has pioneered the model for the treatment and prevention of serious mental health problems in children and adolescents throughout the course of his career. MST ...
Newborn screening increases survival outcome for patients with severe combined immunodeficiency
2011-01-28
(WASHINGTON, January 27, 2011) –Severe Combined Immunodeficiency (SCID) occurs in just one out of every 50,000 to 100,000 births in the United States, yet it is the most serious primary immunodeficiency disorder.[1] A study published today in Blood, the Journal of the American Society of Hematology (ASH), demonstrates that babies with SCID who are diagnosed at birth and receive a hematopoietic stem cell transplant (HSCT), which is the transplantation of blood-forming stem cells, have significantly improved survival.
SCID is a rare group of genetic disorders characterized ...
Opposites may attract, but they don't make better parents
2011-01-28
A study by experts at the University of Exeter has revealed that couples with similar personalities make much better parents than those with different dispositions – at least in the world of zebra finches.
Researchers found birds expressing strong personality traits, such as aggressive behaviour or a willingness to explore, did a much better job of raising young if they had a like-minded partner. Where couples were markedly different in personality, chicks didn't fare as well – being less well-fed and in poorer condition.
The research paper, published in the journal ...
Yearly mammograms from age 40 save 71 percent more lives, study shows
2011-01-28
ANN ARBOR, Mich. — A new study questions the controversial U.S. Preventative Service Task Force recommendations for breast cancer screening, with data that shows starting at a younger age and screening more frequently will result in more lives saved.
The study analyzed the same data looked at by the task force, which issued its guidelines on mammography screening in November 2009. The study authors compared the task force's recommendations for screening every other year in women 50-74 to American Cancer Society guidelines of screening every year in women 40-84.
The ...
Scientists determine what makes an orangutan an orangutan
2011-01-28
For the first time, scientists have mapped the genome--the genetic code--of orangutans. This new tool may be used to support efforts to maintain the genetic diversity of captive and wild orangutans. The new map of the orangutan genome may also be used to help improve our understanding of the evolution of primates, including humans.
Partially funded by the National Science Foundation, the orangutan study appears in the Jan. 27 issue of Nature. It was conducted by an international team of scientists led by Devin P. Locke of the Genome Center at Washington University.
Conservation ...
On the hunt for universal intelligence
2011-01-28
We have developed an 'anytime' intelligence test, in other words a test that can be interrupted at any time, but that gives a more accurate idea of the intelligence of the test subject if there is a longer time available in which to carry it out", José Hernández-Orallo, a researcher at the Polytechnic University of Valencia (UPV), tells SINC.
This is just one of the many determining factors of the universal intelligence test. "The others are that it can be applied to any subject – whether biological or not – at any point in its development (child or adult, for example), ...
Study shows smaller rows contribute to more soybean yields in colder climates
2011-01-28
Madison, WI January 27, 2011 – Soybean production has continued to increase in the Northeast United States with more and more first time growers planting the crop and many experienced growers planting alongside corn crops. To save on time and expenses, some farmers plant soybeans with a corn planter in 30-inch rows instead of 7.5-inch rows with the regularly used grain drill.
Dr. William Cox, a Cornell University scientist, investigated the response of two soybean varieties in row widths of 7.5, 15, and 30 inches at four seeding rates in a study funded by a USDA Hatch ...
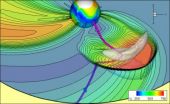
First large-scale, physics-based space weather model transitions into operation
2011-01-28
The first large-scale, physics-based space weather prediction model is transitioning from research into operation.
Scientists affiliated with the National Science Foundation (NSF) Center for Integrated Space Weather Modeling (CISM) and the National Weather Service reported the news today at the annual American Meteorological Society (AMS) meeting in Seattle, Wash.
The model will provide forecasters with a one-to-four day advance warning of high speed streams of solar plasma and Earth-directed coronal mass ejections (CMEs).
These streams from the Sun may severely disrupt ...
Altered gene protects some African-Americans from coronary artery disease
2011-01-28
A team of scientists at Johns Hopkins and elsewhere has discovered that a single alteration in the genetic code of about a fourth of African-Americans helps protect them from coronary artery disease, the leading cause of death in Americans of all races.
Researchers found that a single DNA variation - having at least one so-called guanine nucleotide in a base pair instead of a combination without any guanine - on a gene already linked to higher risk of coronary disease in other races is linked in blacks to decreased risk. Specifically, the study showed that otherwise ...
Surgery for obstructive sleep apnea reduces daytime drowsiness
2011-01-28
DETROIT – Patients with obstructive sleep apnea who undergo surgery to improve their breathing get a better night's sleep and therefore are less drowsy during the day, according to a new study from Henry Ford Hospital in Detroit.
The study finds surgery greatly reduces daytime sleepiness – a common side effect from this disorder in which the upper airway is partially or completely blocked during sleep – when compared to other non-surgical treatments for obstructive sleep apnea.
"This study validates what patients have told us regarding their improved alertness after ...