Measuring methane
Researchers develop technique to measure methane gas from cattle
2011-03-02
(Press-News.org) MADISON, WI, MARCH 1, 2011 – Methane is an extremely potent greenhouse gas. Wetlands, gas hydrates, permafrost, termites, oceans, freshwater bodies, non-wetland soils, are all natural sources of atmospheric methane; however, the majority of methane presence ca n be accredited to human-related activities. These activities include: such as fossil fuel production, biomass burning, waste management and animal husbandry. The release of methane into the atmosphere by cattle and other large grazing mammals is estimated to account for 12 to 17% of the total global methane release.
Recently, scientists developed a methane release measuring technique as way of tracking the discharge of the gas without disrupting the regular management of the herd. This is part of a collaborative research study conducted by researchers from Agriculture and Agri-Food Canada's Lethbridge Research Centre, the Commonwealth Scientific and Industrial Research Organization, and the University of Melbourne in Australia.
Cattle were fitted with global positioning devices to track their movements and wind speed and direction were constantly measured. Unlike previous studies in which a few cattle were handled daily and methane measurements were taken directly, this technique centered on using open-path lasers to obtain a short-term measurement of methane release from an entire grazing herd. For instance in one study, the technique was used to take repeated measurements of methane concentration every 10 minutes directly above the height of the 18 cattle in the paddock. According to the results, the technique developed so well it can account for 77% of methane release at a single point in a paddock.
Sean McGinn, the author of the study describes the technique as a "significant advancement in assessing greenhouse gas emissions from the cattle industry."
Collaborative research is continuing to further measure methane release from other agricultural sources. The full study is published in the January/February 2011 issue of the Journal of Environmental Quality.
INFORMATION: END
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2011-03-02
Scientists now have a better understanding of why spider silk fibers are so incredibly strong. Recent research, published by Cell Press on February 15th in Biophysical Journal, describes the architecture of silk fibers from the atomic level up and reveals new information about the molecular structure that underlies the amazing mechanical characteristics of this fascinating natural material.
Spiders spin silk, which is remarkably strong and stretchy, to use in webs and to suspend themselves. "Silk fibers exhibit astonishing mechanical properties. They have an ultimate ...
2011-03-02
WEST LAFAYETTE, Ind. - A Purdue University researcher is leading an effort to create a new scientific field that will use sound as a way to understand the ecological characteristics of a landscape and to reconnect people with the importance of natural sounds.
Soundscape ecology, as it's being called, will focus on what sounds can tell people about an area. Bryan Pijanowski, an associate professor of forestry and natural resources and lead author of a paper outlining the field in the journal BioScience, said natural sound could be used like a canary in a coal mine. Sound ...
2011-03-02
CHAMPAIGN, lll. — A review of more than 160 studies of human and animal subjects has found "clear and compelling evidence" that – all else being equal – happy people tend to live longer and experience better health than their unhappy peers.
The study, in the journal Applied Psychology: Health and Well-Being, is the most comprehensive review so far of the evidence linking happiness to health outcomes. Its lead author, University of Illinois professor emeritus of psychology Ed Diener, who also is a senior scientist for the Gallup Organization, of Princeton, N.J., analyzed ...
2011-03-02
Alcoholism is a tough addiction to kick. Eventually, most people return to drinking. But some Dutch and German psychological scientists have tested a short-term regime that promises to help alcoholics stay sober. Their study is published in Psychological Science, a journal of the Association of Psychological Science.
Heavy drinkers tend to behave impulsively in response to temptation. Meanwhile, their "reflective," or controlled, responses—the thoughts that would help them resist drinking—are often weak. Most therapies, including Cognitive Behavior Therapy, primarily ...
2011-03-02
Mild heart failure patients with a particular condition that results in disorganized electrical activity throughout the heart benefit substantially from cardiac resynchronization therapy with defibrillator (CRT–D), according to a study published in the American Heart Association journal Circulation.
In patients with the condition, known as left bundle branch block or LBBB, CRT-D therapy reduced heart failure progression and the risk of ventricular tachyarrhythmias, fast and potentially life-threatening heart rhythms. Heart failure patients without LBBB did not receive ...
2011-03-02
Many people suffer from a devastating condition known as critical limb ischemia (CLI) that can lead to muscle wasting and even amputation. The disease is linked to the blockage of blood flow to the skeletal muscle and current treatment options include rehabilitative exercise and surgical bypass of blood vessels. New preclinical research suggests there may be a way to restore blood supply in skeletal muscle without traditional intervention.
Scientists at The University of Texas Health Science Center at Houston (UTHealth) and the Salk Institute for Biological Studies ...
2011-03-02
WASHINGTON, March 1—The world's largest international conference on
optical communications will take place March 6-10 at the Los Angeles Convention Center. The Optical Fiber Communication Conference and Exposition/National Fiber Optic Engineers Conference (OFC/NFOEC) is the premier telecom meeting where experts from industry and academia share their results, experiences, and insights on the future of electronic and wireless communication and optical technologies. More than 10,000 attendees and an exhibit with 500 companies are expected.
CONFERENCE HIGHLIGHTS
Plenary ...
2011-03-02
An AIDS vaccine tested in people, but found to be ineffective, influenced the genetic makeup of the virus that slipped past. The findings suggest new ideas for developing HIV vaccines.
The results were published Feb. 27 in Nature Medicine.
This is the first evidence that vaccine-induced cellular immune responses against HIV-1 infection exert selective pressure on the virus. "Selective pressure" refers to environmental demands that favor certain genetic traits over others.
The senior author of the multi-institutional study is Dr. James I. Mullins, University of Washington ...
2011-03-02
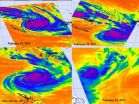
Tropical Cyclone Atu had a brief but memorable life last week, and NASA's Atmospheric Infrared Sounder (AIRS) instrument that flies aboard NASA's Aqua satellite captured a day-by-day look at its growth and death.
AIRS provides infrared images of atmospheric phenomena, oceans and land areas around the world. Basically, infrared data takes the temperature of these things. When NASA's Aqua satellite flew over Tropical Cyclone Atu from February 21 through the 25 it saw thunderstorm cloud tops grow colder as the clouds grew higher and thunderstorms became more powerful. When ...
2011-03-02
WASHINGTON -- NASA's Glory spacecraft is scheduled for launch on Friday, March 4. Technical issues with ground support equipment for the Taurus XL launch vehicle led to the scrub of the original Feb. 23 launch attempt. Those issues have been resolved.
The March 4 liftoff from Vandenberg Air Force Base, Calif., is targeted for 5:09:43 a.m. EST, in the middle of a 48-second launch window. Spacecraft separation occurs 13 minutes after launch.
Data from the Glory mission will allow scientists to better understand how the sun and tiny atmospheric particles called aerosols ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Measuring methane
Researchers develop technique to measure methane gas from cattle