(Press-News.org) MADISON, WI, September 9, 2010 – Cotton growers can produce more cotton if they plant early, but not without irrigation. That's the finding of an article published in the September-October 2010 Agronomy Journal, a publication of the American Society of Agronomy.
Bill Pettigrew, a scientist with the USDA-Agricultural Research Service in Stoneville, Mississippi, tested the performance of cotton under irrigated and non-irrigated plots, with half the plots being planted early (first week of April) and half being planted in the more tradition time period, around the 1st week of May.
Previous research indicated that planting earlier in the year increased cotton yields. This is likely because the peak blooming period shifts closer to the longest day of the year (in June), avoiding the typically drier months of the year, July and August. The additional sunlight associated with longer days also allows the plants to take in more sunlight during their growing season.
However, most of this research was done on irrigated crops. Pettigrew's study found that while early planting does increase yield, it does so only with irrigation. Early planting increased cotton production in of two of the four years of the study with irrigation. However, the non-irrigated plots never saw increased production from early planting, and even saw a 13% decrease in yield one year.
Conducted from 2005-2008, the only year that irrigation did not increase yield was 2005, when the study area was hit by Hurricane Katrina.
Pettigrew concluded that early planting clearly needs irrigation to increase cotton yields. This attribute implies that if Mississippi Delta producers don't have irrigation capabilities, they should probably not adopt an early planting strategy.
The results from this research can be used by cotton researchers, extension specialists, consultants and producers as an unbiased source of information to aid in making cotton production decisions.
INFORMATION:
The full article is available for no charge for 30 days following the date of this summary. View the abstract at https://www.agronomy.org/publications/aj/abstracts/102/5/1379.
A peer-reviewed international journal of agriculture and natural resource sciences, Agronomy Journal is published six times a year by the American Society of Agronomy, with articles relating to original research in soil science, crop science, agroclimatology and agronomic modeling, production agriculture, and software. For more information visit: www.agronomy.org/publications/aj
The American Society of Agronomy (ASA) www.agronomy.org, is a scientific society helping its 8,000+ members advance the disciplines and practices of agronomy by supporting professional growth and science policy initiatives, and by providing quality, research-based publications and a variety of member services.
Early cotton planting requires irrigation
Without irrigation, early-planted cotton fails to achieve yield improvements
2010-09-10
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Promising treatment for metastatic melanoma 'fast tracked' by FDA
2010-09-10
HACKENSACK, N.J. (September 9, 2010) — Researchers from the John Theurer Cancer Center at Hackensack University Medical Center played an important role in a study that led to the Food & Drug Administration's (FDA) recent fast tracking of ipilimumab, a promising treatment for metastatic melanoma. The FDA based its decision largely on the results of a pivotal study published in the New England Journal of Medicine on August 19, 2010 – the same day the agency accepted Bristol-Myers Squibb's application for the drug's approval and granted the application priority review status.
Ipilimumab ...
AGU journal highlights
2010-09-10
The following highlights summarize research papers that have been recently published in Journal of Geophysical Research-Atmospheres (JGR-D) and Geophysical Research Letters (GRL).
In this release:
Landmass shape affects extent of Arctic sea ice
Estimating how much rain forests intercept
How compliant fault zones respond to nearby earthquakes
Measuring the rate of mountain building in New Zealand
Interplanetary magnetic field causes changes in the polar cap ionosphere
Oxygen and hydrogen follow different escape paths from Venus's atmosphere
Anyone ...
Strategy discovered to prevent Alzheimer's-associated traffic jams in the brain
2010-09-10
SAN FRANCISCO, CA – September 9, 2010 – Amyloid beta (Αβ) proteins, widely thought to cause Alzheimer's disease (AD), block the transport of vital cargoes inside brain cells. Scientists at the Gladstone Institute of Neurological Disease (GIND) have discovered that reducing the level of another protein, tau, can prevent Aβ from causing such traffic jams.
Neurons in the brain are connected to many other neurons through long processes called axons. Their functions depend on the transport of diverse cargoes up and down these important pipelines. Particularly ...
The cost of over-triage on our nation's health system
2010-09-10
Researchers at the University of California, San Diego School of Medicine have identified "secondary over-triage" as a potential area of cost savings for our nation's health care. The phenomenon of over-triage occurs when patients are transferred twice, and discharged from a second facility in less than 24 hours. These findings will be published in the September 10th issue of The Journal of Trauma.
"By looking at the number of times patients are transferred, we can evaluate the overall efficiency of our trauma system and its impact on healthcare costs," said Hayley Osen, ...
Flying fish glide as well as birds
2010-09-10
We're all familiar with birds that are as comfortable diving as they are flying but only one family of fish has made the reverse journey. Flying fish can remain airborne for over 40s, covering distances of up to 400m at speeds of 70km/h. Haecheon Choi, a mechanical engineer from Seoul National University, Korea, became fascinated by flying fish when reading a science book to his children. Realising that flying fish really do fly, he and his colleague, Hyungmin Park, decided to find out how these unexpected fliers stay aloft and publish their discovery that flying fish glide ...
Lack of trust in hospitals a major deterrent for blood donation among African-Americans
2010-09-10
Disparities in healthcare between races exist in the United States. A new study published in the journal Transfusion explores why African Americans donate blood at lower rates than whites. The findings reveal that there is a significant distrust in the healthcare system among the African American community, and African Americans who distrust hospitals are less likely to donate.
Led by Beth H. Shaz, MD, Chief Medical Officer of the New York Blood Center in New York, New York, researchers created a survey to explore reasons for low likelihood of blood donation in African ...
BEK Communications Looks to Mariner's xVu Service to Better Manage Local IPTV Programming
2010-09-10
BEKTV utilizing industry leading service assurance tool to gain viewership insight
Fiber to the Home (FTTH) Conference, Las Vegas, NV, September 9th, 2010: BEK Communications, the innovative telecommunications company serving south-central North Dakota, announced today their use of xVu as a means of gaining improved insight of their local programming. A key element of BEK's strategy as a multi-faceted telecom company is their exclusive hometown programming. Through BEKTV, BEK Communications broadcasts such specialized local features as BEK Sports, BEK Life and BEK Local ...
In attracting mates, male bowerbirds appear to rely on special optical effect
2010-09-09
Bowerbird males are well known for making elaborate constructions, lavished with decorative objects, to impress and attract their mates. Now, researchers reporting online on September 9 in Current Biology, a Cell Press journal, have identified a completely new dimension to these showy structures in great bowerbirds. The birds create a staged scene, only visible from the point of view of their female audience, by placing pebbles, bones, and shells around their courts in a very special way that can make objects (or a bowerbird male) appear larger or smaller than they really ...
Mental maturity scan tracks brain development
2010-09-09
Five minutes in a scanner can reveal how far a child's brain has come along the path from childhood to maturity and potentially shed light on a range of psychological and developmental disorders, scientists at Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis have shown.
Researchers assert this week in Science that their study proves brain imaging data can offer more extensive help in tracking aberrant brain development.
"Pediatricians regularly plot where their patients are in terms of height, weight and other measures, and then match these up to standardized curves ...
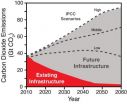
Main climate threat from CO2 sources yet to be built
2010-09-09
Stanford, CA— Scientists have warned that avoiding dangerous climate change this century will require steep cuts in carbon dioxide emissions. New energy-efficient or carbon-free technologies can help, but what about the power plants, cars, trucks, and other fossil-fuel-burning devices already in operation? Unless forced into early retirement, they will emit carbon dioxide into the atmosphere for decades to come. Will their emissions push carbon dioxide levels beyond prescribed limits, regardless of what we build next? Is there already too much inertia in the system to curb ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Jeonbuk National University researchers develop DDINet for accurate and scalable drug-drug interaction prediction
IEEE researchers achieve 20x signal boost in cerebral blood flow monitoring with next-generation interferometric diffusing wave spectroscopy
IEEE researchers achieve low-power ultrashort mid-IR pulse compression
Deep-sea natural compound targets cancer cells through a dual mechanism
Antibiotics can affect the gut microbiome for several years
Study: Electrical stimulation can restore ability to move limbs, receive sensory feedback after spinal cord injury
Rice scientists unveil new tool to watch quantum behavior in action
Gene-based therapies poised for major upgrade thanks to Oregon State University research
Extreme heat has extreme effects r—but some like it hot
Blood marker for Alzheimer’s may also be useful in heart and kidney diseases
Climate extremes hinder early development in young birds
Climate policies: The swing voters that determine their fate
Building protection against infectious diseases with nanostructured vaccines
Oval orbit casts new light on black hole - neutron star mergers
Does online sports gambling affect substance use behaviors?
How do rapid socio-environmental transitions reshape cancer risk?
Do abortion bans affect birth rates and food-assistance costs?
Can artificial intelligence help reduce the carbon footprint of weather forecasting models?
Mangrove forests are short of breath
Low testosterone, high fructose: A recipe for liver disaster
SKKU research team unravels the origin of stochasticity, a key to next-generation data security and computing
Flexible polymer‑based electronics for human health monitoring: A safety‑level‑oriented review of materials and applications
Could ultrasound help save hedgehogs?
attexis RCT shows clinically relevant reduction in adult ADHD symptoms and is published in Psychological Medicine
Cellular changes linked to depression related fatigue
First degree female relatives’ suicidal intentions may influence women’s suicide risk
Specific gut bacteria species (R inulinivorans) linked to muscle strength
Wegovy may have highest ‘eye stroke’ and sight loss risk of semaglutide GLP-1 agonists
New African species confirms evolutionary origin of magic mushrooms
Mining the dark transcriptome: University of Toronto Engineering researchers create the first potential drug molecules from long noncoding RNA
[Press-News.org] Early cotton planting requires irrigationWithout irrigation, early-planted cotton fails to achieve yield improvements