(Press-News.org) OAK BROOK, Ill. (April 11, 2011) – New research suggests that magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) could help detect Alzheimer's disease (AD) at an early stage, before irreversible damage has occurred, according to a new study published online and in the June print edition of Radiology.
With no known treatment to alter its course, AD exacts an enormous toll on society. The Alzheimer's Association estimates that 5.4 million Americans are living with the disease today, and the cumulative costs for care could top $20 trillion over the next four decades. As a result, there is growing interest in tests that could identify individuals at risk for AD at an early stage, when memory preservation may still be possible. Brain volume measurement with MRI is one promising area of research.
"One of the things that made our study novel was that we looked at patients who were cognitively normal at baseline, rather than people with mild cognitive impairment," said lead author Gloria C. Chiang, M.D., radiology resident at University of California San Francisco.
For the study, researchers looked at whether automated brain volume measurements on MRI could accurately predict future memory decline in elderly people with normal cognitive ability. They assessed 149 participants with an initial baseline MRI scan and a neuropsychological assessment.
Follow-up exams two years later showed that 25 of the 149 initially cognitively normal participants, or 17 percent, had memory decline.
While previous research has focused on the medial temporal lobe of the brain, which is strongly associated with memory, researchers looked at volume changes across a number of regions in the temporal and parietal lobes. The parietal lobe is primarily associated with the processing of sensory information and is involved in a number of cognitive and language processes.
The predictive accuracy of the classification model increased as the number of brain regions included in the model increased. Models that took into account several areas of both the temporal and parietal lobes had an 81 percent accuracy rate in discriminating between cognitively normal people with and without memory decline.
The findings illuminated how the interaction between these brain regions may play a key role in memory loss.
"Previous models have included regions of the brain as isolated variables," Dr. Chiang said. "Our study showed that volume loss in multiple regions that may be interconnected had a greater impact on memory decline. We found that automated temporal and parietal volumes identified those at risk for future memory decline with high accuracy."
The study represents another step in the process of incorporating imaging into the diagnosis and management of Alzheimer's disease, according to Dr. Chiang.
"We can see so much with MRI, but right now there's no way to definitively diagnose AD with imaging," she said. "The goal in the future is to have a screening device to monitor cognitive decline and diagnose AD."
###
"Identifying Cognitively Healthy Elderly Individuals with Subsequent Memory Decline by Using Automated MR Temporoparietal Volumes." Collaborating with Dr. Chiang were Philip S. Insel, M.S., Duygu Tosun, Ph.D., Norbert Schuff, Ph.D., Diana Truran-Sacrey, B.A., Sky Raptentsetsang, B.S., Clifford R. Jack Jr., M.D., Michael W. Weiner, M.D.
Radiology is edited by Herbert Y. Kressel, M.D., Harvard Medical School, Boston, Mass., and owned and published by the Radiological Society of North America, Inc. (http://radiology.rsna.org/)
RSNA is an association of more than 46,000 radiologists, radiation oncologists, medical physicists and related scientists committed to excellence in patient care through education and research. The Society is based in Oak Brook, Ill. (RSNA.org)
For patient-friendly information on MRI, visit RadiologyInfo.org.
MRI may contribute to early detection of Alzheimer's
2011-04-12
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Stress wrecks intestinal bacteria, could keep immune system on idle
2011-04-12
COLUMBUS, Ohio – Stress not only sends the human immune system into overdrive – it can also wreak havoc on the trillions of bacteria that work and thrive inside our digestive system.
New research suggests that this may be important because those bacteria play a significant role in triggering the innate immune system to stay slightly active, and thereby prepared to quickly spring into action in the face of an infection.
But exactly how stress makes these changes in these bacteria still isn't quite clear, researchers say.
"Since graduate school, I've been interested ...
Media's focus on ideal body shape can boost women's body satisfaction -- for a while
2011-04-12
COLUMBUS, Ohio – When researchers had college-age women view magazines for five straight days that only included images of women with thin, idealized body types, something surprising happened: the readers' own body satisfaction improved.
But the boost in body image came with a catch. Those women whose body satisfaction improved the most also were more likely to report that they engaged in dieting behaviors such as skipping meals or cutting carbohydrates during the course of the study.
That suggests these women may be inspired by the images they view and become momentarily ...
Scientists identify a surprising new source of cancer stem cells
2011-04-12
FINDINGS: Certain differentiated cells in breast tissue can spontaneously convert to a stem-cell-like state, according to Whitehead Institute researchers. Until now, scientific dogma has stated that differentiation is a one-way path; once cells specialize, they cannot return to the flexible stem-cell state on their own. These findings hold true for normal mammary cells as well as for breast cancer cells.
RELEVANCE: These findings may redefine how researchers view cancer stem cells – the cells capable of seeding new tumors at primary and distant sites in the body. Therapies ...
The world's smallest wedding rings
2011-04-12
This release is available in German.
FRANKFURT. Creating artificial structures from DNA is the objective of DNA nanotechnology. This new discipline, which combines biology, physics, chemistry and material science makes use of the ability of the natural DNA-strains' capacity for self assembly. Smileys or small boxes, measuring only 10s of nanometers (10 one-billionths of a meter) were created from DNA in a drop of water. Prof Alexander Heckel and his doctoral student Thorsten Schmidt from the "Cluster of Excellence for Macromolecular Complexes" at Goethe University were ...
Tuberculosis strain spread by the fur trade reveals stealthy approach of epidemics
2011-04-12
Patience may be a virtue in a person, but in an infectious disease, it is insidious. Witness tuberculosis, which can lie dormant in a human host for decades before bursting forth into infection. TB's stealthy nature has made it difficult to decipher how it spreads, seriously hampering efforts to control it. The World Health Organization estimates that a third of the people on Earth are infected.
Now, a study led by Stanford scientists has provided new insights into the behavior of tuberculosis by tracing the travels of a particular strain of the disease that was unintentionally ...
Ambulatory Providers Overly Optimistic about Reaching Meaningful Use
2011-04-12
Although nearly 80 percent of ambulatory providers that have purchased an EMR are confident they will qualify for meaningful use (MU) in 2011, a closer look at what functionalities they have actually implemented reveals that most still have significant holes to fill, according to a KLAS report. Over two thirds of the surveyed providers are not sharing medical records electronically with patients, and nearly half have not implemented clinical decision support (CDS) rules, two key MU requirements.
The report, "Ambulatory EMR: A KLAS Guide to Meaningful Use Success," presents ...
Excessive nitrogen harms the economy and environment -- first Europe-wide assessment published
2011-04-12
A major new study finds that nitrogen pollution is costing each person in Europe around £130 - £650 (€150 – €740 Euros) a year. The first European Nitrogen Assessment (ENA) is launched at a conference today in Edinburgh, Scotland.
The study, carried out by 200 experts from 21 countries and 89 organizations, estimates that the annual cost of damage caused by nitrogen across Europe is £60 - £280 billion (€70 -320 billion), more than double the extra income gained from using nitrogen fertilizers in European agriculture.
Professor Bob Watson Chief Scientific Advisor to ...
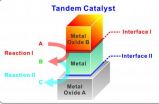
Berkeley Lab researchers report tandem catalysis in nanocrystal interfaces
2011-04-12
In a development that holds intriguing possibilities for the future of industrial catalysis, as well as for such promising clean green energy technologies as artificial photosynthesis, researchers with the U.S. Department of Energy (DOE)'s Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory (Berkeley Lab) have created bilayered nanocrystals of a
metal-metal oxide that are the first to feature multiple catalytic sites on nanocrystal interfaces. These multiple catalytic sites allow for multiple, sequential catalytic reactions to be carried out selectively and in tandem.
"The demonstration ...
Pop Cult Studio's Mark Mushkin is Currently Producing TV Shows to be Pitched to Google and YouTube as Content for a New Wave of Media Headed for America's Living Room
2011-04-12
Pop Cult Studio's Mark Mushkin is currently producing TV shows as content for a new wave of media headed for America's living room.
The Internet and TV are engaged to be married and there are big name companies scheduled to attend. Google and YouTube are looking to purchase TV shows to distribute on a network of channels being set up in preparation for the next generation of TV's that will connect to the Internet.
Pop Cult Studios' Executive Producer Mark Mushkin says, "We plan to take advantage of this opportunity to get our new TV shows seen by these major distributors." ...
Shootingstars provide clues to likely response of plants to global warming
2011-04-12
Many scientists are concerned that plant and animal species may face extinction due to global warming, but biologists at Washington University in St. Louis are trying to predict exactly what will happen to them. Which species will migrate? Which evolve? Which change their behavior? Which become extinct?
Rather than peer into the future, they are looking backward, exploring how species alive today survived global warming at the end of the Pleistocene and asking whether their responses provide any guidance for us today.
For his dissertation Brad Oberle, a doctoral candidate ...