Study shows tranquil scenes have positive impact on brain
2010-09-14
(Press-News.org) Tranquil living environments can positively affect the human brain function, according to researchers at the University of Sheffield.
The research, which was published in the journal NeuroImage, uses functional brain imaging to assess how the environment impacts upon our brain functions.
The findings demonstrated that tranquil environmental scenes containing natural features, such as the sea, cause distinct brain areas to become 'connected' with one another whilst man-made environments, such as motorways, disrupt the brain connections.
The research involved academics from the University's Academic Unit of Clinical Psychiatry, Academic Radiology and the School of Architecture, along with the School of Engineering, Design and Technology at the University of Bradford and the Institute of Medicine and Neuroscience at Jülich, Germany. The team carried out functional brain scanning at the University of Sheffield to examine brain activity when people were presented with images of tranquil beach scenes and non-tranquil motorway scenes.
They utilised the fact that waves breaking on a beach and traffic moving on a motorway produce a similar sound, perceived as a constant roar, and presented the participants with images of tranquil beach scenes and non-tranquil motorway scenes while they listened to the same sound associated with both scenes.
Using brain scanning that measures brain activity they showed that the natural, tranquil scenes caused different brain areas to become 'connected' with one another – indicating that these brain regions were working in sync. However, the non-tranquil motorway scenes disrupted connections within the brain.
Dr Michael Hunter, from the Sheffield Cognition and Neuroimaging Laboratory (SCANLab) based in Academic Clinical Psychiatry within the University of Sheffield's Department of Neuroscience, said: "People experience tranquillity as a state of calmness and reflection, which is restorative compared with the stressful effects of sustained attention in day-to-day life. It is well known that natural environments induce feelings of tranquillity whereas manmade, urban environments are experienced as non-tranquil. We wanted to understand how the brain works when it perceives natural environments, so we can measure its experience of tranquillity."
Professor Peter Woodruff, from SCANLab, said: "This work may have implications for the design of more tranquil public spaces and buildings, including hospitals, because it provides a way of measuring the impact of environmental and architectural features on people's psychological state. The project was a real collaborative effort, bringing together researchers from Psychiatry, Radiology and Architecture at the University of Sheffield, as well as Engineering at the University of Bradford and the Institute of Medicine and Neuroscience at Jülich, Germany."
INFORMATION: END
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2010-09-14
INDIANAPOLIS – A new study led by Elizabeth Poposki, Ph.D., assistant professor of psychology in the School of Science at Indiana University-Purdue University Indianapolis, may help employers identify employees who enjoy multitasking and are less inclined to quit jobs involving multitasking. The study presents a new tool developed to measure preference for multitasking, information which may be of interest to bosses who tire of repeatedly hiring and training new employees.
A growing number of individuals must multitask at work and positions requiring a significant amount ...
2010-09-14
A record-breaking 429 White-shouldered Ibis Pseudibis davisoni have just been recorded in Cambodia, making the known global population much larger than previously thought. With so many birds remaining in the wild the chances of conservation success are greatly improved – welcome news for this Critically Endangered bird species.
The University of East Anglia (UEA), UK, brought together a group of conservationists for a coordinated survey of 37 roost sites across Cambodia. Participants came from the Cambodian Forestry Administration and General Department for Administration ...
2010-09-14
New research from North Carolina State University will help medical examiners and others identify human remains of those killed during the recent earthquake in Chile, as well as the bodies of the "disappeared" who were killed during the Pinochet administration.
"We have developed population-specific identification criteria for the Chilean population, which will help us determine the stature and biological sex of skeletal remains," says Dr. Ann Ross, an associate professor of sociology and anthropology at NC State and lead author of a paper describing the research.
"My ...
2010-09-14
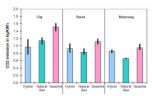
Hybrid cars and those fuelled by natural gas produce significantly less carbon dioxide (CO2) than equivalent vehicles running on gasoline. In the course of a study undertaken on behalf of the Swiss Federal Office for the Environment (FOEN), the results of which were recently published, Empa has investigated the CO2 emission behavior of current hybrid cars. A comparison with gasoline and natural gas fuelled vehicles concludes that hybrid vehicles are the cleanest during inner-city driving whilst natural gas fuelled cars do best on the motorway. When driven in rural areas, ...
2010-09-14
Seamless fabric that can be sprayed on to skin and other surfaces to make clothes, medical bandages and even upholstery will be demonstrated this Thursday, in advance of the Science in Style spray-on fashion show next week at Imperial College London.
Dr Manel Torres is a Spanish fashion designer and academic visitor at Imperial, where he has collaborated with Paul Luckham, Professor of Particle Technology from the Department of Chemical Engineering, to create a seamless material called Fabrican Spray-on fabric that can be sprayed directly onto the body, using aerosol ...
2010-09-14
MIAMI -- September 14, 2010 --There is a significant disparity between knowledge and attitudes on the dangers of skin cancer among male and female medical students in Florida according to a new study by a joint team of researchers from Ben-Gurion University of the Negev and the University of Miami Miller School of Medicine. The study was published in the American Medical Association's Archives of Dermatology.
While their overall knowledge was judged to be satisfactory there was a significant difference between male and female students' knowledge survey scores: 93.1 percent ...
2010-09-14
PROVIDENCE, R.I. [Brown University] — Researchers at Brown University and Women & Infants Hospital have invented the first artificial human ovary, an advance that provides a potentially powerful new means for conducting fertility research and could also yield infertility treatments for cancer patients. The team has already used the lab-grown organ to mature human eggs.
"An ovary is composed of three main cell types, and this is the first time that anyone has created a 3-D tissue structure with triple cell line," said Sandra Carson, professor of obstetrics and gynecology ...
2010-09-14
RICHMOND, Va. (Sept. 14, 2010) – An international team of researchers has identified a risk gene for schizophrenia, including a potentially causative mutation, using genome-wide association data-mining techniques and independent replications.
The results of the research, led by Xiangning Chen, Ph.D., associate professor of psychiatry and human and molecular genetics in Virginia Commonwealth University's School of Medicine and the Virginia Institute for Psychiatric and Behavioral Genetics, and Kenneth S. Kendler, M.D., professor of psychiatry and human and molecular genetics ...
2010-09-14
Researchers from the Congenital Cardiovascular Interventional Study Consortium (CCISC) who evaluated the intermediate and long-term results of stent implantation for aortic coarctation found that cumulative intermediate success was 86%, and cumulative long-term success was 77%. Results of this study appear in the October issue of Catheterization and Cardiovascular Interventions, a journal published by Wiley-Blackwell on behalf of The Society for Cardiovascular Angiography and Interventions.
Coarctation, or narrowing, of the aorta, restricts blood flow to the lower extremities ...
2010-09-14
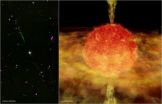
Evidence that a star has recently engulfed a companion star or a giant planet has been found using NASA's Chandra X-ray Observatory. The likely existence of such a "cannibal" star provides new insight into how stars and the planets around them may interact as they age.
The star in question, known as BP Piscium (BP Psc), appears to be a more evolved version of our Sun, but with a dusty and gaseous disk surrounding it. A pair of jets several light years long blasting out of the system in opposite directions has also been seen in optical data. While the disk and jets ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Study shows tranquil scenes have positive impact on brain