(Press-News.org) Washington, D.C. (September 14, 2010) -- A new "on-chip" method for sorting and identifying bacteria has been created by biomedical engineers at Taiwan's National Cheng Kung University. The technique, developed by Hsien-Chang Chang, a professor at the Institute of Biomedical Engineering and the Institute of Nanotechnology and Microsystems Engineering, along with former graduate student I-Fang Cheng and their colleagues, is described in the AIP journal Biomicrofluidics.
Using roughened glass slides patterned with gold electrodes, the researchers created microchannels to sort, trap, and identify bacteria. The technique uses surface enhanced Raman spectroscopy. This type of spectroscopy, says Chang, "is based on the measurement of scattered light from the vibration energy levels of chemical bonds following excitation in a craggy metal surface, which enhances the vibration energy." Different components like proteins or other chemical components on the surface of bacteria become attached to the craggy gold zone; when excited, these components cause representative peaks at different wavelengths, creating spectral "fingerprints."
Although some species of bacteria could show very similar signatures because the components on their surfaces are almost the same, says Chang, bacteria from different genera are distinguishable using the technique.
"In the future, different species of fungi could also be sorted based on their different electrical or physical properties by optimizing conditions such as the flow rate, applied voltage, and frequency," he says. "This portable device could be used for preliminary screening for the pathogenic targets in bacteria-infected blood, urethral irritation, and of raw milk and for food monitoring."
INFORMATION:
The article, " A dielectrophoretic chip with a roughened metal surface for on-chip SERS analysis of bacteria" by I-Fang Cheng (National Cheng Kung University), Chi-Chang Lin (Tunghai University), Dong-Yi Lin and Hsien-Chang Chang (National Cheng Kung University) appears in the journal Biomicrofluidics. http://link.aip.org/link/biomgb/v4/i3/p034104/s1
Journalists may request a free PDF of this article by contacting jbardi@aip.org
ABOUT BIOMICROFLUIDICS
Biomicrofluidics is an online open-access journal published by the American Institute of Physics to rapidly disseminate research in elucidating fundamental physicochemical mechanisms associated with microfluidic and nanofluidic phenomena as well as novel microfluidic and nanofluidic techniques for diagnostic, medical, biological, pharmaceutical, environmental, and chemical applications. See: http://bmf.aip.org/
ABOUT AIP
The American Institute of Physics is a federation of 10 physical science societies representing more than 135,000 scientists, engineers, and educators and is one of the world's largest publishers of scientific information in the physical sciences. Offering partnership solutions for scientific societies and for similar organizations in science and engineering, AIP is a leader in the field of electronic publishing of scholarly journals. AIP publishes 12 journals (some of which are the most highly cited in their respective fields), two magazines, including its flagship publication Physics Today; and the AIP Conference Proceedings series. Its online publishing platform Scitation hosts nearly two million articles from more than 185 scholarly journals and other publications of 28 learned society publishers.
Washington, D.C. (September 14, 2010) -- Some disasters and crises are related to each other by more than just the common negative social value we assign to them. For example, earthquakes, homicide surges, magnetic storms, and the U.S. economic recession are all kindred of a sort, according to a theoretical framework presented in the journal CHAOS, which is published by the American Institute of Physics.
The researchers who developed this framework contend that these four types of events share a precursory development pattern -- a specific change of scale in indicators ...
Washington, D.C. (September 14, 2010) -- Because one of the main bottlenecks in determining the structure of protein molecules is producing good isolated single crystals, improved crystallization techniques would be useful in a wide range of genomics and pharmaceutical research.
Research reported in The Journal of Chemical Physics uses fluorescence correlation spectroscopy (FCS) to investigate the processes at the surface of a growing crystal. By focusing a laser on the crystal surface and measuring the resulting fluorescence, FCS can resolve dimensions as small as a ...
Leading international marine scientists are proposing radical changes in the governance of the world's oceans to rescue them from overfishing, pollution and other human impacts.
Based on a successful experiment in Chile, the researchers say a new approach to marine tenure could help to reverse the maritime 'tragedy of the commons' which has led to the depletion of fish stocks worldwide.
"Marine ecosystems are in decline around the world. New transformational changes in governance are urgently required to cope with overfishing, pollution, global changes, and other drivers ...
Tranquil living environments can positively affect the human brain function, according to researchers at the University of Sheffield.
The research, which was published in the journal NeuroImage, uses functional brain imaging to assess how the environment impacts upon our brain functions.
The findings demonstrated that tranquil environmental scenes containing natural features, such as the sea, cause distinct brain areas to become 'connected' with one another whilst man-made environments, such as motorways, disrupt the brain connections.
The research involved academics ...
INDIANAPOLIS – A new study led by Elizabeth Poposki, Ph.D., assistant professor of psychology in the School of Science at Indiana University-Purdue University Indianapolis, may help employers identify employees who enjoy multitasking and are less inclined to quit jobs involving multitasking. The study presents a new tool developed to measure preference for multitasking, information which may be of interest to bosses who tire of repeatedly hiring and training new employees.
A growing number of individuals must multitask at work and positions requiring a significant amount ...
A record-breaking 429 White-shouldered Ibis Pseudibis davisoni have just been recorded in Cambodia, making the known global population much larger than previously thought. With so many birds remaining in the wild the chances of conservation success are greatly improved – welcome news for this Critically Endangered bird species.
The University of East Anglia (UEA), UK, brought together a group of conservationists for a coordinated survey of 37 roost sites across Cambodia. Participants came from the Cambodian Forestry Administration and General Department for Administration ...
New research from North Carolina State University will help medical examiners and others identify human remains of those killed during the recent earthquake in Chile, as well as the bodies of the "disappeared" who were killed during the Pinochet administration.
"We have developed population-specific identification criteria for the Chilean population, which will help us determine the stature and biological sex of skeletal remains," says Dr. Ann Ross, an associate professor of sociology and anthropology at NC State and lead author of a paper describing the research.
"My ...
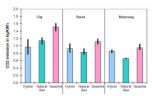
Hybrid cars and those fuelled by natural gas produce significantly less carbon dioxide (CO2) than equivalent vehicles running on gasoline. In the course of a study undertaken on behalf of the Swiss Federal Office for the Environment (FOEN), the results of which were recently published, Empa has investigated the CO2 emission behavior of current hybrid cars. A comparison with gasoline and natural gas fuelled vehicles concludes that hybrid vehicles are the cleanest during inner-city driving whilst natural gas fuelled cars do best on the motorway. When driven in rural areas, ...
Seamless fabric that can be sprayed on to skin and other surfaces to make clothes, medical bandages and even upholstery will be demonstrated this Thursday, in advance of the Science in Style spray-on fashion show next week at Imperial College London.
Dr Manel Torres is a Spanish fashion designer and academic visitor at Imperial, where he has collaborated with Paul Luckham, Professor of Particle Technology from the Department of Chemical Engineering, to create a seamless material called Fabrican Spray-on fabric that can be sprayed directly onto the body, using aerosol ...
MIAMI -- September 14, 2010 --There is a significant disparity between knowledge and attitudes on the dangers of skin cancer among male and female medical students in Florida according to a new study by a joint team of researchers from Ben-Gurion University of the Negev and the University of Miami Miller School of Medicine. The study was published in the American Medical Association's Archives of Dermatology.
While their overall knowledge was judged to be satisfactory there was a significant difference between male and female students' knowledge survey scores: 93.1 percent ...