No support for routine prostate screening, but one-off test at 60 may be beneficial
Research: Screening for prostate cancer: Systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials
2010-09-15
(Press-News.org) Existing evidence from randomised controlled trials does not support routine population screening for prostate cancer, concludes a study published on bmj.com today.
However, a second study also published today suggests that a single test at age 60 could identify men who are most likely to develop and die from prostate cancer. These men could then be monitored more closely, while others could be exempt from further screening.
Prostate cancer is one of the most common cancers among men worldwide. Screening is widely used in many countries, but it remains controversial because experts can't agree whether the benefits of screening outweigh the potential harms and costs of over-diagnosis and over-treatment of healthy men.
In 2006, a review of two randomised controlled trials concluded that there was not enough evidence to support routine prostate cancer screening. Since then, four new trials have been published.
So Professor Philipp Dahm and colleagues at the University of Florida reviewed all six trials, involving 387,286 participants. They found that screening aids in the diagnosis of prostate cancer at an earlier stage, but does not have a significant impact on mortality, and comes at the risk of over-treatment.
The authors say there is insufficient evidence to support actively inviting all men in certain age groups to attend screening for prostate cancer (as happens with breast cancer screening for women), and they suggest men should be better informed about the uncertainties associated with screening.
In the second study, Professor Hans Lilja and colleagues show that a single prostate-specific antigen (PSA) level test at age 60 strongly predicts a man's lifetime risk of diagnosis and death from prostate cancer.
They found that 90% of prostate cancer deaths occurred in men with highest PSA levels at age 60, whereas men with average or low PSA levels had negligible rates of prostate cancer or death by age 85. Their results suggest that at least half of men aged 60 and older might be exempted from further prostate cancer screening, which would reduce over-diagnosis and over-treatment.
In an accompanying editorial, Gerald Andriole, Chief of Urologic Surgery at Washington University School of Medicine, suggests that PSA testing should be tailored to individual risk.
He recommends that young men at high risk of prostate cancer, such as those with a strong family history and higher baseline PSA concentrations, should be followed closely, while elderly men and those with a low risk of disease could be tested less often, if at all. "Approaches such as these will hopefully make the next 20 years of PSA based screening better than the first 20," he says.
INFORMATION: END
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2010-09-15
It is widely known that a healthy lifestyle that includes not smoking, limiting alcohol intake, and maintaining a proper weight reduces disease risk.
In the journal PLoS Medicine, Wei Zheng, M.D., Ph.D., M.P.H., and colleagues at Vanderbilt University Medical Center now report results from a large study quantifying the impact of combining healthy lifestyle factors.
They found that a healthy lifestyle pattern – being normal weight, having low belly fat, participating in regular physical activity, limiting exposure to secondhand cigarette smoke, and consuming higher ...
2010-09-15
Washington, DC, (September 14, 2010) — A new study released today by the American Lung Association, and conducted by researchers at Penn State University, finds that helping smokers quit not only saves lives but also offers favorable economic benefits to states. The study, titled Smoking Cessation: the Economic Benefits, provides a nationwide cost-benefit analysis that compares the costs to society of smoking with the economic benefits of states providing cessation (quit-smoking) coverage. The study comes at an important time, as important cessation benefit provisions ...
2010-09-15
Antibiotics can work miracles, knocking out common infections like bronchitis and tonsillitis. But according to the Center for Disease Control, each year 90,000 people in the U.S. die of drug-resistant "superbugs" ― bacteria like Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA), a deadly form of staph infection resistant to normal antibiotics. Although hospital patients are particularly susceptible as a result of open wounds and weakened immune systems, the bacteria can infect anyone.
Dr. Micha Fridman of Tel Aviv University's Department of Chemistry is now developing the next generation ...
2010-09-15
NEW YORK (Embargoed until September 14, 2010: 5:00 p.m. U.S. Eastern Time)— A new peer-reviewed paper by the Wildlife Conservation Society and other groups reveals an ominous finding: most of the world's last remaining tigers—long decimated by overhunting, logging, and wildlife trade—are now clustered in just six percent of their available habitat. The paper identifies 42 'source sites' scattered across Asia that are now the last hope and greatest priority for the conservation and recovery of the world's largest cat.
The securing of the tiger's remaining source sites ...
2010-09-15
Did I turn off the stove, or did I just imagine it? Memory isn't always reliable. Psychological scientists have discovered all sorts of ways that false memories get created, and now there's another one for the list: watching someone else do an action can make you think you did it yourself.
The team of psychological scientists who found the new way to create false memories weren't setting out to make a big discovery. They were trying to learn more about imagination, another way that false memories get created. But then in an experiment, they found that people who had watched ...
2010-09-15
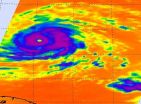
NASA satellites provide infrared images to forecasters that show temperature, and today's imagery of powerful Hurricane Igor showed the storm's perfect form and the warm ocean waters around it that are keeping it fueled. NASA's infrared data also revealed a huge difference of 170 degrees between the cold cloud tops in Hurricane Igor and the warm sea surface temperatures powering it below.
When NASA's Aqua satellite passed over Igor on Sept. 14 at 14:47 UTC (10:47 a.m. EDT) the Atmospheric Infrared Sounder (AIRS) instrument captured icy cold cloud top temperatures in ...
2010-09-15
New research findings from the Université de Montréal reveals that children as young as four are able to understand and use irony. This study, published recently in the British Journal of Developmental Psychology, may impact the way parents communicate with their family.
"Previous studies concluded that irony wasn't understood before the age of eight or ten," says Stephanie Alexander, a postdoctoral student at the Université de Montréal's Department of Social and Preventive Medicine and senior author of the study. "However, these studies were mostly done in a laboratory ...
2010-09-15
OAK RIDGE, Tenn., Sept. 14, 2010 -- As industries and consumers increasingly seek improved battery power sources, cutting-edge microscopy performed at the Department of Energy's Oak Ridge National Laboratory is providing an unprecedented perspective on how lithium-ion batteries function.
A research team led by ORNL's Nina Balke, Stephen Jesse and Sergei Kalinin has developed a new type of scanning probe microscopy called electrochemical strain microscopy (ESM) to examine the movement of lithium ions through a battery's cathode material. The research, "Nanoscale mapping ...
2010-09-15
(Garrison, NY) The most politically charged feature of the health reform law is the mandate that legal residents have health insurance. Within weeks of the law's passage, twenty states had filed lawsuits charging that the mandate is unconstitutional because it gives the federal government more power than it actually has. The state lawsuits are widely expected to reach the Supreme Court next year. Legal scholar Lawrence O. Gostin writes that the health insurance mandate rests on firm legal ground.
Under the mandate, which goes into effect in 2014, the federal government ...
2010-09-15
Students who enter medical school with high debt levels, low scores on the Medical College Admissions Test (MCAT) or who are non-white are more likely to face difficulties that may prevent graduation or hinder acceptance into a residency program if they do graduate, according to a nationwide study of students enrolled in MD programs.
The research, from Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis, is reported Sept. 15 in the Journal of the American Medical Association.
The study of more than 84,000 students who entered U.S. medical schools from 1994-1999 showed ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] No support for routine prostate screening, but one-off test at 60 may be beneficial
Research: Screening for prostate cancer: Systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials