(Press-News.org) A new treatment that treats a subset of stroke patients by combining minimally invasive surgery, an imaging technique likened to "GPS for the brain," and the clot-busting drug t-PA appears to be safe and effective, according to a multicenter clinical trial led by Johns Hopkins researchers.
The novel treatment, detailed for the first time at this week's European Stroke Conference in Hamburg, Germany, was developed for patients with intracerebral hemorrhage (ICH), a bleed in the brain that causes a clot to form within brain tissue. This clot builds up pressure and leaches inflammatory chemicals that can cause irreversible brain damage, often leading to death or extreme disability. The usual treatments for ICH—either general supportive care such as blood pressure control and ventilation, which is considered the current standard of care, or invasive surgeries that involve taking off portions of the skull to remove the clot—have similar mortality rates, ranging from 30 to 80 percent depending on the size of the clot.
Seeking to improve these mortality rates and surviving ICH patients' quality of life, Daniel Hanley, M.D., professor of neurology at the Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine, and his colleagues developed and tested the new treatment on 60 patients at 12 hospitals in the United States, Canada, the United Kingdom and Germany. They compared their results to those of 11 patients who received only supportive care.
After neurologists diagnosed patients in the treatment group with ICH at these hospitals, surgeons drilled dime-sized holes in patients' skulls close to the clot location. Using high-tech neuro-navigational software that provides detailed brain images, the physicians threaded catheters through the holes and directly into the clots. They used these catheters to drip t-PA into the clot for up to three days at one of two doses, either 0.3 mg or 1 mg, every eight hours.
The researchers found that clot size in patients treated with either dose shrunk by more than half, compared to only 1 percent in patients who received only supportive care. Comparison of daily CT scans showed that patients in the treatment group whose catheters were most accurately placed through the longest part of the clot had the most effective clot size reduction.
Those in the treatment group and the supportive care group had about a 10 percent mortality rate at 30 days after treatment, lower than the typically high mortality rates expected for this condition. After following the patients out for six months, the researchers found that the treated patients scored significantly higher on a test that measures the ability to function in daily life compared to those who received supportive care.
Overall, Hanley says, the new treatment appears to be a viable and promising alternative to the current standard treatments of supportive care or invasive surgery.
"We're confirming that patients do recover better if we remove as much of the clot as we can, but gentle removal appears to be key," he says. "Reducing the clot's size with a minimally invasive method seems to be pivotal for optimizing patient recovery."
Hanley and his colleagues plan to continue investigating the treatment in a larger multicenter trial.
INFORMATION:
For more information, go to:
http://www.hopkinsmedicine.org/neurology_neurosurgery/experts/profiles/team_member_profile/3025177BF83694B3005AD5D8BEC128C6/Daniel_Hanley
http://www.hopkinsmedicine.org/neurology_neurosurgery/
http://mistietrial.com/default.aspx
END
The study, commissioned by the National Institute for Health and Clinical Excellence (NICE) and undertaken by the UK Centre for Tobacco Control Studies (UKCTCS), reviewed published studies from between 1990 and 2007 to establish success rates for the NHS smoking cessation services. It found that older smokers are more likely than young smokers to successfully quit, some men appear to be more successful at quitting than women despite the fact that more women attend the smoking cessation services, and more disadvantaged groups face greater challenges when giving up smoking.
The ...
How can someone with perfectly normal hearing become deaf to the world around them when their mind is on something else? New research funded by the Wellcome Trust suggests that focusing heavily on a task results in the experience of deafness to perfectly audible sounds.
In a study published in the journal Attention, Perception, & Psychophysics, researchers at UCL (University College London) demonstrate for the first time this phenomenon, which they term 'inattentional deafness'.
"Inattentional deafness is a common everyday experience," explains Professor Nilli Lavie ...
On May 18th, 2011, The Hampton E-commerce Grant Program approved Markomm, an Internet Marketing Firm, to be one of its approved E-Commerce Service Providers. This allows Hampton, VA based businesses to use Markomms Internet Marketing Services as part of the program. Eligible business can receive up to $6000 of grant money and apply it toward Markomms Internet Marketing Services.
The Hampton IDA along with the assistance of the Hampton Department of Economic Development has created an E-Commerce Grant Program aimed at assisting Hampton businesses in order to optimize ...
How do females select partners? Darwin's initial idea that the fittest males would be the most desirable and would therefore be most likely to secure partners has represented a cornerstone of evolutionary theory since the publication of "The Descent of Man" in 1871. Darwin proposed that secondary sexual characteristics enabled females to see at a glance which male was "best", i.e. best for every female. This male would be the chosen partner as he would pass on the best possible genes to the next generation, thereby increasing the fitness of the species.
Towards the ...
A bacteria which infects people with cystic fibrosis could help combat other antibiotic-resistant microbes, according to a team from Cardiff and Warwick Universities.
Continuous use of existing antibiotics means that resistant bacteria are now causing major health problems all over the world. New antibiotics are urgently needed to combat the emergence of multidrug-resistant bacteria such as the MRSA superbug.
Now a surprising source of hope has emerged in the form of Burkholderia, a group of bacteria which can cause severe lung infections in people with the genetic ...
A team of researchers from the Royal Institute and Observatory of the Navy (ROA) in Cádiz (Spain) has developed a method to track the movement of geostationary objects using the position of the stars, which could help to monitor space debris. The technique can be used with small telescopes and in places that are not very dark.
Objects or satellites in geostationary orbit (GEO) can always be found above the same point on the Equator, meaning that they appear immobile when observed from Earth. By night, the stars appear to move around them, a feature that scientists have ...
This neat and tidy software can help in organizing your thoughts as they day races by, eliminating the problem of finding the notes you know are somewhere on your hard drive. Save all that time spent looking for bank account numbers, PINs, addresses and phone numbers. Now it is cheap and easy to store all your notes, to-do lists, memos and business data in one organized place, so you can find them quickly when you need them. Along with logging your daily activities, so you can effectively track how you use your time.
AlfaPad Notes Organizer uses an intuitive, double-paned ...
Research from the University of Warwick shows a trip to the zoo can boost your child's science and conservation education more than books or classroom teaching alone.
In research conducted at ZSL London Zoo, more than 3,000 school children aged between seven and 14 were asked about their knowledge of animals, habitat and conservation and then tested again after their trip.
The results show that 53% had a positive change in educational or conservation-related knowledge areas, personal concern for endangered species or new empowerment to participate in conservation ...
Halfpricesoft.com(www.halfpricesoft.com) released a new version of its employee attendance and time software, ezTimeSheet. This update is the software developer's response to customers' requests for increased reporting options.
ezTimeSheet software makes it easy and affordable to automate employee attendance management processes and slashes the time to run payroll for small businesses. This employee attendance and time tracking software was designed specifically for small business owners and HR department managers. And the newly released update version is more powerful ...
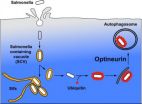
FRANKFURT. Salmonella is widely prevalent in the animal kingdom. The reason we do not suffer from severe intestinal infections very often is due to our body's defence system, which manages to digest invading bacteria. This is why, generally speaking, a healthy human being will only fall ill if he consumes more than 100.000 salmonella bacteria via a contaminated food source, such as eggs or meat. An international team of researchers, led by Prof. Ivan Dikic from the Goethe University in Frankfurt has now found out how body cells recognise salmonella and render it harmless. ...