(Press-News.org) (Santa Barbara, Calif.) –– Scientists at UC Santa Barbara and other institutions say their new research is expected to profoundly affect the field of ecology and can assist the management of ecosystems, including forests, lakes, and oceans. And it's all because of parasites.
The research, published this week in the journal Science, includes parasites in a comprehensive study of ecosystems. By doing so, the scientists say they have revealed new ecological rules.
"The major finding of our research is that all types of animals –– parasites or otherwise –– appear to follow exactly the same rule for how common they are," said Ryan Hechinger, lead author and associate research biologist with the Marine Science Institute at UCSB.
"This includes birds, fishes, insects, crabs, clams, and all the parasites that live inside and on them," said Hechinger. "They all seem to follow the same rule. And the rule is simple. You can predict how common an animal is just by knowing how big an individual is and how high in the food chain it is."
Hechinger explained that body size is important because it determines how much food an animal needs. A given amount of food supports fewer big animals than small animals because each big animal needs more food. The food chain is important because the higher an animal is in the food chain, the less food there is and, therefore, the less common that species is.
According to the scientists, they did something no one has previously done: They went into an ecosystem and paid attention to parasites, treating them as equal players with other animals. "We realized that despite being small, parasites feed high up the food chain and might break the rule that smaller animals are more common," said co-author Kevin Lafferty, ecologist with the U.S. Geological Survey at UCSB.
The data were collected at three estuaries in Southern California and Baja California. The researchers counted and weighed parasites and other animals before documenting that parasites were indeed less common than other small animals.
"Paying attention to parasites was central to the study," said co-author Armand Kuris, professor of zoology at UCSB. "Parasites are at least half of all biodiversity. And they are different in some very basic ways than other life forms. However, ecological science usually ignores them. How can we possibly understand how life works if we don't look at half of the species –– the parasites?
"Considering parasites helped us find the right theory, see the true patterns in nature, and better test the theory," Kuris said. "In addition to body size, the general rule for animal abundance must factor in the food chain and let both small and large animals be top consumers."
The scientists also discovered a second general rule: that the amount of biomass produced by a population does not depend on the body size of the animals in the population, or on what type of animal –– bird, fish, crab, or parasite.
"If this rule is general, it means an aphid population can produce the same amount of biomass as a deer population," said Lafferty. "Furthermore, tapeworms that feed on the deer population produce less biomass than the deer, but can produce the same as a mountain lion population that also feeds on the deer."
"Predicting animal abundance is one of the most basic and useful things ecological science can provide for management and basic research," said Hechinger. "This simple rule helps with that because it may apply to all life forms and can easily be applied to complex ecosystems in the real world."
INFORMATION:
Additional co-authors include Andy Dobson of Princeton University and the Santa Fe Institute, and James Brown of the University of New Mexico.
The research was partly funded by the joint National Science Foundation-National Institutes of Health's Ecology of Infectious Diseases program.
Parasites help reveal new ecological rules
2011-07-22
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
INFORMS: CARE positions disaster relief with promising discipline of humanitarian logistics
2011-07-22
Operations research models developed by a team at the Georgia Institute of Technology helped CARE International pick three locations worldwide to supply relief quickly to victims of earthquakes, floods, and other natural disasters, according to a paper in a journal of the Institute for Operations Research and the Management Sciences (INFORMS®).
"Pre-Positioning of Emergency Items for CARE International" is by Serhan Duran, currently at the Middle East Technical University in Ankara Turkey, and by Marco A. Gutierrez and Pinar Keskinocak of the H. Milton Stewart School ...
Health-care reform must involve psychologists, medical providers, educate patients
2011-07-22
COLUMBIA, Mo. ¬— While some members of Congress and others are trying to repeal the healthcare reform law that was passed in 2010, known as the "Patient Protection and Affordable Care Act," medical providers have begun to implement requirements as the law slowly phases in over the next several years. For reform to be successful, one University of Missouri public health expert has determined that professional associations for psychologists and other medical providers need to be at the forefront of the planning stages, and that everyone, including providers and patients, ...
INFORMS journal announces special issue on using logistics, analytics in humanitarian relief
2011-07-22
In the wake of the devastating Japanese tsunami, the 2010 Haitian earthquake, and the recent threat of pandemic flu, a new issue of the journal Interfaces: The INFORMS Journal on the Practice of Operations Research is dedicated to improving responses to disasters, health crises, and acute public issues, according to the Institute for Operations Research and the Management Sciences (INFORMS®).
The Interfaces special issue on Humanitarian Logistics: Doing Good with Good O.R. is edited by Ozlem Ergun, Pinar Keskinocak, and Julie Swann, the directors of the Georgia Tech ...
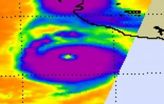
NASA satellite video and images show Dora become a major hurricane
2011-07-22
A new image and video of major Hurricane Dora were released today from NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Md.
Satellites provide a bird's eye view of a hurricane's eye, and NASA noticed Hurricane Dora's eye from several of them. Infrared imagery from NASA's Aqua satellite provided forecasters with a clear view of a cloud-free eye in hurricane Dora as she strengthens near Category 5 status today. Meanwhile the GOES-11 satellite captured a movie of Dora's intensification over the last two days that clearly shows a developing eye.
The Atmospheric Infrared ...
Social media study: Conservatives were top tweeters in 2010 elections
2011-07-22
ANN ARBOR, Mich.---The results of a study on candidates' use of Twitter in the 2010 midterm elections suggest that Republicans and Tea Party members used the social medium more effectively than their Democratic rivals.
The University of Michigan study, among the first to examine the Tea Party's social media strategies, also showed that analyzing Twitter activity can lead to good predictions of election winners.
Various social media tools have become a key part of campaign strategies in recent years. In 2010, nearly a quarter of online adults used social networks including ...
MS research: Myelin influences how brain cells send signals
2011-07-22
COLUMBUS, Ohio – The development of a new cell-culture system that mimics how specific nerve cell fibers in the brain become coated with protective myelin opens up new avenues of research about multiple sclerosis. Initial findings suggest that myelin regulates a key protein involved in sending long-distance signals.
Multiple sclerosis (MS) is an autoimmune disease characterized by damage to the myelin sheath surrounding nerve fibers. The cause remains unknown, and it is a chronic illness affecting the central nervous system that has no cure.
MS has long been considered ...
Smartphone making your eyes tired?
2011-07-22
Rockville, Md. — Several reports indicate that prolonged viewing of mobile devices and other stereo 3D devices leads to visual discomfort, fatigue and even headaches. According to a new Journal of Vision study, the root cause may be the demand on our eyes to focus on the screen and simultaneously adjust to the distance of the content.
Scientifically referred to as vergence-accommodation, this conflict and its effect on viewers of stereo 3D displays are detailed in a recent Journal of Vision article, The Zone of Comfort: Predicting Visual Discomfort with Stereo Displays. ...
UCLA scientists complete first mapping of molecule found in human embryonic stem cells
2011-07-22
Stem cell researchers at UCLA have generated the first genome-wide mapping of a DNA modification called 5-hydroxymethylcytosine (5hmC) in embryonic stem cells, and discovered that it is predominantly found in genes that are turned on, or active.
The finding by researchers with the Eli and Edythe Broad Center of Regenerative Medicine and Stem Cell Research at UCLA may prove to be important in controlling diseases like cancer, where the regulation of certain genes plays a role in disease development.
"Any way you can control genes will be hugely important for human ...
An eye gene colors butterfly wings red
2011-07-22
Red may mean STOP or I LOVE YOU! A red splash on a toxic butterfly's wing screams DON'T EAT ME! In nature, one toxic butterfly species may mimic the wing pattern of another toxic species in the area. By using the same signal, they send a stronger message: DON'T EAT US!
Now several research teams that include Smithsonian scientists in Panama, have discovered that Heliconius butterflies mimic each other's red wing patterns through changes in the same gene.
Not only does this gene lead to the same red wing patterns in neighboring species, it also leads to a large variety ...
U of M researchers may have discovered key to help women fight infections during pregnancy
2011-07-22
MINNEAPOLIS / ST. PAUL (July 21, 2011) – A normal but concerning consequence of pregnancy is the fact that pregnant women are more susceptible to infection. University of Minnesota Medical School researchers have identified the underlying mechanisms for this physiologic immune suppression that may lead to new therapies to help ward off infections during pregnancy.
In pregnancy, immune system suppressing cells (called regulatory T cells) increase in number to protect the baby from attack by the mother's immune system. Because these cells are busy protecting the developing ...