(Press-News.org) Conventional wisdom would say that blocking a hole would prevent light from going through it, but Princeton University engineers have discovered the opposite to be true. A research team has found that placing a metal cap over a small hole in a metal film does not stop the light at all, but rather enhances its transmission.
In an example of the extraordinary twists of physics that can occur at very small scales, electrical engineer Stephen Chou and colleagues made an array of tiny holes in a thin metal film, then blocked each hole with an opaque metal cap. When they shined light into the holes, they found that as much as 70 percent more light came through when the holes were blocked than when they were open.
"The common wisdom in optics is that if you have a metal film with very small holes and you plug the holes with metal, the light transmission is blocked completely," said Chou, the Joseph Elgin Professor of Engineering. "We were very surprised."
Chou said the result could have significant implications and uses. For one, he said, it might require scientists and engineers to rethink techniques they have been using when they want to block all light transmission. In very sensitive optical instruments, such as microscopes, telescopes, spectrometers and other optical detectors, for example, it is common to coat a metal film onto glass with the intention of blocking light. Dust particles, which are unavoidable in metal film deposition, inevitably create tiny holes in the metal film, but these holes have been assumed to be harmless because the dust particles become capped and surrounded by metal, which is thought to block the light completely.
"This assumption is wrong -- the plug may not stop the leakage but rather greatly enhance it," Chou said.
He explained that in his own field of nanotechnology, light is often used in a technique called photolithography to carve ultrasmall patterns in silicon or other materials. Thin metal film patterns on a glass plate serve as a mask, directing light through certain locations of the plate and blocking other locations. Given the new finding, engineers ought to examine whether the mask blocks the light as expected, Chou said.
Conversely, Chou said, the newly discovered "blocking" technique might be used in situations when a boost in light transmission is desired. In near-field microscopy, for example, scientists view extremely fine details by passing light through a hole as tiny as billionths of a meter in diameter. With the new technique, the amount of light passing through the hole -- and thus the amount of information about the object being viewed -- can be increased by blocking the hole.
Chou and colleagues stumbled on the phenomenon of enhanced light transmission through a blocked hole in their research on developing ultrasensitive detectors that sense minute amounts of chemicals, with uses ranging from medical diagnostics to the detection of explosives. These detectors use a thin metal film with an array of holes and metal disks to boost faint signals produced when laser light encounters a molecule, allowing much greater sensitivity in identifying substances.
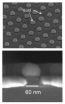
In one of their experimental detectors, the researchers studied transmission of light through an array of tiny holes that were 60 nanometers (billionths of a meter) in diameter and 200 nanometers apart in a gold film that was 40 nanometers thick. Each tiny hole was capped with a gold disk that was 40 percent larger than the hole. The disks sat on top of the holes with a slight gap between the metal surface and the disks.
The researchers pointed a laser at the underside of the film and tested to see if any of the laser light went through the holes, past the caps, and could be detected on the other side. To their surprise, they found that the total light transmission was 70 percent higher with the holes blocked by the metal disks than without blockers. The researchers repeated the same experiment shining the light in the opposite direction -- pointing at the side with the caps and looking for transmitted light under the film -- and found the same results.
"We did not expect more light to get through," Chou said. "We expected the metal to block the light completely."
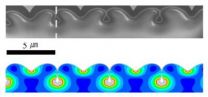
Chou said the metal disk acts as a sort of "antenna" that picks up and radiates electromagnetic waves. In this case, the metal disks pick up light from one side of the hole and radiate it to the opposite side. The waves travel along the surface of the metal and leap from the hole to the cap, or vice versa depending on which way the light is traveling. Chou's research group is continuing to investigate the effect and how it could be applied to enhance the performance of ultrasensitive detectors.
INFORMATION:
The researchers published their findings Oct. 7 in the journal Optics Express, and it quickly became one of the most downloaded papers. In addition to Chou, the team included graduate student Wen-Di Li and postdoctoral researcher Jonathan Hu in the Department of Electrical Engineering. The work is sponsored in part by the Defense Advanced Research Agency and the National Science Foundation.
Blocked holes can enhance rather than stop light going through
2011-11-23
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Martin Banks Adds New Social Security Disability Attorney
2011-11-23
The law firm of Martin Banks has expanded its Social Security Disability and Long-Term Disability practice with the addition of Associate, Maria E. Harris. Ms. Harris focuses her practice exclusively on Social Security and Long-Term Disability law. Prior to joining the firm, Ms. Harris practiced at an international defense firm litigating insurance matters in the areas of life, health, disability and ERISA claims. She has also previously served as a law clerk in the Family Division of the Superior Court of New Jersey.
In 2007, Ms. Harris earned her law degree from Widener ...
Moffitt Cancer Center researchers find men less willing to be screened for cancer
2011-11-23
TAMPA, Fla. -- Although men have higher cancer mortality rates than women, they are less willing to be screened for cancer, according to a study conducted by researchers at Moffitt Cancer Center in Tampa, Fla., and colleagues at Sanoa Consulting LLC, Muscle Shoals, Ala., and the New York University College of Dentistry.
The study, which was funded by the National Institute of Dental and Craniofacial Research/National Institutes of Health, was conducted in New York City, Baltimore, Maryland and San Juan, Puerto Rico, through a random-dial telephone survey of 1,148 adult ...
L-arginine: Supplement tested on fit, athletic men shows no advantage
2011-11-23
One of the most recent, popular supplements for athletes looking to boost performance comes in the form of a naturally-occurring amino acid called L-arginine.
The reason for its popularity is twofold says Scott Forbes, a doctoral student in exercise physiology. "First, L-arginine is a precursor for nitric oxide that is known to improve blood flow, which in turn may aid the delivery of important nutrients to working muscles and assist with metabolic waste product removal. Secondly, L-arginine has been shown to increase growth hormone levels in the blood."
The benefits ...
Use of retail medical clinics rises 10-fold over 2-year period, study finds
2011-11-23
Use of retail medical clinics located in pharmacies and other retail settings increased 10-fold between 2007 and 2009, according to a new RAND Corporation study.
The determining factors in choosing a retail medical clinic over a physician's office were found to be age, health status, income and proximity to the clinic. No link between availability of a primary care physician and retail clinic use was found.
The study was published in the American Journal of Managed Care.
The RAND team used data from a commercially-insured population of 13.3 million to describe ...
Nanowrinkles, nanofolds yield strange hidden channels
2011-11-23
PROVIDENCE, R.I. -- Wrinkles and folds are ubiquitous. They occur in furrowed brows, planetary topology, the surface of the human brain, even the bottom of a gecko's foot. In many cases, they are nature's ingenious way of packing more surface area into a limited space. Scientists, mimicking nature, have long sought to manipulate surfaces to create wrinkles and folds to make smaller, more flexible electronic devices, fluid-carrying nanochannels or even printable cell phones and computers.
But to attain those technology-bending feats, scientists must fully understand the ...
Burton Celebrates 150 Years of the Tuxedo
2011-11-23
Burton, leading British menswear retailer, has revealed several different ways in which the classic tuxedo can be worn. As the Christmas party season approaches, the tux, which is due to celebrate its 150th birthday, can be a key item to own. The tux is best known as a special occasion suit, traditionally worn with a bowtie; however, Burton has found that it's more versatile than one might initially think.
According to Burton, the tux has become a cool and contemporary piece of clothing, and can be worn and styled in a multitude of different ways. For example, the menswear ...
British Airways Launches Flights and Holidays to Mauritius from London Gatwick
2011-11-23
British Airways is changing its Mauritius timetable to give customers an extra day in the sun this winter.
Flights back from the Indian Ocean isle will take off 12 hours later than at present, creating more time for relaxation before travellers have to get their flights to London.
The better timing coincides with the route being switched from Heathrow to Gatwick, further strengthening the airline's premium leisure programme at the airport. British Airways has recently opened the new state-of-the-art terminal extension at Gatwick, which will be home to all British ...
Breast Cancer and the Environment: IOM report release Dec. 7
2011-11-23
Although women have little or no control over some of the risk factors for breast cancer, such as those related to aging and genetics, they may be able to reduce their chances for developing the disease by avoiding certain environmental risks. BREAST CANCER AND THE ENVIRONMENT: A LIFE COURSE APPROACH, a new report from the Institute of Medicine, assesses the breast cancer risk posed by various environmental factors, identifies actions that offer potential to reduce women's risk for the disease, and recommends targets for future research. The report, sponsored by Susan ...
UO chemists develop liquid-based hydrogen storage material
2011-11-23
EUGENE, Ore. -- University of Oregon chemists have developed a boron-nitrogen-based liquid-phase storage material for hydrogen that works safely at room temperature and is both air- and moisture-stable -- an accomplishment that offers a possible route through current storage and transportation obstacles.
Reporting in a paper placed online ahead of publication in the Journal of the American Chemical Society, a team of four UO scientists describes the development of a cyclic amine borane-based platform called BN-methylcyclopentane. In addition to its temperature and stability ...
Rezidor Announces the Radisson Blu Hotel, Belgrade in Serbia
2011-11-23
Rezidor, a rapidly expanding global hotel company, has announced plans for a new hotel, the Radisson Blu Hotel, Belgrade. The property, which features 236 rooms, is already under construction and will welcome the first guests in Q4 2013. It is Rezidor's first hotel in Serbia and the hotel group is now present in 64 countries across Europe, Middle East and Africa.
Kurt Ritter, President and CEO of Rezidor, said: "We are delighted to come to Serbia. The country is an emerging nation, and Belgrade a vibrant, dynamic city with 1.7 million inhabitants where we see a ...