(Press-News.org) LOS ALAMOS, New Mexico -- The idea that one can create a field of science out of thin air, just because of societal and policy need, is a bold concept. But for the emerging field of sustainability science, sorting among theoretical and applied scientific disciplines, making sense of potentially divergent theory, practice and policy, the gamble has paid off.
In the current issue of the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, scientists from Los Alamos National Laboratory, Santa Fe Institute, and Indiana University analyzed the field's temporal evolution, geographic distribution, disciplinary composition, and collaboration structure.
"We don't know if sustainability science will solve the essential problems it seeks to address, but there is a legitimate scientific practice in place now," said Luís Bettencourt of Los Alamos National Laboratory and Santa Fe Institute, first author on the paper, "Evolution and structure of sustainability science."
The team's work shows that although sustainability science has been growing explosively since the late 1980s, only in the last decade has the field matured into a cohesive area of science. Thanks to the emergence of a giant component of scientific collaboration spanning the globe and an array of diverse traditional disciplines, there is now an integrated scientific field of sustainability science as an unusual, inclusive, and ubiquitous scientific practice.
The researchers used an exhaustive literature search to determine if the field can truly be categorized as a legitimate science, using population modeling and documenting technical papers' evolution over time, worldwide author distribution, range of sciences involved, and the collaboration structure of the participants. Many of these techniques form the basis of a new science of science, which allows researchers to analyze and predict the development of scientific and technological fields.
The researchers ask, "How has it been changing, and who are its contributors in terms of geographic and disciplinary composition? Most important, is the field fulfilling its ambitious program of generating a new synthesis of social, biological, and applied disciplines, and is it spanning locations that have both the capabilities and needs for its insights?"
Bettencourt said that they concluded that the field is both applied and basic, spanning worldwide institutions, governments, and corporations, but the key is the collaboration network that evolved in about the year 2000. "This has never been done, starting a worldwide scientific field defined mainly by the need for informed global social practice and policy," Bettencourt said, "but sustainability science shows that it can be done."
###
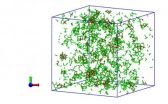
Interactive graphic available: Global collaboration network of sustainability science. The maps show number of authors in cities worldwide (red columns) and their coauthorship networks (green lines). Thicker lines indicate a greater number of collaborations between places. The interactive Google Earth map is available at http://www.santafe.edu/~bettencourt/sustainability/.
Authors: Luís M. A. Bettencourt, Santa Fe Institute and Los Alamos National Laboratory Theoretical Division; and Jasleen Kaur, Center for Complex Networks and Systems Research, School of Informatics and Computing, Indiana University, Bloomington, Indiana.
About Los Alamos National Laboratory
Los Alamos National Laboratory, a multidisciplinary research institution engaged in strategic science on behalf of national security, is operated by Los Alamos National Security, LLC, a team composed of Bechtel National, the University of California, The Babcock & Wilcox Company, and URS for the Department of Energy's National Nuclear Security Administration.
Los Alamos enhances national security by ensuring the safety and reliability of the U.S. nuclear stockpile, developing technologies to reduce threats from weapons of mass destruction, and solving problems related to energy, environment, infrastructure, health, and global security concerns.
Is sustainability science really a science?
Los Alamos and Indiana University researchers say yes
2011-11-24
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
How old yeast cells send off their daughter cells without the baggage of old age
2011-11-24
Kansas City, MO -- The accumulation of damaged protein is a hallmark of aging that not even the humble baker's yeast can escape. Yet, aged yeast cells spawn off youthful daughter cells without any of the telltale protein clumps. Now, researchers at the Stowers Institute for Medical Research may have found an explanation for the observed asymmetrical distribution of damaged proteins between mothers and their youthful daughters.
Reporting in the Nov. 23, 2011, issue of Cell the research team, led by Stowers investigator Rong Li, Ph.D., proposes that the limited mobility ...
Introducing the monarch butterfly genome
2011-11-24
The Monarch butterfly is famous for its ability to travel up to 2,000 miles from North America to central Mexico every fall. Now, it's enjoying fame of a different sort. In the November 23rd issue of Cell, researchers report the full genomic sequence of this iconic butterfly. The new genome is the first for any butterfly. It is also the first complete genome of any long-distance migrant.
"With this genome sequence in hand, we now have an overwhelming number of opportunities to understand the genetic and molecular basis of long-distance migration," says Steven Reppert ...
Is short stature associated with a 'shortage' of genes?
2011-11-24
New research sifts through the entire genome of thousands of human subjects to look for genetic variation associated with height. The results of the study, published by Cell Press in the December issue of the American Journal of Human Genetics, suggest that uncommon genetic deletions are associated with short stature.
Height is a highly heritable trait that is associated with variation in many different genes. "Despite tremendous recent progress in finding common genetic variants associated with height, thus far these variants only explain about 10% of the variation ...
UMMS scientists present draft sequence of monarch butterfly genome
2011-11-24
WORCESTER, Mass. – Each fall millions of monarch butterflies from across the eastern United States use a time-compensated sun compass to direct their navigation south, traveling up to 2,000 miles to an overwintering site in a specific grove of fir trees in central Mexico. Scientists have long been fascinated by the biological mechanisms that allow successive generations of these delicate creatures to transverse such long distances to a small region roughly 300 square miles in size. To unlock the genetic and regulatory elements important for this remarkable journey, neurobiologists ...
Researchers discover clues to developing more effective antipsychotic drugs
2011-11-24
Researchers from Mount Sinai School of Medicine, have identified the pattern of cell signaling induced by antipsychotic drugs in a complex composed of two brain receptors linked to schizophrenia. The discovery should allow researchers to predict the effectiveness of novel compounds for the treatment of schizophrenia and other serious mental disorders and may accelerate the development of better antipsychotic drugs. The findings are published in the November 23 issue of Cell.
Until now, the molecular mechanism through which current treatments for schizophrenia achieve ...
Big pest, small genome
2011-11-24
SALT LAKE CITY, Nov. 23, 2011 – A University of Utah biologist and an international research team decoded the genetic blueprint of the two-spotted spider mite, raising hope for new ways to attack the major pest, which resists pesticides and destroys crops and ornamental plants worldwide.
The voracious mites, which technically are not insects, can eat more than 1,100 plant species – a rare trait. The mites' newly revealed and sequenced genome contains a variety of genes capable of detoxifying pesticides as well as toxins plants use to defend themselves, the scientists ...
Hours of Service Rules for Commercial Truck Drivers Traveling Through Atlanta
2011-11-24
Almost a year ago, the Federal Motor Carrier Safety Administration (FMCSA) proposed new limits on Hours of Service (HOS) rules for commercial drivers. While the intent was to improve highway safety for all who travel by limiting fatigue among truck drivers, the proposed changes have come under fire from trucking advocacy groups as having little impact on highway safety. The proposed changes in hours of service have not yet been finalized.
Existing Hours of Service Limitations for Commercial Drivers
HOS regulations generally apply to all drivers of commercial vehicles. ...
Supercool
2011-11-24
SALT LAKE CITY -- We drink water, bathe in it and we are made mostly of water, yet the common substance poses major mysteries. Now, University of Utah chemists may have solved one enigma by showing how cold water can get before it absolutely must freeze: 55 degrees below zero Fahrenheit.
That's 87 degrees Fahrenheit colder than what most people consider the freezing point of water, namely, 32 F.
Supercooled liquid water must become ice at minus 55 F not just because of the extreme cold, but because the molecular structure of water changes physically to form tetrahedron ...
Dana-Farber/Children's Hospital Boston study identifies possible therapy for radiation sickness
2011-11-24
BOSTON—A combination of two drugs may alleviate radiation sickness in people who have been exposed to high levels of radiation, even when the therapy is given a day after the exposure occurred, according to a study led by scientists from Dana-Farber Cancer Institute and Children's Hospital Boston.
Mouse studies of other potential therapies suggest they would be effective in humans only if administered within a few minutes or hours of radiation exposure, making them impractical for use in response to events involving mass casualties. In contrast, the larger time window ...
UN overhaul required to govern planet's life support system: Experts
2011-11-24
Reducing the risk of potential global environmental disaster requires a "constitutional moment" comparable in scale and importance to the reform of international governance that followed World War II, say experts preparing the largest scientific conference leading up to next June's Rio+20 Earth Summit.
Stark increases in natural disasters, food and water security problems and biodiversity loss are just part of the evidence that humanity may be crossing planetary boundaries and approaching dangerous tipping points. An effective environmental governance system needs to ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Hairdressers could be a secret weapon in tackling climate change, new research finds
Genetic risk for mental illness is far less disorder-specific than clinicians have assumed, massive Swedish study reveals
A therapeutic target that would curb the spread of coronaviruses has been identified
Modern twist on wildfire management methods found also to have a bonus feature that protects water supplies
AI enables defect-aware prediction of metal 3D-printed part quality
Miniscule fossil discovery reveals fresh clues into the evolution of the earliest-known relative of all primates
World Water Day 2026: Applied Microbiology International to hold Gender Equality and Water webinar
The unprecedented transformation in energy: The Third Energy Revolution toward carbon neutrality
Building on the far side: AI analysis suggests sturdier foundation for future lunar bases
Far-field superresolution imaging via k-space superoscillation
10 Years, 70% shift: Wastewater upgrades quietly transform river microbiomes
Why does chronic back pain make everyday sounds feel harsher? Brain imaging study points to a treatable cause
Video messaging effectiveness depends on quality of streaming experience, research shows
Introducing the “bloom” cycle, or why plants are not stupid
The Lancet Oncology: Breast cancer remains the most common cancer among women worldwide, with annual cases expected to reach over 3.5 million by 2050
Improve education and transitional support for autistic people to prevent death by suicide, say experts
GLP-1 drugs like Ozempic could cut risk of major heart complications after heart attack, study finds
Study finds Earth may have twice as many vertebrate species as previously thought
NYU Langone orthopedic surgeons present latest clinical findings and research at AAOS 2026
New journal highlights how artificial intelligence can help solve global environmental crises
Study identifies three diverging global AI pathways shaping the future of technology and governance
Machine learning advances non targeted detection of environmental pollutants
ACP advises all adults 75 or older get a protein subunit RSV vaccine
New study finds earliest evidence of big land predators hunting plant-eaters
Newer groundwater associated with higher risk of Parkinson’s disease
New study identifies growth hormone receptor as possible target to improve lung cancer treatment
Routine helps children adjust to school, but harsh parenting may undo benefits
IEEE honors Pitt’s Fang Peng with medal in power engineering
SwRI and the NPSS Consortium release new version of NPSS® software with improved functionality
Study identifies molecular cause of taste loss after COVID
[Press-News.org] Is sustainability science really a science?Los Alamos and Indiana University researchers say yes