(Press-News.org) If all the UK's discarded wrapping paper and Christmas cards were collected and fermented, they could make enough biofuel to run a double-decker bus to the moon and back more than 20 times, according to the researchers behind a new scientific study.
The study, by scientists at Imperial College London, demonstrates that industrial quantities of waste paper could be turned into high grade biofuel, to power motor vehicles, by fermenting the paper using microorganisms. The researchers hope that biofuels made from waste paper could ultimately provide one alternative to fossil fuels like diesel and petrol, in turn reducing the impact of fossil fuels on the environment.
According to some estimates 1.5 billion cards and 83 square kilometres of wrapping paper are thrown away by UK residents over the Christmas period. They currently go to landfill or are recycled in local schemes. This amount of paper could provide 5-12 million litres of biofuel, say the researchers, enough to run a bus for up to 18 million km.
"If one card is assumed to weigh 20g and one square metre of wrapping paper is 10g, then around 38,300 tonnes of extra paper waste will be generated at Christmas time," said study author Dr Richard Murphy from the Department of Life Sciences at Imperial College London. "Our research shows that it would be feasible to build waste paper-to-biofuel processing plants that give energy back as transport fuel."
Co-author and PhD student Lei Wang, also from Imperial's Department of Life Sciences, said: "The fermentation process could even cope with festive paper and card which has been 'contaminated' with the likes of glitter and sellotape. The cellulose molecules in sellotape would be broken down into glucose sugars and then fermented into ethanol fuel, just like the paper itself. Insoluble items like glitter are easy to filter out as part of the process."
Dr Murphy added: "People should not stop recycling their discarded paper and Christmas cards because at the moment there is no better solution. However, if this technology can be developed further, waste paper might ultimately provide a great, environmentally friendly alternative to fossil fuels. There's more work to do to assess the effectiveness and benefits of the technology, but we think it has significant potential."
In the study, published this month in the Royal Society of Chemistry journal Energy and Environmental Science, the researchers describe how they fermented different types of paper and cardboard in the laboratory to assess how chemically and economically feasible it is to turn them into ethanol fuel. They found that it is not only possible in laboratory experiments but should be economically viable on a large scale as well.
Across the year, around 60 per cent of the UK's waste paper is collected for recycling or other waste management schemes, which equates to around 8 million tonnes. The scientists say that using a well-tested fermentation method and a novel cocktail of efficient and cheap chemical enzymes, their system could be scaled up to the size of existing industrial processing plants and be used to convert 2000 tonnes of waste paper per day into biofuels.
There is already an urgent need for councils to prevent reusable materials like cardboard and paper being sent to landfill sites, saving money and avoiding unnecessary waste, a message echoed by the Mayor of London Boris Johnson in a speech about Recycle for London's Nice Save campaign this week. This new research shows that in addition to recycling, waste materials can be used to generate energy, and some of that can be as valuable vehicle fuel.
High grade ethanol, such as that made in this study, can be (and already is) blended with fossil-based petrol to make a fuel with lower greenhouse gas balance than conventional petrol for cars and vans, and can also be used to power large diesel vehicles like buses and trucks, if modifications are made to their engines. This approach is already used in Brazil, the USA and the EU, among other regions, where ethanol biofuels are being made from sugar cane, grain and other crops. Most of the UK's biofuel is currently imported from abroad.
The authors of this study are now analysing the environmental performance of bioethanol made from waste paper using life cycle assessment (LCA) and comparing it with the conventional transport fuel petrol. LCA is an environmental management tool that evaluates the 'cradle-to-grave' effects of a product for its influence on a range of environmental impact categories, including its ability to contribute to climate change or soil acidification or to cause algal blooms in fresh water.
###
1. Journal reference: Wang L, Sharifzadeh M, Templer R and Murphy RJ
"Technology performance and economic feasibility of bioethanol production from various waste papers" is published in Energy and Environmental Science DOI: 10.1039/C2EE02935A
2. The maths:
(1) Bioethanol predicted from using Christmas waste is 5.2-12 million
L, energy content of ethanol is 22 MJ/L
(2) Economy mileage for a diesel bus is 39 L/100km (Wikipedia info)
Diesel energy content is 38.6 MJ/L
Bus running needs 15 MJ/km
(3) Bus using bioethanol can run 1.47 km/L
(4) Distance of bus running is 7.6-18 million km
(5) Times travelling to moon (distance is 0.38 million km) is 20-47
times
3. Globally, the annual bioethanol production from waste paper and
cardboard has been estimated by Shi et al. to be in the order of 80 billion litres and world annual consumption of paper products in 2010 (400 million tonnes) could potentially amount up to 129 billion litres if all used papers were completely converted to bioethanol. These estimates suggest waste paper derived bioethanol could deliver a considerable potential to displace a useful proportion of petroleum demand. Overall, this comprehensive techno-economic analysis shows that bioethanol production from waste papers can be economically feasible.
Go to work on a Christmas card
UK's wrapping paper and festive cards could provide energy to send a bus to the moon more than 20 times
2011-12-27
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
UK researchers present findings from Kentucky breast cancer patients with disease relapse
2011-12-27
LEXINGTON, Ky. (Dec. 23, 2011) — The University of Kentucky Markey Cancer Center breast oncologist Dr. Suleiman Massarweh and his research team presented findings from their studies on relapse of breast cancer at the San Antonio Breast Cancer Symposium this month.
The two studies aimed to characterize further risk factors for presentation with metastatic disease or risk of early metastatic relapse after initial therapy. Data for each study was collected from 1,089 patients at the UK Markey Cancer Center between January 2007 and May 2011.
The studies showed that patients ...
Cleveland Clinic researcher discovers genetic cause of thyroid cancer
2011-12-27
Friday, December 23, 2011, Cleveland: Cleveland Clinic researchers have discovered three genes that increase the risk of thyroid cancer, which is has the largest incidence increase in cancers among both men and women.
Research led by Charis Eng, M.D., Ph.D., Chair and founding Director of the Genomic Medicine Institute of Cleveland Clinic's Lerner Research Institute, included nearly 3,000 patients with Cowden syndrome (CS) or CS-like disease, which is related to an increased risk of breast and thyroid cancer.
Mutations in the PTEN gene are the foundation of Cowden ...
What are emotion expressions for?
2011-12-27
That cartoon scary face – wide eyes, ready to run – may have helped our primate ancestors survive in a dangerous wild, according to the authors of an article published in Current Directions in Psychological Science, a journal of the Association for Psychological Science. The authors present a way that fear and other facial expressions might have evolved and then come to signal a person's feelings to the people around him.
The basic idea, according to Azim F. Shariff of the University of Oregon, is that the specific facial expressions associated with each particular emotion ...
Pions don't want to decay into faster-than-light neutrinos, study finds
2011-12-27
When an international collaboration of physicists came up with a result that punched a hole in Einstein's theory of special relativity and couldn't find any mistakes in their work, they asked the world to take a second look at their experiment.
Responding to the call was Ramanath Cowsik, PhD, professor of physics in Arts & Sciences and director of the McDonnell Center for the Space Sciences at Washington University in St. Louis.
Online and in the December 24 issue of Physical Review Letters, Cowsik and his collaborators put their finger on what appears to be an insurmountable ...
A radar for ADAR: Altered gene tracks RNA editing in neurons
2011-12-27
PROVIDENCE, R.I. [Brown University] — To track what they can't see, pilots look to the green glow of the radar screen. Now biologists monitoring gene expression, individual variation, and disease have a glowing green indicator of their own: Brown University biologists have developed a "radar" for tracking ADAR, a crucial enzyme for editing RNA in the nervous system.
The advance gives scientists a way to view when and where ADAR is active in a living animal and how much of it is operating. In experiments in fruit flies described in the journal Nature Methods, the researchers ...
New synthetic molecules treat autoimmune disease in mice
2011-12-27
A team of Weizmann Institute scientists has turned the tables on an autoimmune disease. In such diseases, including Crohn's and rheumatoid arthritis, the immune system mistakenly attacks the body's tissues. But the scientists managed to trick the immune systems of mice into targeting one of the body's players in autoimmune processes, an enzyme known as MMP9. The results of their research appear today in Nature Medicine.
Prof. Irit Sagi of the Biological Regulation Department and her research group have spent years looking for ways to home in on and block members of the ...
Faster, more accurate, more sensitive
2011-12-27
Lightning fast and yet highly sensitive: HHblits is a new software tool for protein research which promises to significantly improve the functional analysis of proteins. A team of computational biologists led by Dr. Johannes Söding of LMU's Genzentrum has developed a new sequence search method to identify proteins with similar sequences in databases that is faster and can discover twice as many evolutionarily related proteins as previous methods. From the functional and structural properties of the identified proteins conclusions can then be drawn on the properties of ...
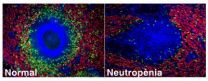
Discovered the existence of neutrophils in the spleen
2011-12-27
This release is available in Spanish.
Barcelona, 23rd of December 2011.- For the first time, it has been discovered that neutrophils exist in the spleen without there being an infection. This important finding made by the research group on the Biology of B Cells of IMIM (Hospital del Mar Research Institute) in collaboration with researchers from Mount Sinai in New York, has also made it possible to determine that these neutrophils have an immunoregulating role.
Neutrophils are the so-called cleaning cells, since they are the first cells to migrate to a place ...
Study links quality of mother-toddler relationship to teen obesity
2011-12-27
COLUMBUS, Ohio – The quality of the emotional relationship between a mother and her young child could affect the potential for that child to be obese during adolescence, a new study suggests.
Researchers analyzed national data detailing relationship characteristics between mothers and their children during their toddler years. The lower the quality of the relationship in terms of the child's emotional security and the mother's sensitivity, the higher the risk that a child would be obese at age 15 years, according to the analysis.
Among those toddlers who had the lowest-quality ...
Memo to pediatricians: Allergy tests are no magic bullets for diagnosis
2011-12-27
An advisory from two leading allergists, Robert Wood of the Johns Hopkins Children's Center and Scott Sicherer of Mt. Sinai Hospital in New York, urges clinicians to use caution when ordering allergy tests and to avoid making a diagnosis based solely on test results.
In an article, published in the January issue of Pediatrics, the researchers warn that blood tests, an increasingly popular diagnostic tool in recent years, and skin-prick testing, an older weapon in the allergist's arsenal, should never be used as standalone diagnostic strategies. These tests, Sicherer ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
The RESIL-Card tool launches across Europe to strengthen cardiovascular care preparedness against crises
Tools to glimpse how “helicity” impacts matter and light
Smartphone app can help men last longer in bed
Longest recorded journey of a juvenile fisher to find new forest home
Indiana signs landmark education law to advance data science in schools
A new RNA therapy could help the heart repair itself
The dehumanization effect: New PSU research examines how abusive supervision impacts employee agency and burnout
New gel-based system allows bacteria to act as bioelectrical sensors
The power of photonics
From pioneer to leader: Alex Zhavoronkov chairs precision aging discussion and presents Luminary Award to OpenAI president at PMWC 2026
Bursting cancer-seeking microbubbles to deliver deadly drugs
In a South Carolina swamp, researchers uncover secrets of firefly synchrony
American Meteorological Society and partners issue statement on public availability of scientific evidence on climate change
How far will seniors go for a doctor visit? Often much farther than expected
Selfish sperm hijack genetic gatekeeper to kill healthy rivals
Excessive smartphone use associated with symptoms of eating disorder and body dissatisfaction in young people
‘Just-shoring’ puts justice at the center of critical minerals policy
A new method produces CAR-T cells to keep fighting disease longer
Scientists confirm existence of molecule long believed to occur in oxidation
The ghosts we see
ACC/AHA issue updated guideline for managing lipids, cholesterol
Targeting two flu proteins sharply reduces airborne spread
Heavy water expands energy potential of carbon nanotube yarns
AMS Science Preview: Mississippi River, ocean carbon storage, gender and floods
High-altitude survival gene may help reverse nerve damage
Spatially decoupling active-sites strategy proposed for efficient methanol synthesis from carbon dioxide
Recovery experiences of older adults and their caregivers after major elective noncardiac surgery
Geographic accessibility of deceased organ donor care units
How materials informatics aids photocatalyst design for hydrogen production
BSO recapitulates anti-obesity effects of sulfur amino acid restriction without bone loss
[Press-News.org] Go to work on a Christmas cardUK's wrapping paper and festive cards could provide energy to send a bus to the moon more than 20 times