(Press-News.org) Copenhagen, Denmark – Important progress has been achieved towards including genomic-level information in the data made freely available through GBIF.
Successful alignment of informatics standards for recording species occurrences and gene-sequence descriptions has opened up new possibilities for integrating the different types of data.
The mapping of three standards was completed at a GBIF-led workshop in Oxford, United Kingdom bringing together experts from Europe, the United States, China and Japan.
A testing programme will shortly begin to bring data from several repositories of genomic information into the GBIF network, using adaptations of the Darwin Core (DwC) standard for sharing biodiversity data.
The developments will fulfill an objective of GBIF's Strategic Plan 2012-16, which calls for the network to accommodate new types of data, in order to give access to information on the estimated 90 per cent of the world's biodiversity still to be discovered – the currency of which will largely be genomic information.
The workshop hosted by Oxford University's e-Research Centre continued the collaboration between GBIF and the Genomics Standards Consortium (GSC), an international community promoting mechanisms to standardize descriptions of genomes and the environmental context in which they occur.
The small group of experts succeeded in completing the mapping or aligning of the Darwin Core, favoured standard for publishing specimen or observation data through GBIF, with the Minimum Information about any (x) Sequence (MIxS), a standard for genomic data developed by the GSC.
The workshop also successfully mapped MIxS with the proposed standard of the DNA Bank Network, known as ABCDDNA.
Two extensions to the Darwin Core Archive (DwC-A) were prototyped, enabling genomic biodiversity data to be published to the GBIF network. The intention is to test this new capability through the following data repositories:
The World Federation of Culture Collections; WFCC is already a GBIF Associate Participant, and its Beijing-based data centre, the World Data Centre for Microorganisms (WDCM), is developing the WFCC Global Catalogue of Microorganisms;
The Moorea Biocode Project, which is creating the first comprehensive inventory of all non-microbial life in a complex tropical ecosystem on a Pacific island, including construction of a library of genetic markers and physical identifiers for every species of plant, animal and fungi;
SILVA, a project based in Germany which provides up to date, quality controlled databases of aligned rRNA sequences from the Bacteria, Archaea and Eukarya domains;
The MicrobeDB.jp project including MEO, which is supported by National Bioscience Database Center (NBDC), Japan;
MG-RAST, a US-based automated analysis platform providing quantitative insights into microbial populations based on sequence data; and
megx.net, a site providing integrated access to environmental and (meta)genomic data for marine microbial ecology.
Commenting on the progress achieved at the workshop, GBIF's Executive Secretary Donald Hobern said, "One of the great challenges for GBIF, and for our many partners around the world, is to help to unify data from different domains to enable researchers to ask new questions, and to ensure that we have access to all relevant resources to understand biodiversity and interactions between biodiversity, human activity and changing environments.
"This workshop gives us the opportunity to make these connections for a wide range of important datasets and positions us all to handle vast amounts of genomic data in future years."
Further information on specific workshop outcomes is available through a new group on the GBIF Community Site at http://community.gbif.org/pg/groups/22216/genomic-biodiversity-data/.
The workshop was a collaboration with the Research Coordination Network for the GSC (RCN4GSC) project, funded by the US National Science Foundation, which is promoting the integration of genomic standards with ecological and species level standards through a series of workshops.
Steps were also taken at the workshop to translate Darwin Core terms into Japanese and Chinese, taking advantage of the participation of experts from those two countries.
INFORMATION:
For further information, contact:
Éamonn Ó Tuama
GBIF Secretariat
eotuama@gbif.org
END
NEW YORK, March 14, 2012 – A new research survey conducted by the Center for the Study of Asian American Health at NYU Langone Medical Center shows the Bangladeshi community in New York City experiences numerous barriers to diabetes care because of limited English proficiency and lack of diabetes awareness. The study, published in the March 2012 issue of the American Journal of Public Health, also found the Bangladeshi community has an interest in participating in community health programs for diabetes prevention and care.
"We need to improve diabetes prevention, and ...
WASHINGTON, March 14, 2012 — The latest episode in the American Chemical Society's (ACS) award-winning "Global Challenges/Chemistry Solutions" podcast series describes the development of a new test that could help track down and prosecute terrorists.
Amid concerns about the threat of terrorist attacks, scientists have been seeking better protection for the U.S. and other nations. One such team has developed a technique that could help authorities catch terrorists and put them out of business. A report on the development appeared in ACS' journal Analytical Chemistry, ...
Scientists at Johannes Gutenberg University Mainz (JGU) in Germany have developed a new method of observing individual proteins. Detailed knowledge of the dynamics of proteins is necessary in order to understand the related biological processes that occur on the molecular level. To date, this information has been obtained by means of labeling proteins with fluorescent substances, but unfortunately this changes the proteins under investigation and thus influences the biological processes that are to be observed. "Our method allows live tracking of individual proteins without ...
The reputation developed by Jamaica Blue Mountain Coffee has made it one of the most desirable and expensive coffees in the world. Blue Mountain coffee from Jamaica is known to have a mild and balanced flavor and lack the bitterness often found in lesser coffees. J. Martinez & Company is one of few companies given the right to import Jamaica Blue Mountain coffee.
Blue Mountain Coffee is protected by a global certification mark, meaning that steps have been taken to ensure that only authentic Blue Mountain coffee, grown in a specific region of the Blue Mountains of ...
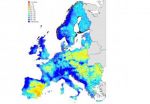
A new assessment of available water resources, published today by the Joint Research Centre (JRC), reveals that large areas in Spain and Eastern Europe have on average less than 200 mm freshwater available every year while the demand for water is three to ten times higher. The report 'Current Water Resources in Europe and Africa' shows variations in yearly freshwater generation from 10 mm to over 500 mm for Europe and from less than 0.1 mm to over 500 mm for Africa. The report outlines existing uncertainties and points to further research efforts needed for improved water ...
CORAL GABLES, FL (March 14, 2012)--Convincing speeches are central to campaigning for elected office, but do our voices affect how we select our leaders? A newly-published paper in Proceedings of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences shows that men and women vote for male and female candidates with lower-pitched voices. Men and women with lower voices were also found to be perceived as more competent, stronger, and more trustworthy. Each of these attributes is known to influence voters.
"Our study asks how voice pitch influences electability, and to my knowledge is ...
NEW YORK (March 14, 2012) -- Nationwide ambulance use by patients suffering from a stroke has not changed since the mid-1990s, even though effective stroke treatments are now available. In a study published in this week's Journal of the American Medical Association (JAMA), researchers at NewYork-Presbyterian Hospital/Weill Cornell Medical Center found that the number of stroke victims transported via ambulance has remained relatively static over the years, highlighting the need for more education about stroke symptoms and the importance of early intervention.
The study, ...
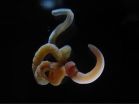
WOODS HOLE, MA—The origin of the exquisitely complex vertebrate brain is somewhat mysterious. "In terms of evolution, it basically pops up out of nowhere. You don't see anything anatomically like it in other animals," says Ariel Pani, an investigator at the Marine Biological Laboratory (MBL) in Woods Hole and a graduate student at the University of Chicago.
But this week in the journal Nature, Pani and colleagues report finding some of the genetic processes that regulate vertebrate brain development in (of all places) the acorn worm, a brainless, burrowing marine invertebrate ...
MAYWOOD, Il. -- A Loyola University Chicago Stritch School of Medicine study has revealed details of the complex molecular process involving a protein that enables cancer cells to establish tumors in distant parts of the body.
The finding could lead the way to new drugs to prevent breast cancer and other cancers from spreading to new sites.
The study by Adriano Marchese, PhD and colleagues is published in the March 16 issue of the Journal of Biological Chemistry, and is now available online.
The study involves a molecule on the surface of cells called CXCR4. There is ...
COLUMBUS, Ohio – Researchers have designed a new version of a labor-tracking tool for pregnant women that they predict could reduce the use of hormonal intervention during labor and lower the number of cesarean sections performed on low-risk, first-time mothers.
The tool, called a partograph, takes into account the most recent research findings that suggest labor is not a linear process, but is instead slower during earlier labor and accelerates gradually as labor advances. A diagnosis of abnormally slow labor is the No. 1 reason that C-sections are performed in low-risk ...