(Press-News.org) SAN DIEGO -- Obesity appears to significantly increase the risk of death tied to sleeping pills, nearly doubling the rate of mortality even among those prescribed 18 or fewer pills in a year, researchers reported Friday.
"Obesity emerged as a marker of increased vulnerability," said Robert Langer, M.D., M.P.H., at the annual American Heart Association's Epidemiology and Prevention | Nutrition, Physical Activity and Metabolism 2012 Scientific Sessions in San Diego.
"The associations between sleeping pills and increased mortality were present, and relatively stronger, even in people aged 18 to 54," said Dr. Langer, a family physician and epidemiologist with the Jackson Hole Center for Preventive Medicine in Jackson, Wyo.
"Obese patients appear particularly vulnerable, perhaps through interaction with sleep apnea," said study co-author Daniel Kripke, M.D., a psychiatrist with Scripps Clinic's Viterbi Family Sleep Center in San Diego.
He noted that sleeping pills were previously associated with more and longer pauses in breathing in people with sleep apnea.
Among obese patients, use of sleeping pills was associated with about one extra death per year for every 100 people who were prescribed the medications, Dr. Langer said.
Additionally, men who took sleeping pills were about twice as likely to die as women who received the medications, after accounting for other factors, he said.
Friday's findings were the latest to emerge from a Scripps Clinic-led study of almost 40,000 patients, which was initially published in late February in the open-access online journal BMJ Open.
(View the paper here: http://bmjopen.bmj.com/content/2/1/e000850.full)
The research was the first to show that eight of the most commonly used hypnotic drugs were associated with increased hazards of mortality and cancer, including the popularly prescribed medications zolpidem (known by the brand name Ambien) and temazepam (also known as Restoril), Dr. Kripke said.
Those drugs had been thought to be safer than older hypnotics because of their shorter duration of action but were found to have associations with excess deaths no different from the older drugs they have largely replaced.
In order to eliminate the possibility that other factors led to the results, study participants who were prescribed sleeping pills were matched with control patients of similar ages, gender and health who did not receive hypnotics.
The newest findings were delivered by Dr. Langer during an oral session at the American Heart Association conference that focused on drug safety.
For obese patients in the study who had an average body mass index of 38.8, the risk of death was 8.1 times higher on average among those who were prescribed the smallest number of pills (18 or fewer annually) when compared with similar study participants who did not take the medications. The mortality rate was 9.3 times higher on average among obese patients receiving the largest number of pills (132 or more annually).
Death was 4.6 times more likely on average among all patients who received any amount of sleeping pills.
The study cast a shadow over a growing segment of the pharmaceutical industry that expanded by 23 percent in the United States from 2006 to 2010 and generated about $2 billion in annual sales.
Using data stored in an electronic medical record that has been in place for more than a decade, the researchers obtained information on almost 40,000 patients cared for by a large integrated health system in the northeastern United States.
The research included 10,531 sleeping pill users who were prescribed the medications for an average of 2.5 years and 23,674 control participants who were not prescribed the drugs. Information came from outpatient clinic visits conducted between Jan. 1, 2002, and Sept. 30, 2006.
"It is important to note that our results are based on observational data, so even though we did everything we could to ensure their validity, it's still possible that other factors explain the associations," said co-author Lawrence E. Kline, D.O., who is medical director of the Viterbi Family Sleep Center. "We hope our work will spur additional research in this area using information from other populations."
Funding for the study came from the Scripps Health Foundation and other philanthropic sources.
The research should prompt physicians to consider alternatives to hypnotic medications, Dr. Kline said.
Clinicians at the Viterbi Family Sleep Center focus on cognitive therapy that teaches patients to better understand the nature of sleep. For example, some people suffering from insomnia might require less than the eight hours of sleep commonly recommended for each night.
Patients also can benefit from practicing good sleeping habits and relaxation, as well as taking advantage of the body's natural clock, which is driven by the rising and setting of the sun, Dr. Kline said. "Understanding how to use the circadian rhythm is a very powerful tool that doesn't require a prescription," he said.
When insomnia results from emotional problems such as depression, doctors should treat the psychological disorder rather than prescribe sleeping pills that could prove to be harmful, Dr. Kripke said.
###
ABOUT SCRIPPS HEALTH
Founded in 1924 by philanthropist Ellen Browning Scripps, Scripps Health is a $2.5 billion non-profit community healthcare system based in San Diego, Calif. Scripps treats a half-million patients annually through the dedication of 2,600 affiliated physicians and
13,000 employees among its five acute-care hospital campuses, home health care services, and an ambulatory care network of physician offices and 23 outpatient centers and clinics. Scripps is also at the forefront of clinical research, genomic medicine, wireless health and graduate medical education. With three highly respected graduate medical education programs, Scripps is a longstanding member of the Association of American Medical Colleges. More information can be found at www.scripps.org.
Obesity raises death risk tied to sleeping pills
New findings delivered at American Heart Association meeting also show heightened risk in men and young adults
2012-03-19
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
NASA sees cyclone Lua strengthening for March 17 landfall
2012-03-19
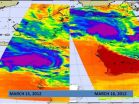
Northern Australia's Pilbara coast is under warnings, alerts and watches as powerful Cyclone Lua nears for a landfall. NASA's Aqua satellite has been providing infrared, visible and microwave data on Lua that have shown forecasters the storm is strengthening on its approach to land.
Two of the most recent infrared images of Cyclone Lua were captured from the Atmospheric Infrared Sounder (AIRS) instrument onboard NASA's Aqua satellite. The AIRS instrument captured infrared images of Cyclone Lua on March 15 at 1741 UTC and March 16 at 0553 UTC. The later image appeared ...
Top Los Angeles Appliance Repair Company, AM PM Appliance Repair, is now Offering Specialty Services for High End Appliances
2012-03-19
There are quite a few things around the house that many take for granted, no matter how often they are used. Individuals will find themselves enjoying the features and utility of high end appliances to cook their food, clean dishes, and help to wash clothes. When these appliances begin to break down, it is going to put an immediate halt to almost everything in the household. For locals that are going to need these devices back up in working condition as quickly and affordably as possible, the leading Los Angeles appliance repair company, AM PM, is now offering specialty ...
Closing hole in the heart no better than drugs in preventing strokes
2012-03-19
MAYWOOD, Il. -- Loyola University Medical Center is one of the major enrollers in a landmark clinical trial that found that plugging a hole in the heart works no better than drugs in preventing strokes.
The study is published in the New England Journal of Medicine. Loyola enrolled 24 patients, one of the highest patient enrolments in the multicenter trial, and more than any other Chicago-area hospital. Principal investigators at the Loyola site are stroke specialist Dr. Michael Schneck and interventional cardiologist Dr. Fred Leya.
About 1 in 4 adults has a small hole ...
2012 Internal Medicine Residency match virtually unchanged from 2011
2012-03-19
PHILADELPHIA -- The number of U.S. medical student seniors at medical schools choosing internal medicine residencies leveled in 2012 after two years of significant increases. According to the 2012 National Resident Matching Program, 2,941 U.S. medical school seniors matched internal medicine, nearly unchanged from 2011 when 2,940 matched internal medicine.
"After seeing increases in 2010 and 2011 for the internal medicine residency match for U.S. medical students, we are disappointed that there was not a bigger increase this year," said Virginia L. Hood, MBBS, MPH, FACP, ...
Mesquite trees displacing Southwestern grasslands
2012-03-19
As the desert Southwest becomes hotter and drier, semi-arid grasslands are slowly being replaced by a landscape dominated by mesquite trees, such as Prosopis velutina, and other woody shrubs, a team of University of Arizona researchers has found.
In a "leaf-to-landscape" approach, the team combined physiological experiments on individual plants and measurements across entire ecosystems to quantify how well grasslands, compared to mesquite trees and woody shrubs, cope with heat and water stress across seasonal precipitation periods.
"Our results show that even the smallest ...
Researchers reveal how a single gene mutation leads to uncontrolled obesity
2012-03-19
Washington, D.C. -- Researchers at Georgetown University Medical Center have revealed how a mutation in a single gene is responsible for the inability of neurons to effectively pass along appetite suppressing signals from the body to the right place in the brain. What results is obesity caused by a voracious appetite.
Their study, published March 18th on Nature Medicine's website, suggests there might be a way to stimulate expression of that gene to treat obesity caused by uncontrolled eating.
The research team specifically found that a mutation in the brain-derived ...
Need for speed
2012-03-19
Like any law-abiding train passenger, a molecule called oskar RNA carries a stamped ticket detailing its destination and form of transport, scientists at the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL) in Heidelberg, Germany, have found. They show that for this molecule, moving in the right direction isn't enough: speed is of the essence. Their study, published online today in Nature Structural & Molecular Biology, also provides clues as to how a single molecule could receive tickets for different destinations, depending on what type of cell it is in.
For a fruit fly ...
Miami Defense Attorney Diana Gonzalez Runs for Judge
2012-03-19
Ferrer Shane, PL is proud to announce that one of its attorneys, Diana E. Gonzalez, is running for Miami-Dade County Court Judge.
Starting her career in 2004, Diana Gonzalez was rapidly promoted up the ranks in the Public Defender's Office, first handling misdemeanor charges, then defending young people in the juvenile division, to ultimately defending clients charged with the most serious felonies - all in the span of just five years, trying everything from a traffic ticket to a murder case.
Having traveled abroad with the U.S. Department of Defense and with USAID ...
New insight into mechanisms behind autoimmune diseases suggests a potential therapy
2012-03-19
LA JOLLA, Calif., March 18, 2012 – Autoimmune diseases, such as Type I diabetes and rheumatoid arthritis, are caused by an immune system gone haywire, where the body's defense system assaults and destroys healthy tissues. A mutant form of a protein called LYP has been implicated in multiple autoimmune diseases, but the precise molecular pathway involved has been unknown. Now, in a paper published March 18 in Nature Chemical Biology, researchers at Sanford-Burnham Medical Research Institute (Sanford-Burnham) show how the errant form of LYP can disrupt the immune system. ...
UMass Amherst theoretical physicists find a way to simulate strongly correlated fermions
2012-03-19
AMHERST, Mass. – Combining known factors in a new way, theoretical physicists Boris Svistunov and Nikolai Prokof'ev at the University of Massachusetts Amherst, with three alumni of their group, have solved an intractable 50-year-old problem: How to simulate strongly interacting quantum systems to allow accurate predictions of their properties.
It could open the door to practical superconductor applications, as well as to solving difficult "many-body" problems in high-energy physics, condensed matter and ultra-cold atoms.
The theoretical breakthrough by Prokof'ev and ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
White House autism briefing linked to swift shifts in prescribing patterns, study finds
Specialist palliative care can save the NHS up to £8,000 per person and improves quality of life
New research warns charities against ‘AI shortcut’ to empathy
Cannabis compounds show promise in fighting fatty liver disease
Study in mice reveals the brain circuits behind why we help others
Online forum to explore how organic carbon amendments can improve soil health while storing carbon
Turning agricultural plastic waste into valuable chemicals with biochar catalysts
Hidden viral networks in soil microplastics may shape the future of sustainable agriculture
Americans don’t just fear driverless cars will crash — they fear mass job losses
Mayo Clinic researchers find combination therapy reduces effects of ‘zombie cells’ in diabetic kidney disease
Preventing breast cancer resistance to CDK4/6 inhibitors using genomic findings
Carbon nanotube fiber ‘textile’ heaters could help industry electrify high-temperature gas heating
Improving your biological age gap is associated with better brain health
Learning makes brain cells work together, not apart
Engineers improve infrared devices using century-old materials
Physicists mathematically create the first ‘ideal glass’
Microbe exposure may not protect against developing allergic disease
Forest damage in Europe to rise by around 20% by 2100 even if warming is limited to 2°C
Rapid population growth helped koala’s recovery from severe genetic bottleneck
CAR-expressing astrocytes target and clear amyloid-β in mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease
Unique Rubisco subunit boosts carbon assimilation in land plants
Climate change will drive increasing forest disturbances across Europe throughout the next century
Enhanced brain cells clear away dementia-related proteins
This odd little plant could help turbocharge crop yields
Flipped chromosomal segments drive natural selection
Whole-genome study of koalas transforms how we understand genetic risk in endangered species
Worcester Polytechnic Institute identifies new tool for predicting Alzheimer’s disease
HSS studies highlight advantages of osseointegration for people with an amputation
Buck Institute launches Healthspan Horizons to turn long-term health data into Actionable healthspan insights
University of Ottawa Heart Institute, the University of Ottawa and McGill University launch ARCHIMEDES to advance health research in Canada
[Press-News.org] Obesity raises death risk tied to sleeping pillsNew findings delivered at American Heart Association meeting also show heightened risk in men and young adults