(Press-News.org) Bethesda, Md. -- Late gestation is a busy time for babies getting ready for life outside the womb, particularly for functions critical to life such as breathing and maintaining an adequate heartbeat. These two functions are connected in mature infants and healthy people throughout life, so measuring their level of connectedness can give doctors a cue about whether an infant is ready to head home or needs to remain in the care of the neonatal intensive care unit (NICU). Current methods to analyze this connection are not yet fully developed, leaving doctors and nurses without an optimal way to deal with periodically missing data or natural variations in breathing or heartbeat. Now, however, researchers in Virginia have found a way around this problem by using a new analytical method that looks for so-called cardiorespiratory interaction using individual breaths and heartbeats and relating the two in time. The findings shed light on which infants may be mature enough to leave the NICU, showing that postnatal age seems to be an indicator of maturity, but birth weight or gestational age at birth are not.
The article is entitled "Breath-By-Breath Analysis of Cardiorespiratory Interaction for Quantifying Developmental Maturity in Premature Infants." It appears in the current edition of the Journal of Applied Physiology, published by the American Physiological Society.
Methodology
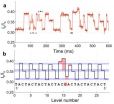
The researchers collected data from the bedside monitors of 1,202 infants cared for in the University of Virginia NICU from January 2009 to June 2011. This data included both electrocardiogram waveforms (an indicator of heartbeats) and chest impedance signals (an indicator of breaths) from both infants considered to have very low birth weights and those with normal birth weights. The researchers paired these two measures in sliding four minute windows, using software to determine whether patterns in breathing correlated with patterns in heartbeats. They also collected other data on these patients, including gestational age at birth (a measure of prematurity), postnatal age (length of time after birth), and age at discharge from the hospital.
Results
The researchers were able to gather 34,600 breathing and heartbeat records for the 1,202 patients, corresponding to an average of 13 days of data for each infant. Their results showed that their analytical method was useful for identifying the link between breathing and heartbeat in this population. Findings revealed that cardiorespiratory interaction steadily increased with each infant's postnatal age. Surprisingly, researchers found no correlation between cardiorespiratory interaction and either birth weight or gestational age at birth, two factors often used to gauge infant maturity. The degree of cardiorespiratory interaction increased over time before the attending physician's decision to discharge each baby from the hospital without respiratory support or cardiorespiratory monitoring, suggesting that each infant's brainstem—a critical structure that controls many functions vital to life—was maturing over time.
Importance of the Findings
These findings suggest that by coupling individual breaths to heartbeats, the researchers were able to avoid the pitfalls of earlier methods. The analytical method used by this research team could be useful for monitoring whether premature infants have developed enough to head home from the hospital without complications.
"Since coupling of organs is correlated with good health, continuously measuring cardiorespiratory interaction may provide early detection of subacute, potentially catastrophic illness. Future studies should test the hypothesis that falling cardiorespiratory interaction precedes clinically evident deterioration," the authors say.
###
Study Team
The study was conducted by Matthew T. Clark, and John L. Hudson of the University of Virginia; Craig G. Rusin, Brooke D. Vergales, Alix Paget-Brown, John Kattwinkel, Douglas E. Lake, and J. Randall Moorman of the University of Virginia Health System; and Hoshik Lee and John B. Delos of the College of William and Mary.
The work was supported by an NICHD GO (Grand Opportunities) Grant.
NOTE TO EDITORS: The article is available online at http://bit.ly/yLip88. For additional information please contact Donna Krupa at dkrupa@the-aps.org, @Phyziochick, or 301-634-7209.
Physiology is the study of how molecules, cells, tissues and organs function to create health or disease. The American Physiological Society (APS; www.the-APS.org/press) has been an integral part of the discovery process for 125 years. To keep up with the science, follow @Phyziochick on Twitter.
New analysis of premature infants' heartbeats, breathing could be cues for leaving NICU
2012-03-27
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Tiny reader makes fast, cheap DNA sequencing feasible
2012-03-27
Researchers have devised a nanoscale sensor to electronically read the sequence of a single DNA molecule, a technique that is fast and inexpensive and could make DNA sequencing widely available.
The technique could lead to affordable personalized medicine, potentially revealing predispositions for afflictions such as cancer, diabetes or addiction.
"There is a clear path to a workable, easily produced sequencing platform," said Jens Gundlach, a University of Washington physics professor who leads the research team. "We augmented a protein nanopore we developed for ...
Wind energy enhancement: UC research establishes real-world wind turbine performance metrics
2012-03-27
VIDEO:
This shows a simulation of wind turbine performance.
Click here for more information.
The production of wind-derived renewable energy is growing, and so, it's important to help wind farm owners operate at higher efficiencies with lower costs.
In fact, figures from the World Wind Energy Association report that installed global capacity for wind-energy production was approximately 240,000 megawatts of power in 2011, up nearly ten fold since 2001.
That growth, which ...
Geologists correct a rift in Africa
2012-03-27
EAST LANSING, Mich. — The huge changes in the Earth's crust that influenced human evolution are being redefined, according to research published today in Nature Geoscience.
The Great Rift Valley of East Africa – the birthplace of the human species – may have taken much longer to develop than previously believed.
""We now believe that the western portion of the rift formed about 25 million years ago, and is approximately as old as the eastern part, instead of much younger as other studies have maintained," said Michael Gottfried, Michigan State University associate professor ...
A 24-karat gold key to unlock the immune system
2012-03-27
Developing a drug or vaccine requires a delicate balancing act with the immune system. On one hand, medications need to escape detection by the immune system in order to perform their function. But vaccinations — de-activated versions of a disease or virus — need to do the reverse. They prompt the immune system to create protective antibodies. But scientists are still stumped by how the immune system recognizes different particles, and how it chooses whether or not to react against them.
Using nanoparticles made of pure gold, Dr. Dan Peer, head of Tel Aviv University's ...
Progress toward new chemotherapy agents
2012-03-27
Advances in chemotherapy have dramatically improved the outlook for many cancer patients, but the side effects of this treatment are daunting. A new generation of chemotherapy drugs with fewer side effects is the goal of Edward J. Merino, assistant professor of chemistry at the University of Cincinnati.
Merino will discuss his efforts toward designing these new anticancer agents Tuesday, March 27, at The Chemistry of Life: Spring National Meeting and Exposition of the American Chemical Society in San Diego.
At that meeting, Merino will show a new anticancer agent ...
Mommy Esquire, Committee of the OC Bar Association, Supporting Working Parent Lawyers
2012-03-27
Newport Beach estate planning attorney and mom, Darlynn Morgan, along with her colleagues and the OCBA President, has recently spearheaded the formation of Mommy Esquire, a committee of the Orange County Bar Association. Women lawyers nationwide seek to achieve that ever-elusive balance of legal work and family life. Hence, in January 2012, Mommy Esquire was formed—the first OCBA committee that focuses specifically on practicing lawyers with school-age children. Estate planning lawyer, Darlynn Morgan, of Morgan Law Group, will serve as Chair of the newly formed committee.
"Mommy ...
Pass the lycopene: Scientist can protect supplements inside food
2012-03-27
WEST LAFAYETTE, Ind. - A Purdue University food scientist has developed a way to encase nutritional supplements in food-based products so that one day consumers might be able to sprinkle vitamins, antioxidants and other beneficial compounds right onto their meals.
Srinivas Janaswamy, a research assistant professor of food science, said many of the nutraceuticals, or nutritional supplements, added to foods today are not structurally stable. Heat, light, oxygen and other external factors could degrade the supplements, rendering them ineffective.
"There are many methods ...
SpeechTrans Gold Now Available on Android Market for Free
2012-03-27
The award winning speech-to-speech translation application with many integrated features, the Speechtrans Gold, is now for free to all Android users. This version of Speechtrans lets you text-to-text, text-to-speech, and two-way Speech to Speech communication translations in multiple languages. This application also lets you have a conversation to any one's telephone around the world and understand each other's language. SpeechTrans has partnered with GetJar rewards to support users to have free access to SpeechTrans technology.
SpeechTrans Gold allows speech-to-speech ...
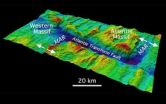
Expedition to undersea mountain yields new information about sub-seafloor structure
2012-03-27
Scientists recently concluded an expedition aboard the research vessel JOIDES Resolution to learn more about Atlantis Massif, an undersea mountain, or seamount, that formed in a very different way than the majority of the seafloor in the oceans.
Unlike volcanic seamounts, which are made of the basalt that's typical of most of the seafloor, Atlantis Massif includes rock types that are usually only found much deeper in the ocean crust, such as gabbro and peridotite.
The expedition, known as Integrated Ocean Drilling Program (IODP) Expedition 340T, marks the first time ...
Red Skelton Tribute Show Displays Artwork and Paintings of the Famous Comedian
2012-03-27
While most American's knew Red Skelton for his starring rolls on radio, in movies and his own television variety show where he was known as the king of comedy and adlibs, few people knew he was pursuing another talent.
Red Skelton started dabbling in painting as a way to relax and unwind. Years of producing a weekly variety show brings great pressure to create new material and routines. The work load can be overwhelming.
Everyone needs a way to relax and the creative side of Red was always working overtime. His wife Georgia, having some experience in the arts, suggested ...