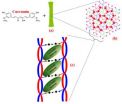
(Press-News.org) Developing a drug or vaccine requires a delicate balancing act with the immune system. On one hand, medications need to escape detection by the immune system in order to perform their function. But vaccinations — de-activated versions of a disease or virus — need to do the reverse. They prompt the immune system to create protective antibodies. But scientists are still stumped by how the immune system recognizes different particles, and how it chooses whether or not to react against them.
Using nanoparticles made of pure gold, Dr. Dan Peer, head of Tel Aviv University's Laboratory of Nanomedicine at the Department of Cell Research and Immunology and the Center for Nanoscience and Nanotechnology, with a team including Drs. Meir Goldsmith and Dalit Landesman-Milo and in collaboration with Prof. Vincent Rotello and Dr. Daniel Moyano from the University of Massachusetts at Amherst, has developed a new method of introducing chemical residues into the immune system, allowing them to note the properties that incur the wrath of immune cells. Because the gold flecks are too small to be detected by the immune system, the immune system only responds when they are coated with different chemical residues.
This breakthrough could lead to an increased understanding of the properties of viruses and bacteria, better drug delivery systems, and more effective medications and vaccinations. Their study was published in the Journal of the American Chemical Society.
A tool for exploration
To begin probing the immune system, researchers used particles of gold, approximately two nanometers in diameter, and covered them with various chemical residues. Only when water-resistant residues were introduced did the immune system respond to their presence. That established a demonstrable link between hydrophobicity — the degree to which a molecule repels water — and the reaction of the immune system.
This idea has a basis in the normal functioning of the immune system, Dr. Peer explains. During cell death, the hydrophobic areas of the cell membrane become exposed. The immune system then realizes that damage has occurred and begins to alert neighboring cells.
The researchers discovered that the same principle held true for the chemicals added to the gold particles' surface. The more "water-hating" the particle is, the more actively the immune system will mobilize against it, he says.
Dr. Peer observes that this is only the first step in a long line of experiments. "We are using these gold particles to tackle the question of how the immune system recognizes different particles, which might include features such as geometry, charge, curvature, and so much more. Now that we know the tool works, we can build on it," he says.
Testing the "Danger Model"
Until now, scientists have developed theories about how the immune system functions, but have lacked the machinery to test these ideas. One such theory is the "Danger Model" by Prof. Polly Matzinger, which hypothesizes that cellular damage interacts with immune cells at the membrane level. Once they identify the foreign molecule as a "danger," the immune cells send signals throughout the immune system. Their initial experiment with hydrophobicity was designed to generate a toolbox for probing this theory, says Dr. Peer, whose investigations included both in vitro and in vivo experiments using mouse immune cells.
In the future, researchers will study various bacterial, viral, or damaged cells and to make the gold nanoparticles even more similar, thereby discovering which elements of dangerous particles are calling the body's immune system to arms. "We now have the capability of using nanomaterials to probe the immune system in a very accurate manner," says Dr. Peer, a breakthrough that could revolutionize the way we understand the immune system.
INFORMATION:
American Friends of Tel Aviv University (www.aftau.org) supports Israel's leading, most comprehensive and most sought-after center of higher learning. Independently ranked 94th among the world's top universities for the impact of its research, TAU's innovations and discoveries are cited more often by the global scientific community than all but 10 other universities.
Internationally recognized for the scope and groundbreaking nature of its research and scholarship, Tel Aviv University consistently produces work with profound implications for the future.
A 24-karat gold key to unlock the immune system
Innovative Tel Aviv University tool for immune system activation could lead to better drug delivery
2012-03-27
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Progress toward new chemotherapy agents
2012-03-27
Advances in chemotherapy have dramatically improved the outlook for many cancer patients, but the side effects of this treatment are daunting. A new generation of chemotherapy drugs with fewer side effects is the goal of Edward J. Merino, assistant professor of chemistry at the University of Cincinnati.
Merino will discuss his efforts toward designing these new anticancer agents Tuesday, March 27, at The Chemistry of Life: Spring National Meeting and Exposition of the American Chemical Society in San Diego.
At that meeting, Merino will show a new anticancer agent ...
Mommy Esquire, Committee of the OC Bar Association, Supporting Working Parent Lawyers
2012-03-27
Newport Beach estate planning attorney and mom, Darlynn Morgan, along with her colleagues and the OCBA President, has recently spearheaded the formation of Mommy Esquire, a committee of the Orange County Bar Association. Women lawyers nationwide seek to achieve that ever-elusive balance of legal work and family life. Hence, in January 2012, Mommy Esquire was formed—the first OCBA committee that focuses specifically on practicing lawyers with school-age children. Estate planning lawyer, Darlynn Morgan, of Morgan Law Group, will serve as Chair of the newly formed committee.
"Mommy ...
Pass the lycopene: Scientist can protect supplements inside food
2012-03-27
WEST LAFAYETTE, Ind. - A Purdue University food scientist has developed a way to encase nutritional supplements in food-based products so that one day consumers might be able to sprinkle vitamins, antioxidants and other beneficial compounds right onto their meals.
Srinivas Janaswamy, a research assistant professor of food science, said many of the nutraceuticals, or nutritional supplements, added to foods today are not structurally stable. Heat, light, oxygen and other external factors could degrade the supplements, rendering them ineffective.
"There are many methods ...
SpeechTrans Gold Now Available on Android Market for Free
2012-03-27
The award winning speech-to-speech translation application with many integrated features, the Speechtrans Gold, is now for free to all Android users. This version of Speechtrans lets you text-to-text, text-to-speech, and two-way Speech to Speech communication translations in multiple languages. This application also lets you have a conversation to any one's telephone around the world and understand each other's language. SpeechTrans has partnered with GetJar rewards to support users to have free access to SpeechTrans technology.
SpeechTrans Gold allows speech-to-speech ...
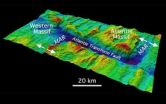
Expedition to undersea mountain yields new information about sub-seafloor structure
2012-03-27
Scientists recently concluded an expedition aboard the research vessel JOIDES Resolution to learn more about Atlantis Massif, an undersea mountain, or seamount, that formed in a very different way than the majority of the seafloor in the oceans.
Unlike volcanic seamounts, which are made of the basalt that's typical of most of the seafloor, Atlantis Massif includes rock types that are usually only found much deeper in the ocean crust, such as gabbro and peridotite.
The expedition, known as Integrated Ocean Drilling Program (IODP) Expedition 340T, marks the first time ...
Red Skelton Tribute Show Displays Artwork and Paintings of the Famous Comedian
2012-03-27
While most American's knew Red Skelton for his starring rolls on radio, in movies and his own television variety show where he was known as the king of comedy and adlibs, few people knew he was pursuing another talent.
Red Skelton started dabbling in painting as a way to relax and unwind. Years of producing a weekly variety show brings great pressure to create new material and routines. The work load can be overwhelming.
Everyone needs a way to relax and the creative side of Red was always working overtime. His wife Georgia, having some experience in the arts, suggested ...
Alexander Meissner to speak at 2nd Epigenetics Drug Discovery conference May 30-31, 2012 Boston, MA
2012-03-27
Alexander Meissner, Assistant Professor at Harvard University will give a keynote presentation on ¡°DNA Methylation Dynamics in Development and Stem Cells¡± at the 2nd Epigenetics in Drug Discovery Conference taking place on May 30-31, 2012 in Boston, MA.
Cytosine methylation in mammals is an epigenetic modification that is largely restricted to CpG dinucleotides and serves multiple critical functions including stable repression of target promoters, maintaining genomic integrity, establishing parent-specific imprinting patterns, and silencing endogenous retrotransposon ...
Genetic risk and stressful early infancy join to increase risk for schizophrenia
2012-03-27
Working with genetically engineered mice and the genomes of thousands of people with schizophrenia, researchers at Johns Hopkins say they now better understand how both nature and nurture can affect one's risks for schizophrenia and abnormal brain development in general.
The researchers reported in the March 2 issue of Cell that defects in a schizophrenia-risk genes and environmental stress right after birth together can lead to abnormal brain development and raise the likelihood of developing schizophrenia by nearly one and half times.
"Our study suggests that if ...
OBX Outfitters Publishes OBX Spring Training Online Resource for Outer Banks Running, Outdoor Events
2012-03-27
Casual apparel and activewear company OBX Outfitters is providing a free online resource for Outer Banks groups and organizations to publicize their springtime charity running and other outdoor events, http://www.obxspringtraining.com.
Additionally, OBX Outfitters is offering a 25% off its North Carolina-Made Find Your Stride activewear for runners and supporters of the events.
"We're committed to helping community organizations in the Outer Banks, and providing free publicity and discounts on our running shirts is just one small way we can make a contribution," ...
CDAA Web Company Announces New Client: William Buck
2012-03-27
CDAA Pty Ltd, an Australian based Certified Web Company, today announced the signing of its newest client, William Buck, a leading firm of Chartered Accountants and advisors in Australia and New Zealand.
CDAA is providing graphic design, web design, web development, web hosting and email marketing services to William Buck to help increase its brand visibility, website traffic and build new client relationships.
"We are partnering with CDAA, a leading-edge Web Company, to design and develop our new website. With CDAA we aim to ensure that our online image is ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Alkali cation effects in electrochemical carbon dioxide reduction
Test platforms for charging wireless cars now fit on a bench
$3 million NIH grant funds national study of Medicare Advantage’s benefit expansion into social supports
Amplified Sciences achieves CAP accreditation for cutting-edge diagnostic lab
Fred Hutch announces 12 recipients of the annual Harold M. Weintraub Graduate Student Award
Native forest litter helps rebuild soil life in post-mining landscapes
Mountain soils in arid regions may emit more greenhouse gas as climate shifts, new study finds
Pairing biochar with other soil amendments could unlock stronger gains in soil health
Why do we get a skip in our step when we’re happy? Thank dopamine
UC Irvine scientists uncover cellular mechanism behind muscle repair
Platform to map living brain noninvasively takes next big step
Stress-testing the Cascadia Subduction Zone reveals variability that could impact how earthquakes spread
We may be underestimating the true carbon cost of northern wildfires
Blood test predicts which bladder cancer patients may safely skip surgery
Kennesaw State's Vijay Anand honored as National Academy of Inventors Senior Member
Recovery from whaling reveals the role of age in Humpback reproduction
Can the canny tick help prevent disease like MS and cancer?
Newcomer children show lower rates of emergency department use for non‑urgent conditions, study finds
Cognitive and neuropsychiatric function in former American football players
From trash to climate tech: rubber gloves find new life as carbon capturers materials
A step towards needed treatments for hantaviruses in new molecular map
Boys are more motivated, while girls are more compassionate?
Study identifies opposing roles for IL6 and IL6R in long-term mortality
AI accurately spots medical disorder from privacy-conscious hand images
Transient Pauli blocking for broadband ultrafast optical switching
Political polarization can spur CO2 emissions, stymie climate action
Researchers develop new strategy for improving inverted perovskite solar cells
Yes! The role of YAP and CTGF as potential therapeutic targets for preventing severe liver disease
Pancreatic cancer may begin hiding from the immune system earlier than we thought
Robotic wing inspired by nature delivers leap in underwater stability
[Press-News.org] A 24-karat gold key to unlock the immune systemInnovative Tel Aviv University tool for immune system activation could lead to better drug delivery