(Press-News.org) Tropical Storm Daphne has become an extra-tropical storm and is fading fast in the South Pacific Ocean, but not before making its mark on the Fuji Islands. NASA's TRMM satellite compiled rainfall data that revealed flooding rains fell in Fiji.
The low pressure area called System 95P strengthened into Tropical cyclone Daphne ( known in Fiji as 19F) at 0300 UTC on April 2, 2012. At that time, Daphne was near 19.8 South and 172.7 East, about 340 miles west-southwest of Suva, Fiji and bringing heavy rains to the islands. By April 2, those heavy rains had claimed at least three lives in Fiji and sent thousands of people to evacuation centers, news reports said. Heavy rains washed out roads, severed drinking water supplies, downed power lines, and hampered communications.
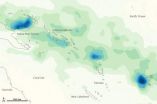
A rainfall image created using data from NASA's Tropical Rainfall Measuring Mission (TRMM) satellite showed totals between Papua New Guinea and Fiji from March 26 to April 2, 2012. The heaviest rainfall totaled more than 600 millimeters, or 24 inches. The lightest rainfall measured less than 75 millimeters or 3 inches.
Areas of intense rain occurred within a wide band of precipitation between the Pacific Ocean and the Coral Sea in late March and early April. Although much of the precipitation fell over open ocean, some of the heaviest rain fell on Fiji—in particular, on the large island of Viti Levu.
The rains left homes underwater and led to landslides, including one near a resort and another near a hospital. The government of Fiji requested that airlines stop flying travelers to the country until further notice, and planes began arriving empty at Fiji airports in order to evacuate stranded tourists.
As Fiji coped with floods, Tropical Cyclone Daphne threatened to inundate the islands again. A bulletin from the Fiji Meteorological Service reported that, as of 6:00 p.m. local time on April 2, 2012, Daphne was located roughly 540 kilometers (335 miles) west-southwest of Nadi, a city on the west coast of Viti Levu.
This map is based on data from the Multisatellite Precipitation Analysis produced at NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center, which estimates rainfall by combining measurements from many satellites and calibrating them using rainfall measurements from the TRMM satellite.
On April 3, 2012 the final warning on Tropical Storm Daphne was issued as it is being battered by wind shear and quickly weakening. At 1500 UTC (11 a.m. EDT), Daphne's maximum sustained winds dropped down to 40 knots (46 mph/74 kph), and the extent of the strongest winds shrank to 240 nautical miles (276 miles/444.5 km) from the center (it was as large as 300 nautical miles (345 miles/555.6 km) early in the day). Daphne's last location was near 32.0 South and 174.0 West, and it was speeding to the south at 25 knots (28.7 mph/46.3 kph). Daphne has transitioned into an extra-tropical storm, and is expected to fade in the next day or two.
INFORMATION:
Now Extra-Tropical Daphne, left flooding behind in Fuji on NASA satellite imagery
2012-04-05
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
GOES satellite movie tracked tornadic Texas trouble
2012-04-05
A powerful weather system moved through eastern Texas and dropped at least 15 tornadoes in the Dallas suburbs. NASA created an animation of data from NOAA's GOES-13 satellite that shows the frontal system moving through the region yesterday.
NOAA's Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite, GOES-13, captures visible and infrared images of weather over the eastern U.S. every 15 minutes, and captured the movement of the weather system that generated the Texas twisters. The 23 second movie runs from April 2 at 1615 UTC through April 4 at 1615 UTC (11:15 a.m. CDT), ...
Quantum control protocols could lead to more accurate, larger scale quantum computations
2012-04-05
(Santa Barbara, Calif.) –– A protocol for controlling quantum information pioneered by researchers at UC Santa Barbara, the Kavli Institute of Nanoscience in Delft, the Netherlands, and the Ames Laboratory at Iowa State University could open the door to larger-scale, more accurate quantum computations. Their findings, in a paper titled "Decoherence-protected quantum gates for a hybrid solid-state spin register," are published in the current issue of the journal Nature.
"Although interactions between a quantum bit ('qubit') and its environment tend to corrupt the information ...
Watts Water Technologies Joins HomeSphere
2012-04-05
Watts Water Technologies and HomeSphere, Inc. announced today they have entered into a joint agreement to offer Watts Water Technologies brands BLUCHER, BRAE, Dormont, Watts and Watts Radiant to HomeSphere's network of builders using HomeSphere's technology-driven solutions.
Watts Water Technologies, based in North Andover, Mass., joins more than 75 manufacturing brands currently using HomeSphere's BRI lead generation and marketing program to produce new builder leads and strengthen existing business, thus growing their market share through increased homebuilder sales. ...
Clinical insight improves treatment with new lung cancer drug
2012-04-05
AURORA, Colo. (April 4, 2012) - Men experience a marked drop in their testosterone levels when taking a targeted therapy to control a specific type of lung cancer. That's according to a University of Colorado Cancer Center study published in the April issue of Cancer, the official journal of the American Cancer Society.
Investigators at CU Cancer Center looked at the hormone levels in men with anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK) positive advanced non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) taking crizotinib, after a 35-year-old man on the drug reported symptoms that are often attributed ...
Dino eggs shape Easter eggs, says new study
2012-04-05
An international group of researchers has helped to determine that dinosaurs have shaped the Easter eggs we buy in the high street.
Scientists investigating whether 70 million-year-old fossil eggs found in the Pyrenees were laid by birds, or their dinosaur ancestors, have published their findings in the current issue of the journal Palaeontology.
And researchers from the University of Leicester have extended the study further by comparing Easter egg shapes to those of birds' and dino eggs.
The authors of the Pyrenees research, Nieves Lopez-Martinez of the Universidad ...
Choice 7's Stealth 2.0 E Cigarette Could Save Lives!
2012-04-05
With over 20,000 Stealth 1.0 e cigarette kits already delivered to active duty troops in combat with no LED at the end, so as to not give position away in a combat situation. The Stealth makes life a little safer from snipers and other dangers of war and police actions.
The new Stealth 2.0 battery, announced on the My 7's Blog, comes with a patent pending switch that is as simple as "Tap & Hold", to switch from stealth mode to regular so that you can see your charge information from your batteries. The Stealth battery gives the user the option to have an ...
Superior Restoration Offers Tips for Choosing a Restoration Company
2012-04-05
In 2011, flood damage in the United States caused economic losses of more than $8 billion. In 2010, fires caused more than $11.6 billion in property damage. Each year, floods, fires and other natural disasters combine to create catastrophic financial problems for home and property owners across the country. This expense can be greatly increased if the wrong contractor or restoration specialist is chosen. In some cases, poor restoration can cause irreparable damage to possessions and homes.
Superior Restoration, a San Diego-based water damage, fire and mold remediation ...
Disarming disease-causing bacteria
2012-04-05
Scientists could produce new antibacterial treatments by disarming the molecular pumps bacteria use to bring disease causing molecules in contact with animals and humans.
Research published today in Nature Structure and Molecular Biology showed a protein complex called the Translocation and Assembly Module (TAM), forms a type of molecular pump, allowing bacteria to shuttle key disease causing molecules from inside the bacterial cell where they are made, to the outside surface, priming the bacteria to infect other organisms.
The international research collaboration, ...
Gene mutation identified as contributor to autism spectrum disorders
2012-04-05
There is little argument among experts that autism spectrum disorders (ASD), complex developmental disabilities that vary widely in their severity, are caused by both genetic and environmental factors. Advances in genome sequencing now permit scientists to uncover specific mutations in DNA that are associated with ASD at unprecedented resolution. Such data are vital to understanding the genetic basis of the disorder.
A new study co-authored by UCLA researchers has led to a better understanding of the genetic contribution to autism using this new approach. By comparing ...
To prevent leukemia's dreaded return, go for the stem cells
2012-04-05
Researchers reporting in the April Cell Stem Cell, a Cell Press publication, have found a way to stop leukemia stem cells in their tracks. The advance in mice suggests that a combination approach to therapy might stamp out chronic myeloid leukemia (CML) for good.
That's in contrast to the vast majority of CML patients taking drugs like imatinib (aka Gleevec) today, who often go into remission only to see their cancer return again. It is those lingering leukemia stem cells, which stubbornly resist existing therapies, that fuel the cancer's comeback.
"Imatinib inhibits ...