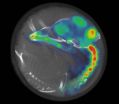
(Press-News.org) Under some conditions, the brains of embryonic chicks appear to be awake well before those chicks are ready to hatch out of their eggs. That's according to an imaging study published online on May 3 in Current Biology, a Cell Press publication, in which researchers woke chick embryos inside their eggs by playing loud, meaningful sounds to them. Playing meaningless sounds to the embryos wasn't enough to rouse their brains.
The findings may have implications not only for developing chicks and other animals, but also for prematurely born infants, the researchers say. Pediatricians have worried about the effects of stimulating brains that are still under construction, especially as modern medicine continues to push back the gestational age at which preemies can reliably survive.
"This work showed that embryo brains can function in a waking-like manner earlier than previously thought—well before birth," said Evan Balaban of McGill University. "Like adult brains, embryo brains also have neural circuitry that monitors the environment to selectively wake the brain up during important events."
That waking-like brain activity appears in a latent but inducible state during the final 20 percent of embryonic life, the researchers found. At that point, sleep-like brain activity patterns also emerge.
Before that major dividing line in development—for the first 80 percent of embryonic life— "embryos are in a state that is neither like sleep nor waking," Balaban said. He suggests it may be useful to compare that state to what happens when people are comatose or under the influence of anesthesia.
This entire line of work was made possible by a new generation of molecular brain imagers developed by Balaban's coauthors Juan-José Vaquero and Manuel Desco at the Universidad Carlos III in Madrid. Those state-of-the art machines can detect very small amounts of tracer molecules and pinpoint them to a tiny region of the brain (about 0.7 mm, or less than 3/100ths of an inch).
The researchers say they were surprised to capture waking-like activity before birth. And there were other surprises, too. The embryo brains they observed showed considerable variation in activity, for one.
Before the emergence of sleep and waking patterns of brain activity, the chick embryos in their study exhibited lots of spontaneous movement, even as their higher-brain regions remained inactive. Once the chicks reached that 80 percent mark in development, higher-brain regions began crackling with activity. At the same time, those physical movements ceased as the embryos entered a sleep-like state.
"The last 30 percent of fetal brain development is a more interesting time than we previously thought, because it's when complex whole-brain functions that depend on coordination of widely separated brain areas first emerge," Balaban said. "Embryos begin to cycle through a variety of brain states and are even capable of showing waking-like brain activity."
That might explain instances of complex fetal and early neonatal learning. "It also raises questions about the longer-term developmental consequences that such brain activity may have, if it is induced before intrinsic brain wiring is sufficiently completed," Balaban said, "for example, in babies born very prematurely. We are excited by the possibility that the techniques developed here can now be used to provide answers to these questions."
INFORMATION:
Balaban et al.: "Waking-like brain function in embryos."
Waking embryos before they are born
2012-05-04
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Exceptional Midcentury, Fine Silver and Rare Art Make Clarke Auction on Monday, May 7th in Larchmont, NY a Collector's Dream Night Out
2012-05-04
Picking has been great this month for the Clarke appraisal team. They have managed once again to put together what -- in the humble opinion of Irish owner and founder, Ronan Clarke - is one of the most diverse and exciting auction offerings in the New York area this month.
While Sotheby's, Doyle's, Christy's, etc. all have great art sales this month, Clarke not only has great art but also a diverse and eclectic mix of midcentury modern, silver, porcelain, rugs, continental furniture and collectibles.
As always, Clarke has its usual gathering of furniture and even ...
Simple assault and ground level fall do not require cervical spine CT
2012-05-04
Cervical spine CT examinations are unnecessary for emergency department (ED) patients who are a victim of "simple assault" or who have a "ground-level fall", unless the patient has a condition that predisposes the patient to spine fracture, a new study finds.
The study, conducted at Grady Memorial Hospital by researchers from the Department of Radiology and Imaging Sciences of the Emory University School of Medicine in Atlanta, found that out of 218 exams for simple assault, there were none that were positive, said Andrew Nicholson, MD, lead author of the study. In the ...
Surgical excision unnecessary in some patients with benign papillomas
2012-05-04
Imaging surveillance is an acceptable alternative to surgical excision in patients with benign papilloma, diagnosed at breast core biopsy without cell abnormalities, a new study shows.
The study, conducted at the Breast Health Center of California Pacific Medical Center in San Francisco, included 119 papillomas diagnosed at core biopsy without abnormal cells. Imaging follow-up of a minimum of two years without surgical excision was performed on 66 lesions; no cancer was found in this group, said Jessica Leung, MD, FACR, lead author of the study. Surgical excision was ...
Study finds 'overmanagement' of benign breast disease
2012-05-04
Contrary to current guidelines, women with benign breast biopsies do not need follow-up at six months; they may not need close surveillance at all, a new study shows.
The study, conducted at Moffitt Cancer Center in Tampa, FL, followed 388 patients for six, 12 and 24 months. No cancer was found in these patients at six and 12 months, said Shannon Reed, MD, one of the authors of the study. "Of the 197 follow-up examinations performed at 24 months, two women were positive for cancer in a different area than had been previously biopsied," said Dr. Reed. An annual ...
Increasing speed of Greenland glaciers gives new insight for rising sea level
2012-05-04
Changes in the speed that ice travels in more than 200 outlet glaciers indicates that Greenland's contribution to rising sea level in the 21st century might be significantly less than the upper limits some scientists thought possible, a new study shows.
"So far, on average we're seeing about a 30 percent speedup in 10 years," said Twila Moon, a University of Washington doctoral student in Earth and space sciences and lead author of a paper documenting the observations published May 4 in Science.
The faster the glaciers move, the more ice and meltwater they release ...
Biologists turn back the clock to understand evolution of sex differences
2012-05-04
Sex differences account for some of the most of the spectacular traits in nature: the wild colours of male guppies, the plumage of peacocks, tusks on walruses and antlers on moose. Sexual conflict – the battle between males and females over mating – is thought to be a particularly potent force in driving the evolution traits that differ in males and females.
However, the genetic processes responsible for producing such traits are not well understood, nor how they evolved from their simpler less elaborate ancestral forms. We tend to assume that each tiny step in evolution ...
Aged hematopoietic stem cells rejuvenated to be functionally younger
2012-05-04
CINCINNATI – Researchers have rejuvenated aged hematopoietic stem cells to be functionally younger, offering intriguing clues into how medicine might one day fend off some of the ailments of old age.
Scientists at Cincinnati Children's Hospital Medical Center and the Ulm University Medicine in Germany report their findings online May 3 in the journal Cell Stem Cell. The paper brings new perspective to what has been a life science controversy – countering what used to be broad consensus that the aging of hematopoietic stem cells (HSCs) was locked in by nature and not reversible ...
The American College of Rheumatology issues guidelines for management of lupus nephritis
2012-05-04
The American College of Rheumatology (ACR) has issued newly created guidelines for the screening, treatment, and management of lupus nephritis—a severe manifestation of systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) where the disease attacks the kidneys. Previously, only general guidelines for SLE existed for clinicians. The guidelines, available today in Arthritis Care & Research, are specific to lupus nephritis and include methods for identifying renal disease, newer therapies, and treatment of pregnant SLE patients with kidney involvement.
The ACR estimates that up to 322,000 ...
Naturally blond hair in Solomon Islanders rooted in native gene, Stanford study finds
2012-05-04
STANFORD, Calif. — The common occurrence of blond hair among the dark-skinned indigenous people of the Solomon Islands is due to a homegrown genetic variant distinct from the gene that leads to blond hair in Europeans, according to a new study from the Stanford University School of Medicine.
"This is one of the most beautiful examples to date of the mapping of a simple genetic trait in humans," said David Reich, PhD, a professor of genetics at Harvard University, who was not involved in the study.
The study identifying the gene responsible for blond hair in the Solomon ...
Double duty: Versatile immune cells play dual roles in human skin
2012-05-04
A new study helps to resolve an ongoing controversy about whether Langerhans cells (LCs) in human skin function to suppress the immune response and promote tolerance to normal human skin and its "friendly" microbial flora or mobilize a lethal attack against harmful foreign invaders. The research, published online May 3rd in the journal Immunity by Cell Press, reveals that, depending on the situation, these versatile immune cells can perform either function.
Adult human skin contains billions of resident immune cells called T cells that provide protection from invading ...